1. Which of the following is NOT a basic component of a mass spectrometer?
|
A. ion source |
||
|
B. mass analyzer |
||
|
C. detector |
||
|
D. diffraction grating |
1. The most abundant ion in a mass spectra, which is assigned a relative abundance of 100, is referred to as the
|
A. Base peak |
||
|
B. Reference peak |
||
|
C. Detection limit |
||
|
D. Blank correlation |
The mass spectra of fluorine
|
a. Is similar to the spectra of bromine and chlorine |
||
|
b. Consists of only one peak, since it is monoisotopic |
||
|
c. Consists of two peaks, separated by two Da |
||
|
d. Consists of two peaks, appearing at 19 Da and 38 Da |
The five peaks in a mass spectrum of chlorine can be attributed to
|
a. Loss of electrons |
||
|
b. Its oxidative ability |
||
|
c. The presence of two abundant isotopes |
||
|
d. All of the above |
Calibration of a mass spectrometer is
|
a. Performed externally, with a known sample measured independently |
||
|
b. Performed internally, with a known sample that is premixed with the unknown |
||
|
c. Unnecessary because the mass detector is highly stable |
||
|
d. Both a and b are correct; calibration can be internal or external |
The x-axis of a mass spectrum typically reports
|
a. Mass to charge (m/z) ratios |
||
|
b. Parts per million (ppm) |
||
|
c. Wavenumbers (cm-1) |
||
|
d. Wavelength (nm) |
If a mass spectra contains peaks at 35 and 37 Da,
|
a. it most likely contains chlorine |
||
|
b. it can be identified as RbBr |
||
|
c. it was analyzed in a gas matrix containing argon |
||
|
d. it was analyzed in a gas matrix containing krypton |
1. MALDI and ESI are
|
a. Ionization methods commonly used for biochemical analysis |
||
|
b. Detection methods used for spectral fingerprinting |
||
|
c. Separation methods used prior to MS analysis |
||
|
d. Mass analysis techniques requiring external calibration |
Tandem mass spectrometers
|
a. Contain two or more mass analyzers |
||
|
b. Can be used for structural studies |
||
|
c. Can be used for sequencing studies |
||
|
d. All of the above |
The molecular ion (M+)
|
a. Is the highest molecular weight peak observed in a spectrum |
||
|
b. Has an assigned relative abundance of 100 |
||
|
c. Represents the parent molecule minus an electron |
||
|
d. Both a and c are correct |
Due to structural stability, the molecular ion peaks are strong in mass spectra of
|
a. alcohols |
||
|
b. aromatics |
||
|
c. alkanes |
||
|
d. carboxylic acids |
Time-of-flight (TOF) mass analyzers
|
a. Allow simultaneous detection of all species and have unlimited mass ranges |
||
|
b. Measure the time required for an ion to travel a known distance, dependent on the mass of the species |
||
|
c. Require extremely high vacuum conditions to avoid collisions of ions and are often paired with pulsed ionization sources |
||
|
d. All of the above |
In a mass spectrum of an alcohol, the molecular ion is usually small or non-existent due to
|
a. Cleavage of the hydroxyl group |
||
|
b. Rearrangement of the molecule to form an ester |
||
|
c. Cleavage of the C-C bond adjacent to the hydroxyl group |
||
|
d. Formation of a dimeric species |
1. If analysis of a nitrogen-containing molecule shows a molecular ion peak with an odd m/z ratio
|
a. It contains an even number of nitrogen atoms |
||
|
b. It contains an odd number of nitrogen atoms |
||
|
c. It has rearranged via the McLafferty rearrangement |
||
|
d. The mass analyzer needs to be recalibrated; nitrogen containing molecules always give an even m/z ratio |
Which of the following is true about sector mass analyzers?
|
a. They are inexpensive and compact |
||
|
b. They have low resolution and sensitivity |
||
|
c. They are incompatible with ESI and MALDI ionization methods |
||
|
d. They can detect only low mass ranges |
Quadrupole and ion trap mass analyzers isolate ions for analysis by
|
a. Varying the applied voltage and radiofrequency potentials |
||
|
b. Accelerating ions through an electric field |
||
|
c. Accelerating ions through a magnetic field |
||
|
d. Desorption from an electrode surface |
Why is inductively coupled plasma (ICP) typically only used as an ionization method for elemental analysis?
