1
How many orbitals would you expect for a system with the following set of quantum numbers?
Choose one answer.
| a. 1 | ||
| b. 3 | ||
| c. 5 | ||
| d. 7 |
Question
2
What is the designation for the subshell with the following set of quantum numbers?
Choose one answer.
| a. 5d | ||
| b. 6f | ||
| c. 6p | ||
| d. The subshell does not exist. |
Question
3
The following set of quantum numbers
Choose one answer.
| a. is representative of a transition metal. | ||
| b. is not allowed. | ||
| c. is representative of a p-block element. | ||
| d. is representative of an element with two valence electrons. |
Question
4
One of the p-orbitals of an unknown element is half filled. Assuming that Hund's rule is upheld, which of the following elements could not be the unknown
element?
Choose one answer.
| a. xenon | ||
| b. silicon | ||
| c. gallium | ||
| d. iodine |
Question
5
Which of these compounds has a nonzero dipole moment?
Choose one answer.
| a. boron trifluoride | ||
| b. water | ||
| c. carbon dioxide | ||
| d. methane |
Question
6
The configuration for cadmium has 48 electrons. How many electrons occupy the 3d orbital?
Choose one answer.
| a. 2 | ||
| b. 6 | ||
| c. 10 | ||
| d. 14 |
Question
7
How many electrons are in the outermost energy shell for promethium (element 61)?
Choose one answer.
| a. 2 | ||
| b. 4 | ||
| c. 8 | ||
| d. 12 |
Question
8
The element represented by this orbital diagram is
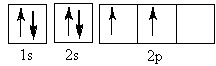
Choose one answer.
| a. lithium. | ||
| b. carbon. | ||
| c. silicon. | ||
| d. nitrogen. |
Question
9
The element represented by this orbital diagram is
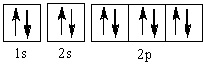
Choose one answer.
| a. chlorine. | ||
| b. argon. | ||
| c. neon. | ||
| d. boron. |
Question
10
In the experimentally observed Zeff values for the 2p elements, we find that the increase in the Zeff for a 2p electron is slightly
smaller between N and O (ΔZeff ≈ 0.62) than between C and N (ΔZeff ≈ 0.69). Which of the following is not a reason for the
differences in the ΔZeff values?
Choose one answer.
| a. Moving from C to N adds an electron to an occupied orbital. | ||
| b. The Zeff value for oxygen is raised due to additional shielding from fluorine. | ||
| c. Moving from N to O pairs two electrons in a single orbital. | ||
| d. The Zeff value decreases with an increase in electron repulsion. |
Question
11
Which element has the largest ionization energy?
Choose one answer.
| a. fluorine | ||
| b. chlorine | ||
| c. bromine | ||
| d. iodine |
Question
12
Which element has the smallest atomic radius?
Choose one answer.
| a. indium | ||
| b. gallium | ||
| c. boron | ||
| d. aluminum |
Question
13
For which of these systems does the metal have a d0 electron configuration?
Choose one answer.
| a. RuNH33+ | ||
| b. MnO4- | ||
| c. CuNO3 | ||
| d. Zn(ClO4)2 |
Question
14
Which element has the lowest electron affinity?
Choose one answer.
| a. argon | ||
| b. chlorine | ||
| c. xenon | ||
| d. bromine |
Question
15
The 4th ionization energy of aluminum is approximately 154 eV. From which orbital is the electron being removed?
Choose one answer.
| a. 2p | ||
| b. 2s | ||
| c. 3p | ||
| d. 3s |
Question
16
For the nitrite ion structure below, what is the formal charge on the nitrogen atom?
Choose one answer.
| a. 1+ | ||
| b. 1- | ||
| c. 2+ | ||
| d. There is no charge on the nitrogen. |
Question
17
The Lewis dot structure for a sulfate ion gives sulfur a formal charge of zero with six bonds. Based on the structure and the Lewis dot theory, which of
the following statements about the sulfur atom is false?
