1
Complete the following sentence. The following pedigree chart shows that the trait under examination would be:

Choose one answer.
|
a. X-linked. |
||
|
b. incomplete dominant. |
||
|
c. Y-linked. |
||
|
d. autosomal recessive. |
Question 2
Huntington’s disease is a late onset dominant disorder. Joe Doe’s father has Huntington’s; no one has Huntington’s disease on the mother’s side of Joe’s family. Use a Punnett Square to predict the probability that Joe inherited Huntington’s from his father.
Choose one answer.
|
a. There is a 25% chance that Joe inherited Huntington’s disease from his father. |
||
|
b. There is a 50% chance that Joe inherited Huntington’s disease from his father. |
||
|
c. There is a 75% chance that Joe inherited Huntington’s disease from his father. |
||
|
d. There is a 100% chance that Joe inherited Huntington’s disease from his father. |
Question 3
If you conduct a monohybrid cross, (Aa x Aa), what is the probability of getting either AA or Aa genotypes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 2/3 |
||
|
b. 4/4 |
||
|
c. 3/4 |
||
|
d. 1/4 |
Question 4
The inflated allele of the pod shape gene is dominant (F); the constricted allele of the pod shape gene is recessive (f). The green allele of the pod color gene is dominant (G); the yellow allele of the pod color gene is recessive (g). Use a Punnett Square to predict the genotype of the offspring if two true breeding pea plants are crossed: the first plant has inflated green pods and the second plant has constricted yellow pods.
Choose one answer.
|
a. The genotype of all offspring is Ff Gg. |
||
|
b. 12.5% of the offspring has FfGg genotype. |
||
|
c. The offspring has parental genotype. |
||
|
d. The genotypic ratio is 3:1. |
Question 5
The inflated allele of the pod shape gene is dominant (F); the constricted allele of the pod shape gene is recessive (f). The green allele of the pod color gene is dominant (G); the yellow allele of the pod color gene is recessive (g). Use Punnett Square to predict the genotype of the offspring of self pollinating FfGg pea plants.
Choose one answer.
|
a. The genotype of all offspring is Ff Gg. |
||
|
b. 12.5% of the offspring has FfGg genotype. |
||
|
c. The offspring has parental genotype. |
||
|
d. The genotypic ratio is 3:1. |
Question 6
What are the genotypes of A, B, and C individuals in the following family pedigree? Use F for the dominant alleles and f for the recessive alleles.
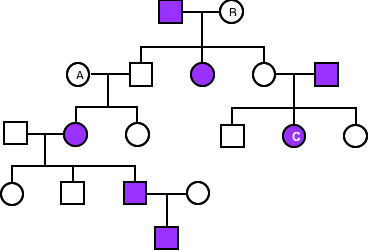
Choose one answer.
|
a. The genotypes of individuals A and B are ff, and C is Ff. |
||
|
b. The genotype of individual A is Ff, B is ff, and C is FF. |
||
|
c. The genotypes of individuals A and B are Ff, and C is ff. |
||
|
d. The genotype of individuals A and B are FF, and C is ff. |
Question 7
What fraction of the offspring will express at least two recessive traits, if a pea plant that is heterozygous for the flower color (purple is dominant and white is recessive), for the seed color (yellow is dominant and green is recessive) and for the pod color (green is dominant and yellow is recessive) is self-pollinating?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 3/4 |
||
|
b. 1/8 |
||
|
c. 3/32 |
||
|
d. 7/64 |
Question 8
What fraction of the offspring will express two recessive traits, if a pea plant that is heterozygous for the flower color (purple is dominant and white is recessive), for the seed color (yellow is dominant and green is recessive), and for the pod color (green is dominant and yellow is recessive) is self-pollinating?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 3/32 |
||
|
b. 1/16 |
||
|
c. 3/8 |
||
|
d. 1/4 |
Question 9
What percentage of the offspring is a homozygote if both parents are heterozygotes? Use a Punnett Square to answer this question.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0% |
||
|
b. 25% |
||
|
c. 50% |
||
|
d. 75% |
Question 10
You open your first greenhouse, and you are eager to create new hybrid plants to sell. You cross a true-breeding tall, purple-flowered rose with a true-breeding short, white-flowered rose. All of your offspring are short, pink-flowered roses. What does this tell you about the phenotypic expression of these characteristics?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The purple and the white alleles exhibit incomplete dominance, while the short allele is dominant to the tall allele. |
||
|
b. The purple and the short alleles are dominant; otherwise, the offspring would be white and tall. |
||
|
c. The pink and the white alleles are codominant; the short allele is dominant to the tall allele. |
||
|
d. The purple and white alleles are recessive; the tall allele is subject to X-inactivation. |
Question 11
Complete the following sentence. If you had a monohybrid cross between two different individuals, you would expect the genotypic ratio to be:
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1:2:1. |
||
|
b. 9:3:3:1. |
||
|
c. 3:1. |
||
|
d. 4:0. |
Question 12
Complete the following sentence. During the process of mitosis, a plant daughter cell that starts out with 50 chromosomes will end up with:
Choose one answer.
|
a. 100 chromosomes. |
||
|
b. 25 chromosomes. |
||
|
c. 75 chromosomes. |
||
|
d. 50 chromosomes. |
Question 13
Complete the following sentence. If you compare female and male gametogeneses in humans, you can determine that:
Choose one answer.