|
a. Only low molecular weight molecules can be analyzed. |
||
|
b. It requires the sample to be dissolved in a carrier gas prior to sample injection. |
||
|
c. All structural information is lost due to extremely high plasma temperatures. |
||
|
d. All of the above are limitations of ICP. |
Fast atom bombardment (FAB) and secondary ion mass spectrometry (SIMS) are useful techniques for
|
a. Trace metal analysis |
||
|
b. Depth profiling |
||
|
c. Protein sequencing |
||
|
d. Halide analysis |
1. The presence of M-15, M-29, and M-43 mass spectral peaks correspond to
|
a. Sequential loss of alkyl groups |
||
|
b. Carbocation rearrangements |
||
|
c. Loss of nitrogen atoms |
||
|
d. Alcohol degradation |
Although the molecular ion is usually absent, aliphatic nitro compounds are indicated by which fragment ion peaks?
|
a. m/z = 32 and m/z = 28, corresponding to O2 and N2 |
||
|
b. m/z = 30 and m/z = 46, corresponding to NO+ and NO2+ |
||
|
c. m/z = 46 and m/z = 58, corresponding to NO2+ and C-NO2+ |
||
|
d. all of the above must be present to indicate an aliphatic nitro compound |
Which MS ionization technique is most useful for component analysis of metal-containing compounds, leaving fragments intact?
|
a. Inductively coupled plasma (ICP) |
||
|
b. Electron impact (EI) |
||
|
c. Matrix assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) |
||
|
d. Electrospray ionization (ESI) |
The negative mode of chemical ionization is best suited for analysis of
|
a. Carbocations |
||
|
b. Halides |
||
|
c. Amines |
||
|
d. Aromatics |
The molecular ion for peak in a spectrum of iso-butane
|
a. Is more abundant than the molecular ion peak in a spectrum of n-butane |
||
|
b. Is less abundant than the molecular ion peak in a spectrum of n-butane |
||
|
c. Is never observed due to stability of the resulting carbocation |
||
|
d. Would appear with the same intensity as the molecular ion peak of n-butane |
Higher mass satellites of molecular ions occur as a result of
|
a. Naturally occurring isotopes |
||
|
b. Formation of dimeric species |
||
|
c. Reactions with the matrix |
||
|
d. Rearrangement of carbocations |
Which of the following statements about UV-Visible spectrophotometers is NOT true?
|
a. Deuterium or tungsten lamps are commonly used as light sources. |
||
|
b. A diode array detector eliminates the need for a monochromator. |
||
|
c. Single-beam and double-beam instruments contain a filter for selecting one wavelength at a time. |
||
|
d. A simultaneous UV-Vis instrument contains mirrors and a monochromator in order to allow simultaneous detection at various wavelengths. |
Basic UV-Visible spectroscopy is designed to analyze samples in what phase?
|
a. Solid (or suspension) phase |
||
|
b. Gas phase |
||
|
c. Solution (or liquid) phase |
||
|
d. Plasma phase |
When analyzing a sample by UV-Vis spectroscopy, if the signal to noise ratio is too low, the results may not be reliable. All of the following are ways to counter this, except:
|
a. Dissolving more or the analyte in the solvent |
||
|
b. Using a solvent with a lower UV cutoff |
||
|
c. Using a smaller cuvette cell |
||
|
d. Pre-concentrating the analyte solution |
1. A sample of 0.10 M triethylamine in hexanes is prepared for analysis. What should be used as the blank reference?
|
a. 0.10 M triethylamine in water |
||
|
b. Triethylamine |
||
|
c. Hexanes |
||
|
d. Heptane |
Which of the following would be the best solvent for a compound with a λmax of 281 nm? You may assume that the compound is completely soluble in each.
|
a. Toluene (UV cutoff = 285 nm) |
||
|
b. Benzene (UV cutoff = 278 nm) |
||
|
c. Acetone (UV cutoff = 329 nm) |
||
|
d. Ethanol (UV cutoff = 205 nm) |
Alkanes exhibit which of the following electronic transitions?
|
a. σ to σ * |
||
|
b. π to π* |
||
|
c. n to σ * |
||
|
d. n to π* |
Alkenes and alkynes exhibit which of the following electronic transitions?
|
a. σ to σ * |
||
|
b. π to π* |
||
|
c. n to σ * |
||
|
d. n to π* |
Which of the following do not primarily exhibit n to σ * electronic transitions?
|
a. amines |
||
|
b. alcohols |
||
|
c. alkenes |
||
|
d. carbonyls |
Which of the following primarily exhibits n to π * electronic transitions?
|
a. carbonyls |
||
|
b. alcohols |
||
|
c. esters |
||
|
d. alkynes |
If cell length is held constant, a Beer’s Law plot of a given analyte will result in a linear relationship between
|
a. Concentration and wavelength |
||
|
b. Transmission intensity and concentration |
||
|
c. Absorbance and concentration |
||
|
d. Transmission intensity and wavelength |
Increasing conjugation in a series of analogous compounds results in a
|
a. Hypsochromic shift |
||
|
b. Bathochromic shift |
||
|
c. Hyperchromic effect |
||
|
d. Hypochromic effect |
Which of the following would result in a hypsochromic shift in the UV spectra?
