1
Question 2
Question 3
In quantum mechanics, electrons can behave as:
Choose one answer.
|
a. waves. |
||
|
b. both waves and particles. |
||
|
c. particles. |
||
|
d. none of these choices. |
Question 4
In quantum mechanics, light can behave as:
Choose one answer.
|
a. waves. |
||
|
b. particles. |
||
|
c. both waves and particles. |
||
|
d. none of these choices. |
Question 5
One phenomenon that demonstrates the particle nature of light is:
Choose one answer.
|
a. light diffraction. |
||
|
b. the photoelectric effect. |
||
|
c. color. |
||
|
d. interference effects. |
Question 6
One phenomenon that demonstrates the wave nature of light is:
Choose one answer.
|
a. diffraction. |
||
|
b. the photoelectric effect. |
||
|
c. blackbody radiation. |
||
|
d. absorption of light by an electron. |
Question 7
Question 8
Question 9
The electronic energy levels of the hydrogen atom are shown in the diagram below. According to the Bohr model of the atom, how many lines will be observed in the atomic emission spectra if the electron is excited to the level with energy of -0.85 eV?
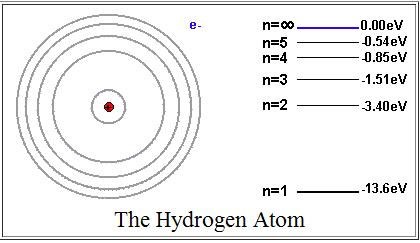
Choose one answer.
|
a. 2 |
||
|
b. 1 |
||
|
c. 4 |
||
|
d. 3 |
Question 10
The electronic energy levels of the hydrogen atom are shown in the following diagram. According to the Bohr model of the atom, how many lines will be observed in the atomic emission spectra if the electron is excited to the level with an energy of -0.54 eV?

Choose one answer.
|
a. 3 |
||
|
b. 5 |
||
|
c. 4 |
||
|
d. 1 |
Question 11
A key piece of evidence for the wave-particle duality of electrons is:
Choose one answer.
|
a. that electrons have momentum. |
||
|
b. that electrons have mass. |
||
|
c. the diffraction of electrons. |
||
|
d. that electrons are attracted to the nucleus in an atom. |
Question 12
A key piece of evidence for the wave-particle duality of light is:
Choose one answer.
|
a. the wavelength of green light. |
||
|
b. the photoelectric effect. |
||
|
c. color of light. |
||
|
d. intensity of light. |
Question 13
Given that a baseball has a mass of 0.14 kg, and the Planck's constant is 6.626 x 10^(-34) J S, what is the de Broglie wavelength (in meters) for the baseball moving at a speed of 40 m/s?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 4.733 x 10^(-33) m |
||
|
b. 8.451 x 10^(33) m |
||
|
c. 1.183 x 10^(-34) m |
||
|
d. 1.657 x 10^(-35) m |
Question 14
Given that the mass of an electron is me = 9.11 x 10^(-31) kg, and the Planck's constant is 6.626 x 10^(-34) J S, what is the de Broglie wavelength (in meters) for an electron moving at a speed of 480,000 m/s?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1.380 x 10^(-39) m |
||
|
b. 6.599 x 10^(8) m |
||
|
c. 7.273 x 10^(-4) m |
||
|
d. 1.515 x 10^(-9) m |
Question 15
The atomic emission spectra of the hydrogen atom show a red line at a wavelength of 656 nm. Given that the speed of light is 3.0 x 10^(8) m/s and Planck's constant is 6.626 x 10^(-34) J S, what is the energy possessed by one photon?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 3.300 x 10^(18) J |
||
|
b. 3.030 x 10^(-19) J |
||
|
c. 1.010 x 10^(-27) J |
||
|
d. 4.573 x 10^(14) J |
Question 16
The atomic emission spectra of the hydrogen atom show a violet line at a wavelength of 434 nm. Given that the speed of light is 3.0 x 10^(8) m/s and Planck's constant is 6.626 x 10^(-34) J S, what is the energy possessed by one photon?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 6.912 x 10^(14) J |
||
|
b. 1.526 x 10^(-27) J |
||
|
c. 4.580 x 10^(-19) J |
||
|
d. 2.180 x 10^(18) J |
Question 17
Question 18
Question 19
Question 20
Question 22
Question 26
Question 29
The energy operator in quantum mechanics, , is called the:
Choose one answer.
|
a. momentum. |
||
|
b. Laplacian. |
||
|
c. Hamiltonian. |
||
|
d. Hermitian. |
Question 30
Question 31
Question 32
Question 33
Acceptable wave functions must satisfy which of the following requirements?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Single valued |
||
|
b. Finite |
||
|
c. Continuous |
||
|
d. All of these choices |
Question 34
A physical requirement on an acceptable wave function is that it must be:
Choose one answer.