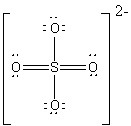
Choose one answer.
| a. The sulfur disobeys the octet rule. | ||
| b. Sulfur has more valence electrons than oxygen. | ||
| c. Sulfur has a greater number of electron shells than oxygen. | ||
| d. Sulfur is less electronegative than oxygen. |
Question
18
The AX3E structure notation best describes which molecule?
Choose one answer.
| a. H2O | ||
| b. SF4 | ||
| c. NH3 | ||
| d. XeF4 |
Question
19
What is the molecular geometry of BCl3?
Choose one answer.
| a. square planar | ||
| b. octahedral | ||
| c. tetrahedral | ||
| d. trigonal planar |
Question
20
What is the bond order for the Be2 molecule?
Choose one answer.
| a. 0 | ||
| b. 1 | ||
| c. 2 | ||
| d. 3 |
Question
21
According to molecular orbital theory, which molecule is the most stable?
Choose one answer.
| a. N2 | ||
| b. C2 | ||
| c. B2 | ||
| d. Be2 |
Question
22
The crystal field splitting diagram shown here represents a _________ complex.
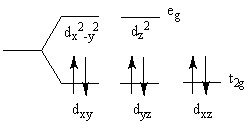
Choose one answer.
| a. high-spin iron(II) | ||
| b. low-spin iron(II) | ||
| c. high-spin iron(III) | ||
| d. low-spin iron(III) |
Question
23
The reaction between hexaamminechromium(III) perchlorate and an excess amount of _________ would definitely lead to the following crystal field splitting
diagram.
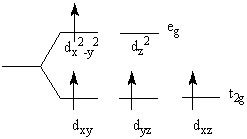
Choose one answer.
| a. water | ||
| b. oxalic acid | ||
| c. ammonia | ||
| d. hydrobromic acid |
Question
24
Which orbital would you expect to be the LUMO for a O22- peroxide ion?
Choose one answer.
| a. 2pσ | ||
| b. 2pπ | ||
| c. 2pσ* | ||
| d. 2pπ* |
Question
25
The crystal field splitting diagram shown here represents
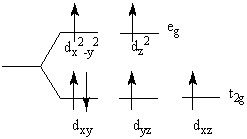
Choose one answer.
| a. [Co(NH3)6]3-. | ||
| b. [NiCl6]4-. | ||
| c. [Ni(NH3)6]2+. | ||
| d. [CoF6]3-. |
Question
26
The crystal field splitting diagram shown here represents
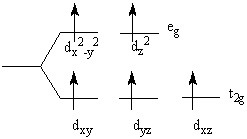
Choose one answer.
| a. paramagnetic [FeCl6]3+. | ||
| b. paramagnetic [Fe(CN)6]3+. | ||
| c. diamagnetic [Co(NH3)6]3+. | ||
| d. diamagnetic [CoF6]2+. |
Question
27
The chemical formula for potassium hexacyanorhodium(III) is
Choose one answer.
| a. K3[Rh(CN)6]. | ||
| b. Na2[Rh(CN)6]. | ||
| c. Na2[Rh(NH3)6]. | ||
| d. K[Rh(CN)6]. |
Question
28
The proper name for the Na[PtCl3(NH3)] complex is
Choose one answer.
| a. amminetrichloroplatinate(II) ion. | ||
| b. sodium amminetrichloroplatinate(II). | ||
| c. sodium amminetrichloroplatinate(IV). | ||
| d. potassium amminetrichloroplatinate(II). |
Question
29
Which complex would you expect to be blue in an aqueous solution?
Choose one answer.
| a. [Ni(CO)6]3+ | ||
| b. [Ru(bipy)3]2+ | ||
| c. [FeCl6]3+ | ||
| d. [Co(CN)6]3- |
Question
30
What geometry would you expect [Pt(CN)4]2- complex to have?