|
a. Saturation of a double bond |
||
|
b. Dehydration of an alcohol to form a double bond |
||
|
c. Cyclization of an aliphatic compound |
||
|
d. Addition of an amino group |
Which of the following is a FALSE statement about molar absorptivity coefficients?
|
a. Molar absorptivities will be the same for each peak, regardless of wavelength, for a molecule’s UV-Vis spectrum. |
||
|
b. Molar absorptivities can be used to compare the ability to absorb light at a given wavelength of different chromophores. |
||
|
c. Molar absorptivity coefficients are calculated based on absorbance and concentration of the solution. |
||
|
d. Molar absorptivity coefficients for organic molecules are typically 10,000 M-1cm-1. |
An absorbance value of zero corresponds to 100% transmittance. What does an absorbance value of 2 correspond to?
|
a. 0% transmittance |
||
|
b. 1% transmittance |
||
|
c. 98% transmittance |
||
|
d. 80% transmittance |
Which of the following describes the correct relationship between absorbance and transmission?
|
a. A = log (T) |
||
|
b. A = log (1/T) |
||
|
c. T = log (A) |
||
|
d. T = log (1/A) |
Why does increased conjugation cause a shift to higher wavelengths?
|
a. It decreases the distance (ΔE) between the HOMO and LUMO levels. |
||
|
b. It increases the distance (ΔE) between the HOMO and LUMO levels. |
||
|
c. It causes the vibrational and rotational levels of the molecules to become excited. |
||
|
d. It changes the types of electronic transitions available from π - π * to n - π *. |
The Woodward-Fieser Rules are useful for
|
a. Predicting where a maximum absorbance should occur |
||
|
b. Differentiating between cis- and trans- conformations of dienes |
||
|
c. Determining the position of a substituent relative to a carbonyl group |
||
|
d. All of the above |
The peaks in a UV-Vis spectrum are broad because
|
a. The vibrational and rotational transitions are superimposed upon the electronic transitions. |
||
|
b. The detectors cannot differentiate specific wavelengths, but rather give a range of possible wavelengths. |
||
|
c. Electronic transitions occur slowly with respect to the instrumental time scale. |
||
|
d. They represent a Boltzman distribution, where some molecules become excited before others. |
Beta-carotene is a highly absorbing chromophore. Which solvent would be the best choice for analysis?
|
a. Methylene bromide |
||
|
b. Benzene |
||
|
c. Hexyne |
||
|
d. Ethanol |
In general, when calculating empirical values for λ max, the result of adding a substituent group is a
|
a. Bathochromic shift |
||
|
b. Hypsochromic shift |
||
|
c. Hyperchromic effect |
||
|
d. Hypochromic effect |
The Woodward-Fieser Rules for conjugated carbonyl compounds
|
a. Are the same as the rules for dienes |
||
|
b. Include a solvent correction value |
||
|
c. Only include substitutes directly adjacent to the carbonyl group |
||
|
d. Can also be applied to benzene derivatives |
When preparing a calibration curve for sample analysis, it is best to
|
a. Prepare each sample “from scratch” to avoid cross contamination. |
||
|
b. Prepare a stock solution and use serial dilution for the remaining standards. |
||
|
c. Only use two data points to ensure a straight line. |
||
|
d. Use very concentrated solutions to ensure a good signal. |
The x-axis of a UV-Vis spectrum is usually reported as wavelength in nm. The y-axis can be reported as
|
a. Molar absorptivity ( ε ) |
||
|
b. log ( ε ) |
||
|
c. Absorbance (A) |
||
|
d. all of the above |
Which of the following sample cells should be used if you wish to measure a carbonyl transition around 300 nm?
|
a. fused silica |
||
|
b. plastic |
||
|
c. glass |
||
|
d. Any of the above would work |
Which of the following lists the electromagnetic radiation in correct order by increasing wavelengths?
|
a. X-rays, microwave, infrared radiation, radio waves |
||
|
b. Gamma rays, ultraviolet radiation, microwaves, radio waves |
||
|
c. Microwaves, visible radiation, gamma rays, X-rays |
||
|
d. Radio waves, gamma rays, infrared radiation, microwaves |
Instrumentation for infrared analysis closely resembles
|
a. A UV-Visible spectrophotometer |
||
|
b. An NMR spectrometer |
||
|
c. A mass spectrometer |
||
|
d. An electrochemical cell |
Hooke’s law dictates that the IR stretching frequencies are dependent on
|
a. Bond strength and molar masses of the atoms |
||
|
b. The number of lone pairs and dipole moment of the bond |
||
|
c. The effective nuclear charge and polarizability of the bond |
||
|
d. The magnetic spin and hybridization of the atoms |
Keeping all other variables the same, as bond strength decreases,
|
a. Wavenumber of the IR stretch decreases |
||
|
b. Wavenumber of the IR stretch increases |
||
|
c. Wavelength and wavenumber of the IR stretch decrease |
||
|
d. Wavelength of the IR stretch decreases |
Keeping all other variables the same, which of the following bonds would have the lowest IR stretching frequency?