|
a. female and male gametogeneses are homologous throughout: both result in four different gametes derived from the primary gametocyte through meiotic cell division. |
||
|
b. female and male gametogeneses are homologous, because both result in the production of gametes through meiosis; however, while one primary spermatocyte gives rise to four sperm cells, one primary oocyte gives rise to only one oocyte. |
||
|
c. female and male gametogeneses are not homologous, because one primary spermatocyte gives rise to four sperm cells, while one primary oocyte gives rise to only one oocyte. |
||
|
d. female and male gametogeneses are not homologous, because one primary spermatocyte gives rise to four sperm cells through meiosis; one primary oocyte gives rise to the secondary oocyte through meiosis, but the oocyte is the result of mitotic cell division. |
Question 14
Cystic fibrosis is an inherited autosomal recessive disease. Assume that a mother has cystic fibrosis and that there is a technique to analyze the polar bodies for the presence of the cystic fibrosis alleles. Is it possible to determine if the oocyte has a cystic fibrosis allele through the analysis of the polar bodies? Why, or why not?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Yes, it is possible, because the polar bodies and the oocyte are daughter cells that are derived from the parental primary oocyte through cell division. |
||
|
b. Yes, it is possible but only from the second polar body, because it is genetically identical to the oocyte. |
||
|
c. No, it is not possible, because the polar bodies and the oocyte are daughter cells that are derived from the parental primary oocyte through meiosis. |
||
|
d. No, it is not possible from the second polar body, but it is possible to determine from the first polar body. |
Question 15
Fill in the blank. In meiosis I, _______ determines the number of chromosomes in the gametes. This is an essential process that serves to keep the same number of chromosomes in the embryo that will be formed when the gametes get together.
Choose one answer.
|
a. equational division |
||
|
b. reductional division |
||
|
c. kinetochore separation |
||
|
d. polar separation |
Question 16
Fruit flies and grasshoppers are diploid organisms. The haploid number of fruit flies is 4, and the haploid number of grasshoppers is 23. If no crossing over takes place, which organism produces a greater variety of zygotes, and why?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The grasshoppers, because 223 times 223 is greater than 24 times 24 |
||
|
b. The grasshoppers, because 223 is greater than 24 |
||
|
c. The grasshoppers, because 2 times 23 is greater than 2 times 4 |
||
|
d. The fruit flies, because they have a smaller haploid number |
Question 17
Grasshoppers have 23 homologous chromosome pairs. Assuming that no crossing over takes place, how many genetically different gametes can potentially be made by a grasshopper?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 223 |
||
|
b. 232 |
||
|
c. 46 |
||
|
d. 4 |
Question 18
How many unique daughter cells result from meiotic or mitotic cell division of a cell, which has three homologous chromosome pairs?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Both mitosis and meiosis results in daughter cells that are identical to each other and to the parental cell; thus, there will be no unique daughter cells. |
||
|
b. There will be no unique daughter cells after mitosis; there will be four different daughter cells after meiosis, and these cells will also be different from the parental cell. |
||
|
c. There will be no unique daughter cells after meiosis; there will be eight different daughter cells after mitosis, and these cells will also be different from the parental cell. |
||
|
d. There will be no unique daughter cells after mitosis; there will be six different daughter cells after meiosis, and these cells will also be different from the parental cell. |
Question 19
Which of the following is less prone to cancer development, and why?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Epithelial tissue, because the tumor suppressor level is higher than the protooncogen level in this tissue |
||
|
b. Lymphatic cell, because the lymphatic system is not exposed to UV radiation |
||
|
c. Neuronal tissue, because the cell proliferation is low in the neuronal tissue |
||
|
d. Tendon, because oncogens cannot induce excessive cell division in this tissue due to special constraints |
Question 20
Which of the following statements best describes a mutation that contributes to cancer development?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The conversion of a tumor suppressor to an oncogene contributes to cancer development, because oncogenes turn on the cell cycle check point genes. |
||
|
b. The conversion of an oncogene to a proto-oncogene contributes to cancer development, because this results in excessive cell cycle control. |
||
|
c. The overexpression of a proto-oncogene contributes to cancer development, because proto-oncogenes turn off the cell cycle check point genes. |
||
|
d. The overexpression of an oncogene contributes to cancer development, because this results in excessive cell division. |
Question 21
You are a geneticist who uses Neurospora to study recombination, and you observe the following spore color patterns. Note that Ascus is the package that the spores were formed in. What do you conclude from this diagram?
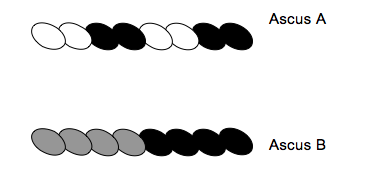
Choose one answer.
|
a. Crossing over occurred as Ascus B was forming but did not occur in Ascus A. |
||
|
b. Crossing over did not occur. |
||
|
c. Crossing over occurred as Ascus A was forming but did not occur in Ascus B. |
||
|
d. Crossing over occurred as Ascus A and Ascus B were forming. |
Question 22
Complete the following sentence. Mendel’s law of independent assortment indicates that:
Choose one answer.