Choose one answer.
| a. trigonal bipyrimidal | ||
| b. tetragonal | ||
| c. tetrahedral | ||
| d. square planar |
Question
31
A rhombohedral crystal system has which characteristics?
Choose one answer.
| a. a ≠ b ≠ c, α = β = γ = 90° | ||
| b. a = b = c, α = β = γ ≠ 90° | ||
| c. a = b = c, α = β = γ = 90° | ||
| d. a ≠ b ≠ c, α = β = γ ≠ 90° |
Question
32
The complex MXLY has the crystal coordinate system seen below. Of the 14 Bravais lattices, to which could MXLY
belong?

Choose one answer.
| a. base-centered orthorhombic | ||
| b. face-centered cubic | ||
| c. body-centered orthorhombic | ||
| d. base-centered monoclinic |
Question
33
How many spheres/atoms are contained in a face-centered cubic unit cell?
Choose one answer.
| a. 2 | ||
| b. 4 | ||
| c. 6 | ||
| d. 8 |
Question
34
Which of the following statements concerning amorphous solids is false?
Choose one answer.
| a. Unlike crystalline solids, amorphous solids lack a repeating unit cell, leading to a random organization of atoms. | ||
| b. Unlike crystalline solids, amorphous solids tend to lose structural organization as their lattices extend. | ||
| c. Amorphous solids are said to behave as supercooled liquids, leading to an ease in transitioning between physical states. | ||
| d. The formation of amorphous solids is aided by the rapid cooling of a molten compound. |
Question
35
Which of the following is not a characteristic of covalent solids?
Choose one answer.
| a. high melting point | ||
| b. low electrical conductivity | ||
| c. high level of hardness | ||
| d. high water solubility |
Question
36
How many complete flourine atoms are present in a single unit cell of flourite (CaF2)?
Choose one answer.
| a. 4 | ||
| b. 6 | ||
| c. 8 | ||
| d. 14 |
Question
37
How many spheres/atoms are contained in a simple cubic unit cell?
Choose one answer.
| a. 0 | ||
| b. 1 | ||
| c. 2 | ||
| d. 4 |
Question
38
Which halogen would form a binary rubidium compound (RbX) with the longest bond length?
Choose one answer.
| a. fluorine | ||
| b. chlorine | ||
| c. bromine | ||
| d. iodine |
Question
39
Which ion has the smallest radius?
Choose one answer.
| a. selenium | ||
| b. tellurium | ||
| c. oxygen | ||
| d. sulfur |
Question
40
Which of the following statements about the 14 Bravais unit cells is incorrect?
Choose one answer.
| a. The unit cell is the simplest repeating unit in the crystal lattice. | ||
| b. Opposing faces of a unit cell are parallel. | ||
| c. Each unit cell edge is equivalent in length. | ||
| d. Each unit cell edge connects equivalent points/atoms. |
Question
41
Using the table below, determine the crystal lattice energy of KBr.
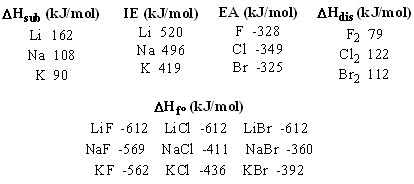
Choose one answer.
| a. -604 kJ/mol | ||
| b. -660 kJ/mol | ||
| c. -740 kJ/mol | ||
| d. -819 kJ/mol |
Question
42
Cesium and sodium are Group 1 metals, but the coordination number of cesium in the CsCl unit cell is 8, whereas the coordination number of sodium in the
NaCl unit cell is 6. What allows cesium to have a larger coordination number?
Choose one answer.
| a. Sodium has a larger ionic radius than cesium, allowing for less anion attraction. | ||
| b. Due to its size, cesium makes more contact with adjacent anions than sodium does. | ||
| c. The NaCl radius ratio is greater than that of CsCl, forcing anions farther from the metal cation. | ||
| d. Chlorine is too electronegative to be completely compatible with sodium. |
Question
43
How many complete NaCl molecules are found in the rock salt unit cell?