|
a. positive everywhere. |
||
|
b. normalizable. |
||
|
c. reliable. |
||
|
d. none of these choices. |
Question 35
Question 36
Question 37
In solving the Schrödinger equation for the particle in a box system, satisfying the boundary conditions imposes:
Choose one answer.
|
a. the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. |
||
|
b. zero-point energy. |
||
|
c. quantization of energy. |
||
|
d. all of these choices. |
Question 38
In solving the Schrödinger equation for the harmonic oscillator, satisfying the boundary conditions imposes:
Choose one answer.
|
a. quantization of energy. |
||
|
b. the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. |
||
|
c. zero-point energy. |
||
|
d. all of these choices. |
Question 39
The phenomenon that wave functions can extend into the classically forbidden region, i.e., the region where a classical particle would have negative kinetic energy, is termed:
Choose one answer.
|
a. quantization. |
||
|
b. quantum mechanical tunneling. |
||
|
c. normalization. |
||
|
d. zero-point energy. |
Question 40
Which of the following is TRUE about tunneling?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It occurs in the harmonic oscillator system. |
||
|
b. It is the phenomenon that wave functions can extend into the classically forbidden region, i.e., the region where a classical particle would have negative kinetic energy. |
||
|
c. It becomes less as the mass of particle increases. |
||
|
d. All of these choices |
Question 41
The vibrational frequency for the hydrogen chloride molecule HCl is 2886 cm^(-1). Assuming the diatomic vibration can be treated as a harmonic oscillator, calculate the zero-point energy for HCl:
Choose one answer.
|
a. 2.87 x 10^(-22) J |
||
|
b. 5.74 x 10^(-20) J |
||
|
c. 0 |
||
|
d. 2.87 x 10^(-20) J |
Question 42
The vibrational frequency for the hydrogen bromide molecule (HBr) is 2558 cm^(-1). Assuming the diatomic vibration can be treated as a harmonic oscillator, calculate the zero-point energy for HBr.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0 |
||
|
b. 5.08 x 10^(-20) J |
||
|
c. 2.54 x 10^(-20) J |
||
|
d. 1.27 x 10^(-20) J |
Question 43
The energy gap between two adjacent quantum states for the rigid rotor system:
Choose one answer.
|
a. is a constant. |
||
|
b. increases as the quantum number becomes larger. |
||
|
c. decrease as the quantum number becomes larger. |
||
|
d. none of these choices. |
Question 44
Question 45
Question 46
Question 47
Question 48
Question 49
Question 50
Question 51
Question 52
Question 53
Question 54
Question 55
Wave functions for the hydrogen atom contain nodes. The 4d orbital possesses:
Choose one answer.
|
a. three angular nodes and one radial node. |
||
|
b. four angular nodes and two radial nodes. |
||
|
c. four angular nodes and one radial node. |
||
|
d. two angular nodes and one radial node. |
Question 56
Wave functions for the hydrogen atom can contain nodes. The 5p orbital possesses:
Choose one answer.
|
a. two angular nodes and two radial nodes. |
||
|
b. one angular nodes and three radial nodes. |
||
|
c. five angular nodes and three radial nodes. |
||
|
d. one angular node and five radial nodes. |
Question 57
The solution of the Schrödinger equation for the hydrogen atom resulted in degenerated states for the principal energy levels characterized by the principal quantum number n. For the  ) are:
) are:
Choose one answer.
|
a. (2, 2, 1), (2, 1, -1), (2, 1, 0), (2, 1, 1), and (2, 0, 0). |
||
|
b. (2, 1, -1), (2, 1, 0), (2, 1, 1), and (2, 0, 0). |
||
|
c. (2, 1, -1), (2, 1, 0), (2, 1, 1), (2, 0, -1), (2, 0, 0), and (2, 0, 1). |
||
|
d. (2, 2, -1), (2, 1, -1), (2, 1, 0), and (2, 1, 1). |
Question 58
Question 59
Question 60
Question 61
Question 62
Question 63
Question 64
Question 65
Question 66
Question 67
According to the molecular orbital theory, the bonding order for the carbon monoxide molecule CO is:
Choose one answer.
|
a. 3. |
||
|
b. 3.5. |
||
|
c. 2. |
||
|
d. 2.5. |
Question 68
Question 69
Which of the following statements is FALSE?
Choose one answer.