|
a. genes separate during gamete formation. |
||
|
b. allele pairs separate during gamete formation. |
||
|
c. genes mix through crossing-over. |
||
|
d. alleles are either recessive or dominant. |
Question 23
A hair color gene with allele B for black and b for brown pigment determines the hair pigment in many mammals, e.g., in rodents and doe. Another gene, which is responsible for the pigment deposition, determines whether the hair is actually pigmented or not: D allele of this gene allows pigment deposition, while d allele does not support pigment deposition into the hair shaft. A dd genotype of these animals will have white hair regardless of any B and b alleles expressed. This is an example of which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Epistasis |
||
|
b. Epigenetics |
||
|
c. Dominance |
||
|
d. Imprinting |
Question 24
A man has blood type A, his wife has blood type B, and their daughter has blood type O. The husband files for divorce on the grounds of infidelity, believing that this may not be his biological daughter. Can genetics provide evidence supporting the man’s case? Why, or why not?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Genetics cannot support the man’s case based on the blood types in this family: A and B alleles are dominant over O allele; thus, O blood type is a possibility for the child if both parents are heterozygotes. |
||
|
b. Genetics can support the man’s case based on the blood types in this family: A and B alleles are co-dominant; thus, the child should have AB blood type. O blood type is not a possibility for the child. |
||
|
c. Genetics cannot support the man’s case based on the blood types: blood type alleles are co-dominant; thus, the child should have ABO genotype. |
||
|
d. Genetics can support the man’s case based on the blood types: the inheritance of A and B alleles are incomplete dominant; thus, the child of A and B blood type parents must have AB blood type. |
Question 25
Complete the following sentence. For most genes, we inherit two working copies: one from our mother and one from our father. With imprinted genes, we only inherit one working copy. Every imprinted allele:
Choose one answer.
|
a. is reset during gamete formation. |
||
|
b. may come from either parent by chance. |
||
|
c. is identical to the parental imprinted allele. |
||
|
d. stays imprinted during gamete formation. |
Question 26
Complete the following sentence. Gene penetrance refers to a portion of people:
Choose one answer.
|
a. with an allele who exhibit a trait associated with the allele. |
||
|
b. with a trait that is associated with multiple genes. |
||
|
c. who exhibit a particular trait in a population. |
||
|
d. who has a particular allele in a population. |
Question 27
Fill in the blanks. A continuous phenotypic character, e.g., skin color, suggests ____ inheritance; discrete phenotypes, e.g., white and purple pea plant flowers, suggest ____ inheritance.
Choose one answer.
|
a. epistatic, imprinted |
||
|
b. recessive, dominant |
||
|
c. epigenetic, autosomal |
||
|
d. multigenic, single gene |
Question 28
Jane Doe and Joe Doe both have normal color vision, but their young daughter, Sue, has red-green color blindness. Joe wants a divorce, because he believes that he is not the biological father of Sue, but Jane is in denial. Can a simple Punnet Square provide supporting evidence for Jane or Joe? Why, or why not?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Yes it can. The red-green color blindness allele is dominant, and it is on the X-chromosome; thus, little Sue’s biological father or mother must be red-green colorblind. Joe is not the biological father, because Jane is not red-green colorblind. |
||
|
b. No, it cannot. Red-green color blindness is a recessive autosomal condition; thus, if both parents are carriers, then there is a 50% chance that their daughter would be red-green color blind. |
||
|
c. No, it cannot. Red-green color blindness is maternally imprinted; thus, if Jane is a heterozygote, then there is a 50% chance that their daughter would be color blind. |
||
|
d. Yes, it can. Red-green color blindness allele is recessive, and it is on the X-chromosome; thus, little Sue’s biological father must be red-green colorblind. Joe is not the biological father. |
Question 29
Recent research shows that genomic DNA is highly methylated in normal cells, except the GC-rich reach regions. In contrast, cancer cells are highly methylated in their GC-rich genomic regions as well, but lamin-bound DNA becomes de-methylated in cancer cells. The initial DNA expression differences in normal and cancer cells are attributed to the differences in their DNA methylation levels. This is an example of which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Epigenetic inheritance |
||
|
b. Mendelian inheritance |
||
|
c. Genomic imprinting |
||
|
d. Genomic silencing |
Question 30
Recessive lethal genes were first discovered in 1905 in mice. Which of the following observations led to their discovery?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The altered phenotypic ratios from what was expected for dominant and/or Mendelian inheritance |
||
|
b. The reduced fertility of the homozygous recessive lethal mice |
||
|
c. The altered genotypic ratios from what was expected for dominant and/or Mendelian inheritance |
||
|
d. The reduced number of individuals in the laboratory mice population |
Question 31
What are the genotypes of A, B, and C individuals in the following family pedigree? Use F for the dominant allele and f for the recessive allele.
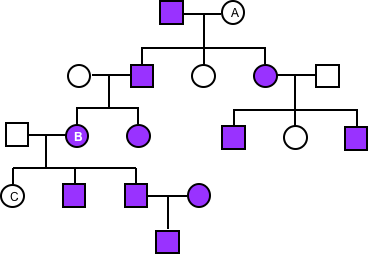
Choose one answer.
|
a. A is XFXf, B is XfXf, and C is XFXf. |
||
|
b. A is XFXF or XFXf, B is XFXf, and C is XFXF or XFXf |
||
|
c. A is XFXf, B is XFXf, and C is XFXF or XFXf. |
||
|
d. A and C are XfXf, and B is XFXf. |
Question 32
What is the inheritance pattern of the trait in the following pedigree?