Choose one answer.
| a. 1 | ||
| b. 4 | ||
| c. 8 | ||
| d. 12 |
Question
44
The coordination numbers of Ca2+ and F- in flourite are _________, respectively.
Choose one answer.
| a. 2 and 4 | ||
| b. 4 and 2 | ||
| c. 4 and 4 | ||
| d. 6 and 4 |
Question
45
A body-centered cubic crystal system is best represented in the unit cell of which crystalline solid?
Choose one answer.
| a. perovskite | ||
| b. NaCl | ||
| c. rutile | ||
| d. CsCl |
Question
46
In a close-packed system, what percentage of the unit cell is occupied by holes?
Choose one answer.
| a. 14 | ||
| b. 26 | ||
| c. 74 | ||
| d. 86 |
Question
47
In a hexagonal close-packed system, the metal atom caps are arranged in an _________ pattern.
Choose one answer.
| a. ABC | ||
| b. AAA | ||
| c. ABB | ||
| d. ABA |
Question
48
For a face-centered cubic crystal system MX, the metal M is located at the coordinates (1/2, 1/2, 1/2). What would you expect the metal's coordination
number to be?
Choose one answer.
| a. 4 | ||
| b. 6 | ||
| c. 8 | ||
| d. 12 |
Question
49
A Madelung constant value near 2.4 would likely represent which compound?
Choose one answer.
| a. barium selenide | ||
| b. beryllium oxide | ||
| c. titanium(II) oxide | ||
| d. strontium chloride |
Question
50
Tetrahedral holes have a coordination number of
Choose one answer.
| a. 4. | ||
| b. 6. | ||
| c. 8. | ||
| d. 12. |
Question
51
How many octahedral holes would you expect to find in a closed-packed crystal containing 8 atoms?
Choose one answer.
| a. 4 | ||
| b. 6 | ||
| c. 8 | ||
| d. 12 |
Question
52
How many tetrahedral holes would you expect to find in a close-packed crystal containing 6 atoms?
Choose one answer.
| a. 4 | ||
| b. 6 | ||
| c. 8 | ||
| d. 12 |
Question
53
What is the size of an octahedral hole in a cubic close-packed system with a radius of 1.5 Ä?
Choose one answer.
| a. 0.310 Ä | ||
| b. 0.414 Ä | ||
| c. 0.621 Ä | ||
| d. 0.932 Ä |
Question
54
What is the size of a tetrahedral hole in a cubic close-packed system with a radius of 1.2 Ä?
Choose one answer.
| a. 0.23 Ä | ||
| b. 0.27 Ä | ||
| c. 0.40 Ä | ||
| d. 0.54 Ä |
Question
55
The MX compound has a radius ratio of 0.51. The metal ion M has the crystal lattice coordinates shown below. Which of the following statements about the MX
compound is false?

Choose one answer.
| a. There are at least three M spheres within the lattice. | ||
| b. The lattice is body centered. | ||
| c. The lattice is close-packed cubic. | ||
| d. The system is hexacoordinate. |
Question
56
A body-centered cubic unit cell has a coordination number of
Choose one answer.
| a. 4. | ||
| b. 6. | ||
| c. 8. | ||
| d. 10. |
Question
57
Steel-a solid solution consisting of carbon atoms seated in the holes of an iron atom structure-is an example of a(n)
Choose one answer.
| a. pure metal. | ||
| b. alkali metal. | ||
| c. substitutional alloy. | ||
| d. interstitial alloy. |
Question
58
Brass-a solid solution consisting of zinc and copper atoms-can be considered a(n) _________ and a(n) _________.