Question 70
Question 71
Question 72
Question 73
Question 74
Question 75
Question 76
Question 77
Question 78
Question 79
The IR spectra for the hydrogen chloride molecule (HCl) display a peak at 2886 cm^(-1). Assuming the diatomic vibration can be treated as a harmonic oscillator, calculate the energy for the first vibrational excited state of HCl.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 8.63 kcal/mol |
||
|
b. 43.17 kcal/mol |
||
|
c. 25.90 kcal/mol |
||
|
d. 17.27 kcal/mol |
Question 80
The IR spectra for the hydrogen bromide molecule (HBr) display a peak at 2558 cm^(-1). Assuming the diatomic vibration can be treated as a harmonic oscillator, calculate the energy for the first vibrational excited state of HBr.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 7.65 kcal/mol |
||
|
b. 22.96 kcal/mol |
||
|
c. 15.30 kcal/mol |
||
|
d. 38.26 kcal/mol |
Question 81
An absorption spectrum for the diatomic molecule hydrogen iodide (HI) appeared in the microwave region. The most likely origin for the observed spectra is:
Choose one answer.
|
a. pure rotational transition. |
||
|
b. pure vibrational transition. |
||
|
c. electronic transition. |
||
|
d. none of these choices. |
Question 82
An absorption spectrum for the diatomic molecule hydrogen bromide HBr appeared at the IR region as shown below. Which of the following is the most likely origin for the observed spectrum?
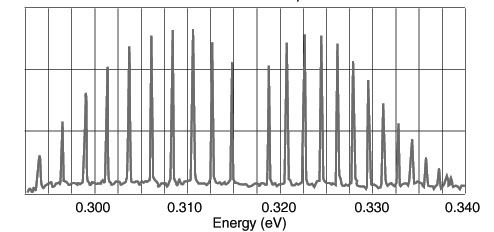
Choose one answer.
|
a. Pure rotational transition |
||
|
b. Pure vibrational transition |
||
|
c. Electronic transition |
||
|
d. Ro-vibrational transition |
Question 83
Question 84
Question 85
Question 86
Question 87
Question 88
Question 89
In a typical ro-vibrational absorption spectrum with a v = 0 to v = 1 transition, which of the following lines occurs at the lowest frequency?
Choose one answer.
|
a. J = 4 to J = 3 |
||
|
b. J = 1 to J = 0 |
||
|
c. J = 3 to J = 4 |
||
|
d. J = 0 to J = 1 |
Question 90
In a typical ro-vibrational absorption spectrum with a v = 0 to v = 1 transition, which of the following lines occurs at the highest frequency?
Choose one answer.
|
a. J = 4 to J = 3 |
||
|
b. J = 0 to J = 1 |
||
|
c. J = 3 to J = 4 |
||
|
d. J = 4 to J = 5 |
Question 91
For which of the following transitions does the frequency of light absorption occur in the UV-V is region for a heteronuclear diatomic molecule like HBr?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Electronic transition |
||
|
b. Rotational transition |
||
|
c. Vibrational transition |
||
|
d. Translational transition |
Question 92
For which of the following transitions is the frequency of light absorption the highest for a heteronuclear diatomic molecule like HBr?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Rotational transition |
||
|
b. Ro-vibrational transition |
||
|
c. Vibrational transition |
||
|
d. Electronic transition |
Question 93
As an electron is excited from a singlet ground state to a singlet excited state of the chlorophyll molecule, what is a possible fate of the electronic excited state?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Fluorescence |
||
|
b. Phosphorescence |
||
|
c. Transference of energy to a nearby receptor molecule |
||
|
d. All of these choices |
Question 94
Question 95
For a certain molecule, the fluorescence spectrum can be a mirror image of the absorption spectrum. Which of the following is NOT a likely contributing factor for the occurrence of the mirror image?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Absorption of light by the vibrational transition obeys the Franck-Condon principle. |
||
|
b. The ground electronic state has very similar vibrational states as the first electronic excited state. |
||
|
c. The emission of light by vibrational transition obeys the Franck-Condon principle. |
||
|
d. Both absorption and emission of light are measured by the same instrument. |
Question 96
For a certain molecule, the fluorescence spectrum can be a mirror image of the absorption spectrum. Which of the following is not a likely contributing factor for the occurrence of the mirror image?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Absorption of light from the ground electronic state starts at the ground vibrational state. |
||
|
b. Both absorption and emission of light are directly proportional to concentration of the molecule |
||
|
c. Emission of light from the electronically excited state starts at the ground vibrational state. |
||
|
d. The Franck-Condon principle governs both absorption and emission of light by the molecule. |
Question 97
Question 98
Question 99
In a NMR experiment, an external magnetic field is applied to the sample. What happens to the protons in a sample?
Choose one answer.
|
a. All protons align opposite to the field. |
||
|
b. Some protons align with the field and some align opposite to it. |
||
|
c. All protons align with the field. |
||
|
d. All protons assume a random orientation. |
Question 100
In a NMR experiment, a radio frequency (RF) signal is applied to the sample, in addition to the magnetic field. What happens to the spins of the sample?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The RF will force all spins to align opposite to the magnetic field. |
||
|
b. The RF will force all spins to assume a random orientation. |
||
|
c. The RF will force all spins to align with the magnetic field. |
||
|
d. The RF will flip the spin so as to prompt a spin transition to a slightly higher energy state. |