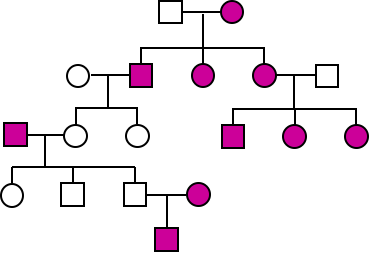
Choose one answer.
|
a. Dominant |
||
|
b. Mitochondrial |
||
|
c. Recessive |
||
|
d. X-linked |
Question 33
If a human (who is diploid) has type A blood and he or she marries another person with type B blood, what are the possible blood types of their offspring?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A, B, and O |
||
|
b. AB only |
||
|
c. A and B only |
||
|
d. A, B, AB, and O |
Question 34
Complete the following sentence. Crossing over cannot increase genetic variety if:
Choose one answer.
|
a. it takes place during gamete formation. |
||
|
b. kinetochore microtubules pull the sister chromatids away from each other very fast. |
||
|
c. the exchanged chromosome segments are identical. |
||
|
d. homologous non-sister chromatids exchange segments. |
Question 35
Genes A, B, and C are located on the same chromosome, and the recombination frequencies between A and B is 46% and between A and C is 13%. Is it possible to determine the linear order of these genes on the chromosome? Why, or why not?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Yes, we can conclude from the recombination frequencies that the order of the genes is ACB. |
||
|
b. Yes, we can conclude from the recombination frequencies that the order of the genes is CAB. |
||
|
c. No, there is not enough data available; the order of the genes can be either ACB or CAB. |
||
|
d. No, there is not enough data available; the order of the genes can be either ACB or BCA. |
Question 36
In a three-point test cross, one parent is triple heterozygote for three genes that are on the same chromosome and the other parent is homozygous recessive for the same three genes. The dominant alleles of these genes are A, B, and D; the recessive alleles are a, b, and d. The following table shows how many offspring express certain alleles:
How far are the A and B genes from each other?
How far are the A and B genes from each other?
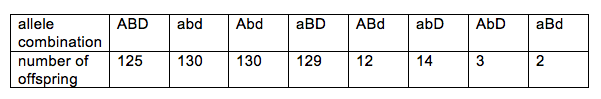
Choose one answer.
|
a. 4.8 cM |
||
|
b. 47.5 cM |
||
|
c. 0.9 cM |
||
|
d. 23.7 cM |
Question 37
In a three-point test cross, one parent is triple heterozygote for three genes that are on the same chromosome and the other parent is homozygous recessive for the same three genes. The dominant alleles of these genes are A, B, and D; the recessive alleles are a, b, and d. The following table shows how many offspring express certain alleles:
How far are the B and D genes from each other?
How far are the B and D genes from each other?
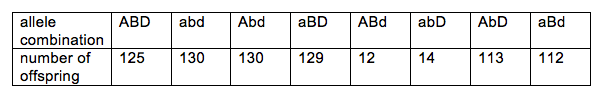
Choose one answer.
|
a. 4.8 cM |
||
|
b. 47.5 cM |
||
|
c. 41.2 cM |
||
|
d. 2.4 cM |
Question 38
The recessive A and B genes are located on the same chromosome, and a testcross is set up with a double heterozygous individual to determine the relative distance between these two genes. The test cross results in 396 offspring that are phenotypically wild type; 400 offspring that express both recessive traits; 96 offspring that express the recessive trait for A gene but are wild type for B; and 104 offspring that express the recessive trait for B gene but are wild type for A. What is the relative distance of A and B genes on the chromosome in centimorgan?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 25 cM |
||
|
b. 20 cM |
||
|
c. 10 cM |
||
|
d. 12.5 cM |
Question 39
The recessive alleles crossveinless (cv) and white (w) are on the Drosophila melanogaster X chromosome. The phenotype of Xcv+w+Y fly is wild type; the phenotype of Xcv-w+Y fly is crossveinless; and the phenotype of Xcv+w-Y fly is white eyed. You want to determine the distance of cv and w, so you set up a cross between a Xcv-w+Xcv+w- female and a wild type male. The male offspring of this cross fall into four groups based on their phenotype: there are 32 wild type males, 28 white eyed and crossveinless males, 275 crossveinless males, and 265 white eyed males. What is the relative distance of the crossveinless and white eye alleles on the X chromosome in Drosophila melanogaster?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 10 cM |
||
|
b. 6 cM |
||
|
c. 12 cM |
||
|
d. 20 cM |
Question 40
What biological process separates genes that are on the same chromosome?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Crossing over |
||
|
b. Epistasis |
||
|
c. Crosslinking |
||
|
d. Epigenetics |
Question 41
Which of the following statements regarding crossing over is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. All crossing over is genetic recombination. |
||
|
b. All genetic recombination is crossing over. |
||
|
c. The appearance of non-parental phenotype combinations is always the result of crossing over. |
||
|
d. The disappearance of non-parental phenotype combinations is always the result of crossing over. |
Question 42
Which of the following statements regarding the recombination frequency during meiosis is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The recombination frequency is higher between genes that are close to each other during meiosis. |
||
|
b. The recombination frequency is higher in prokaryotes than in eukaryotes during meiosis. |
||
|
c. The recombination frequency is random throughout the genome during meiosis. |
||
|
d. The recombination frequency is more frequent in certain regions of the genomes during meiosis. |
Question 43
You are given the following information on genetic distances between paired genes under study. A and B are 22 cM apart; A and C are 12 cM apart; A and D are 5.9 cM apart; and D and C are 6.1 cM apart. If you use this information to construct a genetic map, what is the order of genes on this chromosome?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A D C B or B C D A |
||
|
b. A C B D or D B C A |
||
|
c. A D B C |
||
|
d. D B C A |
Question 44
You want to create a chromosome map that reveals the relationships between four different genes: A, B, G, and H. Through controlled crosses, you learn that A and H are 17.9 cM apart; A and B are 10 cM apart; B and H are 7.9 cM apart; A and G are 2.5 cM apart; and H and G are 20.4 cM apart. In which order are your genes located?