Choose one answer.
| a. substitutional alloy, interstitial alloy | ||
| b. intermetallic alloy, interstitial alloy | ||
| c. substitutional alloy, intermetallic alloy | ||
| d. pure metal, intermetallic alloy |
Question
59
Raising the temperature of a metal serves to
Choose one answer.
| a. ease electron flow over band gaps. | ||
| b. slow down the activity of the atom, promoting a gradual increase in conductivity. | ||
| c. impede conductivity due to increased atom vibration. | ||
| d. allow the metal to behave as a superconductor. |
Question
60
Which of the following statements about superconductors is true?
Choose one answer.
| a. Superconductors are perfectly paramagnetic. | ||
| b. Most superconductors require low temperatures to be efficient. | ||
| c. Superconductors exhibit high resistance to electron flow. | ||
| d. Superconductors exhibit large energy gaps between the valence and conductor bands. |
Question
61
The LUMO of a semiconductor
Choose one answer.
| a. has a limited number of electrons present. | ||
| b. is often separated from the HOMO by an unsurmountable energy gap. | ||
| c. serves as a dopant to the valence band. | ||
| d. serves to provide electrons to the valence band. |
Question
62
Glass and quartz are examples of
Choose one answer.
| a. conductors. | ||
| b. semiconductors. | ||
| c. insulators. | ||
| d. superconductors. |
Question
63
For n-type semiconductors,
Choose one answer.
| a. conduction band electrons outnumber valence band holes. | ||
| b. electron flow is halted due to dopant impurities. | ||
| c. an equal number of valence band holes and conductor band electrons exist, making dopants unnecessary. | ||
| d. doping is facilitated by halides. |
Question
64
The doping of silicon with which element would likely form an p-type semiconductor?
Choose one answer.
| a. phosphorus | ||
| b. boron | ||
| c. antimony | ||
| d. carbon |
Question
65
Which of the following statements about semiconductors is true?
Choose one answer.
| a. Intrinsic superconductors require a dopant to conduct electricity. | ||
| b. Semiconductors have no energy gap between the valence and conductor bands. | ||
| c. Semiconductors increase in conductivity with increasing temperatures. | ||
| d. Intrinsic semiconductors are more efficient than extrinsic semiconductors. |
Question
66
For potassium metal, the 4p band represents the _________ and the _________.
Choose one answer.
| a. LUMO, antibonding orbital | ||
| b. LUMO, bonding orbital | ||
| c. HOMO, nonbonding orbital | ||
| d. HOMO, antibonding orbital |
Question
67
At low temperatures, semiconductors and insulators differ only in
Choose one answer.
| a. valence band composition, with semiconductors and insulators having half- and fully filled HOMOs, respectively. | ||
| b. electron placement, with electrons occupying the conductance bands of semiconductors but not of insulators. | ||
| c. resistivity, with semiconductors being less conductive than insulators with increasing temperatures. | ||
| d. band gap size, with insulator band gaps being greater in energy than those of semiconductors. |
Question
68
A material that is able to maintain zero electrical resistance at temperatures near 30K° is considered a(n)
Choose one answer.
| a. intrinsic semiconductor. | ||
| b. high-temperature superconductor. | ||
| c. low-temperature superconductor. | ||
| d. extrinsic semiconductor. |
Question
69
Which system below represents an n-type semiconductor?
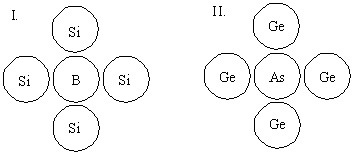
Choose one answer.
| a. I | ||
| b. II | ||
| c. I and II | ||
| d. none of the above |
Question
70
4s-4p band overlap allows calcium to behave as a conductor. How many energy levels are present in the conduction band?
Choose one answer.
| a. 2 | ||
| b. 6 | ||
| c. 8 | ||
| d. 14 |
Question
71
Which system below represents an intrinsic semiconductor?

Choose one answer.
| a. I | ||
| b. II | ||
| c. I and II | ||
| d. none of the above |
Question
72
Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy makes use of liquid helium in order to generate large magnetic fields. The metals involved in creating these
fields are behaving as
Choose one answer.
| a. intrinsic semiconductors. | ||
| b. high-temperature superconductors. | ||
| c. low-temperature superconductors. | ||
| d. extrinsic semiconductors. |
Question
73
For which Lewis base would you expect Cu+ to have the greatest affinity?
Choose one answer.
| a. I- | ||
| b. Br- | ||
| c. Cl- | ||
| d. F- |
Question
74
Under acidic aqueous conditions, the permanganate ion dissociates and forms Mn2+ and 4 mol of water. How many electrons are transferred in this
reaction?
Choose one answer.
| a. 0 | ||
| b. 2 | ||
| c. 5 | ||
| d. 7 |
Question
75
As the oxidation number of a Lewis acid becomes larger (such as Co2+ to Co3+), what happens to its hard/soft acid/base character?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Lewis acid becomes softer. | ||
| b. The Lewis acid becomes harder. | ||
| c. No change is observed. | ||
| d. The Lewis acid behaves as a base. |
Question
76
The pOH of the conjugate base of an unknown acid is 4.17. What is the [H+] concentration of the unknown acid?
Choose one answer.
| a. 2.27 x 10-12 | ||
| b. 1.48 x 10-10 | ||
| c. 6.76 x 10-5 | ||
| d. 4.66 x 10-2 |
Question
77
In a sulfur-based Lewis base, as the oxidation number of sulfur increases (such as SO32- to SO42-), what
happens to its Lewis base character?
Choose one answer.
| a. No change is observed. | ||
| b. The Lewis base becomes harder. | ||
| c. The Lewis base becomes softer. | ||
| d. The Lewis base behaves as an acid. |
Question
78
At room temperature, which hydrogen halide has the lowest boiling point?
Choose one answer.
| a. HI | ||
| b. HF | ||
| c. HCl | ||
| d. HBr |
Question
79
The addition of 4.5x molar excess of aminodimethylsulfoxide (ADMSO) to an ethanolic solution of CuCl2 leads to the formation of
Cu(ADMSO)4. What is the makeup of the metal-ligand bond?
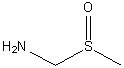
Choose one answer.
| a. C-O | ||
| b. C-C | ||
| c. C-S | ||
| d. C-N |
Question
80
For the reaction of mercury(II) chloride and ammonia, which product is a conjugate Lewis base?
Choose one answer.
| a. NH3 | ||
| b. HgCl2 | ||
| c. Hg(NH3)2 | ||
| d. Cl- |
Question
81
For the reaction below, the hydrogen phosphate ion behaves as a(n)
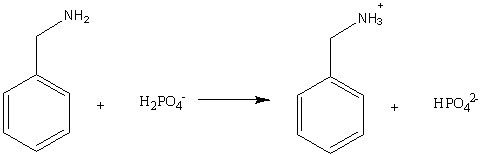
Choose one answer.
| a. acid. | ||
| b. base. | ||
| c. chelator | ||
| d. catalyst. |
Question
82
For the reaction below, water behaves as a(n)
Choose one answer.
| a. acid. | ||
| b. base. | ||
| c. both A and B | ||
| d. none of the above |
Question
83
For the pair of reactions below, which compounds are represented by X, Y, and Z, respectively?
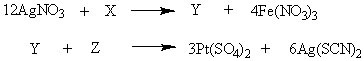
Choose one answer.
| a. FeSO43, 3Ag2SO4, 3Pt(SCN)4 | ||
| b. Fe2(SO4)3, 6Ag2SO4, 3Pt(SCN)4 | ||
| c. Fe2(SO4)3, 6Ag2SO4, 3Pt(SCN)2 | ||
| d. Fe2(SO4)3, 3Ag2SO4, 3Pt(SCN)4 |
Question
84
For which Lewis acid would you expect CO to have the least affinity?