Choose one answer.
|
a. H, B, A, G |
||
|
b. B, H, G, A |
||
|
c. A, B, H, G |
||
|
d. B, H, A, G |
Question 45
Complete the following sentence. Most prokaryotes reproduce asexually and are:
Choose one answer.
|
a. triploid. |
||
|
b. diploid. |
||
|
c. haploid. |
||
|
d. aneuploid. |
Question 46
Fill in the blanks. Karyotyping requires condensed chromosomes; thus, karyotyping uses cells that are in either the _____ stage or the _____ stage of mitosis.
Choose one answer.
|
a. anaphase, telophase |
||
|
b. prointerphase, interphase |
||
|
c. metaphase, prometaphase |
||
|
d. cytokinesis, telophase |
Question 47
The following image shows the primary spermatocyte of a diploid organism that has two homologous chromosome pairs. Cell division of the primary spermatocyte gives rise to the sperm cells in panels A through D. Which frequencies of sperm cells with a different number of chromosomes is the result of non-disjunction during meiosis II?
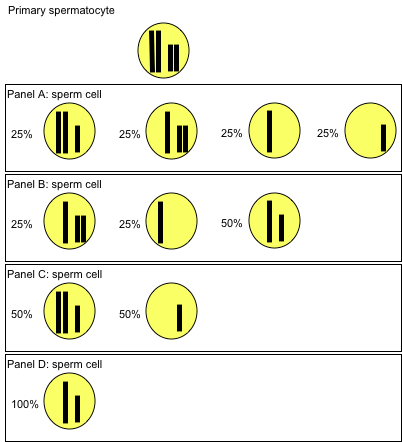
Choose one answer.
|
a. A |
||
|
b. B |
||
|
c. C |
||
|
d. D |
Question 48
The most common aneuploidies in humans are trisomies. Trisomies result in how many chromosomes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 47 |
||
|
b. 43 |
||
|
c. 46 |
||
|
d. 44 |
Question 49
The Philadelphia chromosome influences the structure of human chromosomes 9 and 22, and it causes a rare form of leukemia. Study the following image, and then answer the question: What is the correct term to describe the chromosomal changes that lead to the formation of the Philadelphia chromosome?
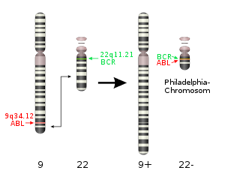
Choose one answer.
|
a. Exchange |
||
|
b. Inverse translocation |
||
|
c. Reciprocal translocation |
||
|
d. Transposition |
Question 50
There are many different types of chromosomal changes, including balanced structural changes, where there is an equal exchange of material, and unbalanced structural changes, where there is an addition or a loss of chromosomal segments. Which of the following is an example of unbalanced structural changes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Duplication |
||
|
b. Inversion |
||
|
c. Inversion |
||
|
d. Mutation |
Question 51
What are the correct terms to describe the chromosomal changes shown on the following image?
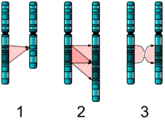
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1. deletion, 2. duplication, and 3. inversion |
||
|
b. 1. addition, 2. replication, 3. crossing |
||
|
c. 1. loss, 2. insertion, 3. translocation |
||
|
d. 1. elimination, 2. doubling, 3. reciprocal inversion |
Question 52
What are the correct terms to describe the chromosomal changes shown on the following image?
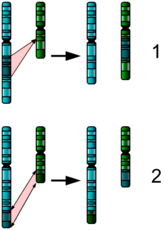
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1. inverse deletion and 2. translocation |
||
|
b. 1. translocation and 2. reciprocal translocation |
||
|
c. 1. transposition and 2. exchange |
||
|
d. 1. elimination and 2. reciprocal inversion |
Question 53
What medical condition may be diagnosed by examining the following image?
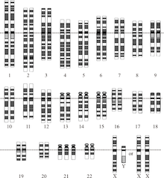
Choose one answer.
|
a. Klinefelter syndrome |
||
|
b. Edward’s syndrome |
||
|
c. Patau syndrome |
||
|
d. Down syndrome |
Question 54
You create a karyotype on a pair of cells: one of which is a somatic cell from the parent and the other of which is from a gamete of that same plant. Your initial banding pattern focuses on a certain order of genes that are under study. The order from the parent plant is C, E, G, H, P. The order from the gamete is C, H, G, E, P. What type of mutation caused this pattern in the gamete?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Duplication |
||
|
b. Deletion |
||
|
c. Inversion |
||
|
d. Aneuploidy |
Question 55
Down syndrome results most often from which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Nondisjunction during meiosis |
||
|
b. Nondisjunction during mitosis |
||
|
c. Folic acid deficiency |
||
|
d. Maternal allele inheritance |
Question 56
After 25 PCR cycles, how much DNA is produced?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 25 times more |
||
|
b. 225 times more |
||
|
c. 252 times more |
||
|
d. 50 times more |
Question 57
Compare and contrast in vivo and in vitro DNA duplication.
Choose one answer.
|
a. The in vivo process always takes place in a cell; the in vitro process always takes place in a thermocycler. |
||
|
b. The in vitro process may involve thermostable DNA polymerase; the in vivo process always utilizes DNA polymerase isolated from Thermus aquaticus. |
||
|
c. The in vivo process uses ribonucleotide primer; the in vitro process uses oligonucleotide primer for DNA polymerase. |
||
|
d. The in vivo process does not use dNTPs; the in vitro process uses dNTPs. |
Question 58
Complete the following sentence. Barbara McClintock performed experiments using maize (corn) with different phenotypes of kernel color. She found that the phenotypic effect of one element (Ds) depended on the presence of another element (Ac). However, she had problems mapping these elements onto the chromosomes, because:
Choose one answer.
|
a. it is technically difficult to determine the phenotypes. |
||
|
b. the structure of the dsDNA was not known yet. |
||
|
c. these elements were jumping on the chromosomes. |
||
|
d. Ds and Ac cancelled each other out. |
Question 59
Complete the following sentence. Microsatellites – otherwise known as simple sequence tandem repeats (SSTRs) – are generally di-, tri-, or tetranucleotides. Microsatellites are useful as genetic markers, because:
Choose one answer.
|
a. they never contain mistakes. |
||
|
b. they are highly variable. |
||
|
c. they are short. |
||
|
d. they are long. |
Question 60
DNA microarrays are used to do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. To identify point mutations |
||
|
b. To analyze DNA fingerprints |
||
|
c. To amplify genomic DNA |
||
|
d. To analyze differential gene expression in tissues |
Question 61
Fill in the blanks. _________ are circular extrachromosomal DNA molecules that are present in varying numbers in the cell, and they can be entirely lost without changing species identity. _____DNA is usually linear, and it determines species identity.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Plasmids, Nuclear |
||
|
b. Mitochondrials, Nuclear |
||
|
c. Organelles, Chromosomal |
||
|
d. Plastids, Chromosomal |
Question 62
PCR is the most commonly used DNA amplification technique. Which of the following lists the steps of PCR in the correct order?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Polymerization, denaturation, melting |
||
|
b. Melting, base-pairing, elongation |
||
|
c. Annealing, melting, polymerization |
||
|
d. Denaturation, annealing, elongation |
Question 63
The following image outlines conventional breeding, transgenesis, and cisgenesis. The aim of all of these techniques is to generate an organism with desired traits. Which of the following technologies uses recombinant DNA?
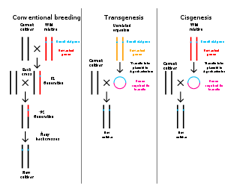
Choose one answer.
|
a. Cisgenesis only |
||
|
b. Transgenesis only |
||
|
c. Transgenesis and cisgenesis |
||
|
d. Transgenesis and conventional breeding |
Question 64
The following image outlines the transposition of mobile elements. Which of the following accurately identifies the names of mobile elements in boxes A and B?
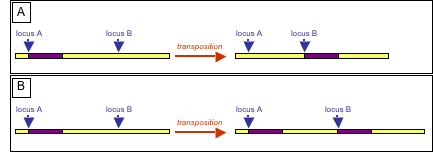
Choose one answer.
|
a. B shows a transposon, and A shows a retrotransposon. |
||
|
b. A shows a transposon, and B shows a retrotransposon. |
||
|
c. A shows a transposon, and B shows a duplicating transposon. |
||
|
d. B shows a duplicating transposon, and A shows a retrotransposon. |
Question 65
The organization of the nuclear genome is not randomized. Recent genome studies have revealed general patterns between organisms. Which of the following is NOT a domain that was noticed?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Interchromatine |
||
|
b. Chromosome |
||
|
c. Nucleolus |
||
|
d. Plasmid |
Question 66
Which of the following statement best describes recombinant DNA?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Recombinant DNA always combines DNA from at least two sources. |
||
|
b. Recombinant DNA is the end-result of every cloning process. |
||
|
c. Recombinant DNA always uses a restriction endonuclease and a ligase. |
||
|
d. Recombinant DNA is always made in the test tube, not in a living cell. |
Question 67
Which of the following statements about class II transposons is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Class II transposons are segments of DNA that move from one place to another through the cut-and-paste mechanism. |
||
|
b. Class II transposons are characterized by their short lengths and stretch of 15 base pairs that occur at each end of the transposon. |
||
|
c. Class II transposons are part of a highly unique group that forms large portions of the genomes of eukaryotes. |
||
|
d. Class II transposons are incorporated through retrotransposition. |
Question 68
Which of the following statements describes mutations?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It only takes one mutation of one base pair to make a large difference in protein production. |
||
|
b. In order to detect a mutation, at least three base pairs must change at the same time. |
||
|
c. Populations are often filled with individuals that have a mutation in the first base of the triplet codon, because this does not make much of a difference in how the protein is made. |
||
|
d. Silent mutations most often happen in the second base of the triplet codon. |
Question 69
Complete the following sentence. The “one gene, one enzyme” theory suggests that:
Choose one answer.
|
a. each gene codes for one characteristic. |
||
|
b. every gene can be correlated to a trait that it impacts. |
||
|
c. each gene codes for the production of a specific enzyme. |
||
|
d. every gene codes for an enzyme that will impact only one trait. |
Question 70
Complete the following sentence. During the process of bacterial conjugation, genetic material is transferred in a unidirectional way from the donor to a recipient. This happens through:
Choose one answer.
|
a. viral transduction. |
||
|
b. transformation. |
||
|
c. R-factor. |
||
|
d. F-factor. |
Question 71
Complete the following sentence. Gene transfer in bacteria is unidirectional, with DNA moving from the donor cell to the recipient cell. Most of the time the donor only gives a part of the DNA, making a:
Choose one answer.
|
a. merozygote. |
||
|
b. homologous pair. |
||
|
c. heterozygote. |
||
|
d. disomy. |
Question 72
Complete the following sentence. Transduction is the transfer of genetic information in bacteria from a donor to a recipient through:
Choose one answer.
|
a. a host DNA. |
||
|
b. a bacteriophage. |
||
|
c. a nuclease. |
||
|
d. a virulent strain. |
Question 73
Frederick Griffith published his observation in 1928 that the nonpathogenic R strain of Streptococcus pneumonia is converted to S pathogenic strain, if the live R strain is mixed with dead S strain bacteria. Griffith’s experiment describes which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Transfection |
||
|
b. Induction |
||
|
c. Transformation |
||
|
d. Transposition |
Question 74
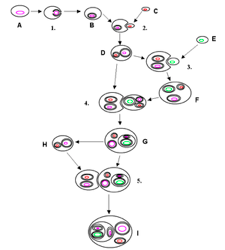
Panels 4 through 6 of the image below illustrate which of the following biological processes?