Choose one answer.
| a. Ag+ | ||
| b. Ru3+ | ||
| c. Be2+ | ||
| d. Zn2+ |
Question
85
For which Lewis acid would you expect H2O to have the greatest affinity?
Choose one answer.
| a. Pt4+ | ||
| b. Cd2+ | ||
| c. Ni2+ | ||
| d. Fe3+ |
Question
86
Which of the following hydrogen halides has the smallest bond enthalpy?
Choose one answer.
| a. HI | ||
| b. HF | ||
| c. HBr | ||
| d. HCl |
Question
87
The combustion of methane gas forms _________ and water.
Choose one answer.
| a. oxalic acid | ||
| b. carbon monoxide | ||
| c. carbon suboxide | ||
| d. carbon dioxide |
Question
88
The reaction of a Group I metal hydroxide with excess nitric acid leads to a series of solid metal nitrates. Of the following, which would you expect to
have the lowest boiling point?
Choose one answer.
| a. RbNO3 | ||
| b. LiNO3 | ||
| c. NaNO3 | ||
| d. KNO3 |
Question
89
Which Group 3 element has the highest melting point?
Choose one answer.
| a. aluminum | ||
| b. boron | ||
| c. indium | ||
| d. gallium |
Question
90
Which diatomic system has the largest bond enthalpy?
Choose one answer.
| a. PbO | ||
| b. SiO | ||
| c. CO | ||
| d. GeO |
Question
91
Nitrogen and phosphorus are Group 5 elements, but nitrogen forms only three bonds, while phosphorus can form up to five. What accounts for the ability of
phosphorus to form more bonds?
Choose one answer.
| a. Phosphorus has an additional electron shell. | ||
| b. Phosphorus has two more valence electrons than nitrogen. | ||
| c. Phosphorus is more electronegative than nitrogen. | ||
| d. Nitrogen has three unpaired electrons in its ground state. |
Question
92
Which Group 6 element has the largest atomic radius?
Choose one answer.
| a. oxygen | ||
| b. sulfur | ||
| c. selenium | ||
| d. tellurium |
Question
93
The molecular formula for chlorous acid is
Choose one answer.
| a. HClO. | ||
| b. HClO2. | ||
| c. HClO3. | ||
| d. HClO4. |
Question
94
Which of the following halogens is a solid at room temperature?
Choose one answer.
| a. bromine | ||
| b. chlorine | ||
| c. iodine | ||
| d. fluorine |
Question
95
While not to the same extent as Group I metals, Group II metals are quite reactive with water. Each metal has a different level of reactivity with water,
but they ultimately follow a well-observed reactivity trend. What is an explanation for the trend observed in water reactivity when moving down from
beryllium to barium?
Choose one answer.
| a. The electronegativity increases with additional electron shells. | ||
| b. The electrons of the larger metals are farther from the nucleus and easier to remove. | ||
| c. The smaller metals have a greater attraction to the lone pairs on the H2O oxygens. | ||
| d. The presence of d-orbital electrons in the larger metals allows for decreased water reactivity. |
Question
96
In the product for the reaction below, what is the oxidation state of phosphorus?
Choose one answer.
| a. 2+ | ||
| b. 3+ | ||
| c. 3- | ||
| d. 5+ |
Question
97
For the reaction below, X could represent which element?
Choose one answer.
| a. calcium | ||
| b. rubidium | ||
| c. indium | ||
| d. silicon |
Question
98
For the reaction below, element X is a _________ element.
Choose one answer.
| a. Group 2 | ||
| b. Group 3 | ||
| c. Group 4 | ||
| d. Group 5 |
Question
99
For the reaction below, X could represent which element?
Choose one answer.
| a. strontium | ||
| b. potassium | ||
| c. magnesium | ||
| d. gallium |
Question
100
For the reaction below, element X is a _________ element.
Choose one answer.
| a. Group 1 | ||
| b. Group 2 | ||
| c. Group 5 | ||
| d. Group 7 |