Choose one answer.
|
a. Transfection |
||
|
b. Transduction |
||
|
c. Induction |
||
|
d. Transposition |
Question 75
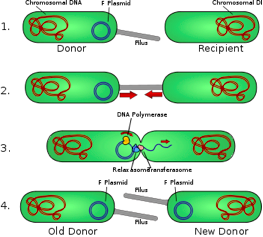
The image below illustrates which of the following biological processes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Conjugation |
||
|
b. Transformation |
||
|
c. Transduction |
||
|
d. Mating |
Question 76
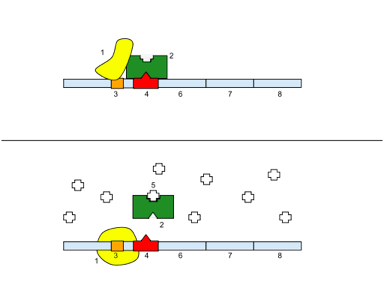
The image below shows gene expression regulation in bacteria. Which of the following statements best describes this process?
Choose one answer.
|
a. This is the Trp operon, which is repressed by tryptophan (5). Tryptophan inactivates the RNA polymerase (2) by removing it from the DNA and leaving the transcription factor (3) behind. |
||
|
b. This is the Trp operon (4), which is repressed by tryptophan (5). Tryptophan inactivates the RNA polymerase (2) by removing it from the DNA and leaving the transcription factors (3 and 4) behind. |
||
|
c. This is the Lac operon, which is induced by allolactose (5). Allolactose inactivates the repressor (2) and allows the RNA polymerase (3) to transcribe the genes. |
||
|
d. This is the Lac operon (4), which is induced by lactose (5). Lactose inactivates the repressor (2) and allows the RNA polymerase (3) to transcribe the genes. |
Question 77
Which of the following is not used to experimentally manipulate gene expression in bacteria?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Transfection |
||
|
b. Transduction |
||
|
c. Induction |
||
|
d. Conjugation |
Question 78
Which of the following statements best describes bacteria?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Introns are removed from the transcript before translation begins. |
||
|
b. Genes that play a role in the same metabolic pathway are organized into an operator. |
||
|
c. The expression of genes that play a role in the same metabolic pathway is orchestrated by upstream enhancers. |
||
|
d. Genes that play a role in the same metabolic pathway are organized into an operon. |
Question 79
Certain species of bacteria always have the ability to utilize lactose as a carbon source. These species can do this with the help of which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The Lac operator |
||
|
b. Positive feedback |
||
|
c. Negative feedback |
||
|
d. The Lac operon |
Question 80
Complete the following sentence. A library of yeast with transposons randomly integrated into yeast genes:
Choose one answer.
|
a. produces overexpression mutants and is also a tool to analyze the natural expression of that gene if the transposon has a reporter gene. |
||
|
b. generates jumping genes and mosaic yeast cell; this is similar to the transposon effect in corn that makes color-colorless strikes in seeds. |
||
|
c. generates transgenic yeast that glows in the dark; thus, it attracts great interest in the bakeries. |
||
|
d. produces gene disruption mutants and is also a tool to analyze the expression of that gene if the transposon has a reporter gene. |
Question 81
Complete the following sentence. Barr bodies, found in mammalian females, are interpreted as inactivated:
Choose one answer.
|
a. Y chromosomes. |
||
|
b. X chromosomes. |
||
|
c. somatic chromosomes. |
||
|
d. autosomes. |
Question 82
Complete the following sentence. Genes within the chloroplast, mitochondria, and nucleus can be transferred back and forth between the organellar and nuclear genomes. Researchers know this, because:
Choose one answer.
|
a. they have physically seen the crossover events on electron micrographs. |
||
|
b. they found genes in the chloroplast that were known to be mitochondrial. |
||
|
c. the endosymbiosis hypothesis predicts such gene transfers. |
||
|
d. proper organellar function requires nuclear gene products. |
Question 83
Complete the following sentence. The C-value paradox states that:
Choose one answer.
|
a. as the body of an organism becomes more complex, the size of the genome will increase. |
||
|
b. there can be a large difference in the size of the genome even between organisms that are similar in body pattern and size. |
||
|
c. as the body of an organism becomes more complex, the size of the genome will decrease. |
||
|
d. prokaryotic genome is not always smaller than the eukaryotic genome. |
Question 84
Complete the following sentence. The fugu genome is 400 Mb and the human genome is 3,000 Mb, and both the fugu and the human genomes have about 30,000 genes. The fugu genome can accommodate the same number of genes as the human genome, because:
Choose one answer.
|
a. only the regulatory regions of the genes differ in animals; all animals have the same number of genes. |
||
|
b. the fugu genome has less exon and less intergene space. |
||
|
c. the fugu genome has smaller introns, less intergene space, and fewer repeats. |
||
|
d. the fugu genome has no intergene space and no repeats. |
Question 85
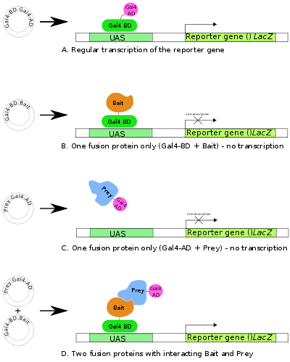
Identify the analytical technique, which is illustrated on the figure.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Yeast two-hybrid system |
||
|
b. Eukaryotic UAS-Gal4 control |
||
|
c. Bacterial transcriptional activation |
||
|
d. Plant gene induction |
Question 86
The image below illustrates which of the following biological processes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Series of bacterial conjugation |
||
|
b. A theory for the origin of eukaryotes |
||
|
c. A theory for the origin of prokaryotes |
||
|
d. Plasmid multiplication in fused bacteria |
Question 87
What percentage of the genes that you find in humans do you also find in flies and in mice?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Approximately 50% in flies and 99% in mice |
||
|
b. 0% in flies and 75% in mice |
||
|
c. Approximately 10% in flies and 75% in mice |
||
|
d. 100% in both flies and mice |
Question 88
Which of the following best describes the difference between a locus and an allele?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A locus refers to the location on the chromosome, whereas an allele is used to refer to the alternative forms that a gene comes in. |
||
|
b. An allele refers to the location on the chromosome, whereas the term locus refers to the alternative forms of the gene. |
||
|
c. A locus refers to the phenotype of the organism, whereas an allele refers to the genotype. |
||
|
d. None of these answers |
Question 89
Which of the following was the first transgenic animal that was available to the American public?
Choose one answer.
|
a. GloFish |
||
|
b. Glowing bacteria |
||
|
c. Glow in the dark cats |
||
|
d. Glowing mice |
Question 90
Complete the following sentence. Neurospora works well for genetics studies, because:
Choose one answer.
|
a. it spends most of its life cycle in diploid condition. |
||
|
b. it spends most of its life cycle in the haploid condition. |
||
|
c. when the zygote undergoes mitosis or meiosis, it spreads. |
||
|
d. its genome is sequenced. |
Question 91
A population of pink and brown butterflies lives in a forest, where the butterflies try to blend in with the trees. Over time, birds find the butterflies to be a tasty source of food. What do you predict will happen to the butterfly population?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They will not change color. |
||
|
b. They will turn pink. |
||
|
c. They will turn brown. |
||
|
d. None of these answers |
Question 92
Complete the following sentence. Evolutionary relationships are often investigated through non-coding DNA sequence data, because:
Choose one answer.
|
a. these regions commonly show evidence of horizontal gene transfer; thus, they simplify the tree construction. |
||
|
b. the repeats in these regions simplify the in silico sequence analysis. |
||
|
c. there are more non-coding regions than coding regions; thus, this approach offers more data to work with. |
||
|
d. mutations in these regions are less influenced by natural selection. |
Question 93
Complete the following sentence. In 2006, news agencies reported on the failure of Bt-cotton crop in India after extreme environmental stress. The crop’s survival chance was lower because of:
Choose one answer.
|
a. harsh weather that no other crop could survive. |
||
|
b. endotoxin toxicity. |
||
|
c. the low diversity in the population. |
||
|
d. the sudden diversity increase in the population. |
Question 94
Complete the following sentence. We can expect genetic differences between human groups that have been geographically separated through human history. However, such differences, if any, would disappear because of:
Choose one answer.
|
a. genetic drift. |
||
|
b. the gene flow. |
||
|
c. growing human populations. |
||
|
d. nonrandom mating. |
Question 95
Fill in the blanks. We can expect an increase in the frequency of recessive disorders in a _____ population, particularly if _____ is in play.
Choose one answer.
|
a. small, the founder effect |
||
|
b. small, nonrandom mating |
||
|
c. large, the bottleneck effect |
||
|
d. large, genetic drift |
Question 96
New genetic variation within populations is mainly caused by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Mutation |
||
|
b. Emigration |
||
|
c. The founder effect |
||
|
d. The bottle neck effect |
Question 97
What are the frequencies of A and a alleles in a population which has 50% AA, 25 % aa, and 25 % Aa individuals?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 25% for the A allele and 75% for the a allele |
||
|
b. 37.5% for the A allele and 62.5% for the a allele |
||
|
c. 62.5% for the A allele and 37.5% for the a allele |
||
|
d. 75% for the A allele and 25% for the a allele |
Question 98
What can be said about “p” and “q”?
Choose one answer.
|
a. p + q = 1 |
||
|
b. 2pq = 1 |
||
|
c. p – q = 0 |
||
|
d. p + 2pq + q = 0 |
Question 99
Which of the following decreases the variety in a population?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Stabilizing selection |
||
|
b. Bidirectional selection |
||
|
c. Disruptive selection |
||
|
d. Directional selection |
Question 100
Which of the following statements about genotype and allele frequencies is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Genotype frequency is always the same as phenotypic frequency. |
||
|
b. Genotype frequency and phenotypic frequency are different. |
||
|
c. Allele frequency always determines gene frequency. |
||
|
d. Allele frequency always determines phenotypic frequency. |
Question 101
Which of the following will not impact the allele frequencies in a population?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Founder effects |
||
|
b. Nonrandom mating |
||
|
c. Bottleneck effect |
||
|
d. Genetic drift |
Question 102
Complete the following sentence. A population will stay in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium if:
Choose one answer.
|
a. the population is evolving. |
||
|
b. the population is not evolving. |
||
|
c. the population is large. |
||
|
d. there is more than one species in the population. |