|
a. C-N |
||
|
b. C-Cl |
||
|
c. C-O |
||
|
d. C-H |
Which of the following is in correct order of decreasing IR stretching frequency?
|
a. Alkynes > alkenes > alkanes |
||
|
b. Alkanes > alkynes > alkenes |
||
|
c. Alkenes > alkynes > alkanes |
||
|
d. Alkynes > alkanes > alkenes |
In non-linear molecules, how many fundamental vibrations may exist (let n = the number of atoms)?
|
a. 3n – 6 |
||
|
b. 3n - 5 |
||
|
c. 2n-6 |
||
|
d. 2n-5 |
Why are some fundamental vibrations not observed?
|
a. They exist outside of the mid-IR (observed) region. |
||
|
b. They are too weak or overlap with other vibrations. |
||
|
c. They are degenerate with other vibrational modes. |
||
|
d. All of the above are correct. |
In order for an IR vibration to be allowed, what condition must be met?
|
a. There must be a change in dipole moment of the molecule. |
||
|
b. There must be a change in the polarizability of the molecule. |
||
|
c. The spin state of the molecule must flip. |
||
|
d. There must be a chromophoric species. |
Which of the following statements about IR spectroscopy is FALSE?
|
a. Absorptions due to C=O bond stretching are generally weak. |
||
|
b. Stretching frequencies are higher than corresponding bending frequencies. |
||
|
c. Single bonds have lower stretching frequencies than triple bonds. |
||
|
d. Conjugation lowers the energy required to cause a bond to stretch. |
The stretching frequency of which functional group would be most useful in the detection of metal ligand complexes?
|
a. O-H |
||
|
b. C-O |
||
|
c. C-Cl |
||
|
d. C-H |
The shift in the C=O stretching frequency in a metal-ligand complex is influenced by all of the following, except
|
a. The electron density of the metal center. |
||
|
b. The geometry of the molecule. |
||
|
c. The electron-donating or electron-withdrawing effects of other ligands. |
||
|
d. The intensity of the infrared source used. |
Pump-probe experiments in infrared spectroscopy can result in information about
|
a. The molecular functional group vibrational lifetimes. |
||
|
b. The mechanisms of radioactive decay. |
||
|
c. The amount of pi-backbonding character in a metal-ligand bond. |
||
|
d. The electronic transition levels within a molecule. |
The vibrational lifetime of molecular functional groups is difficult to study directly because
|
a. They occur on the picoseconds timescale. |
||
|
b. The functional groups undergo rapid isomerizations. |
||
|
c. The electron donating abilities interfere with detection. |
||
|
d. The intense color of the molecules does not allow transmission of the source radiation. |
The fingerprint region of the IR spectra corresponds to
|
a. Bending frequencies |
||
|
b. Stretching frequencies |
||
|
c. Symmetric mode frequencies |
||
|
d. Asymmetric mode frequencies |
How many fundamental vibrations would exist for ethyne (HCCH)?
|
a. 7 |
||
|
b. 6 |
||
|
c. 8 |
||
|
d. 12 |
Within the 3500-3300 cm-1 region, how can primary, secondary, and tertiary amines be distinguished?
|
a. Primary amines have two bands, secondary amines have one band, and tertiary amines have no NH stretch. |
||
|
b. Primary amines have one band, secondary amines have two bands, and tertiary amines have three bands. |
||
|
c. Primary amines have no bands, secondary amines have one band, and tertiary amines have two bands. |
||
|
d. Primary and tertiary amines have intense single bands, while secondary amines have two weak bands. |
Hydrogen bonding causes the hydroxyl IR band to do what?
|
a. Shift to lower frequencies and broaden |
||
|
b. Shift to higher frequencies and sharpen |
||
|
c. Shift to higher frequencies and broaden |
||
|
d. Shift to lower frequencies and sharpen |
Which of the following regions would be most useful in determining the substitution patterns of an alkene?
|
a. The =C-H stretch, occurring between 3100 – 3010 wavenumbers |
||
|
b. The =C-H out-of-plane bend, occurring between 1000 – 650 wavenumbers |
||
|
c. The C=C stretch, occurring at 1660 – 1600 wavenumbers |
||
|
d. None of the above would indicate substitution patterns. |
The aromatic overtone/combination bands (occurring between 2000 and 1667 cm-1) can be useful in determining
|
a. The ring substitution pattern (ortho, meta, para, etc.) |
||
|
b. The number of carbons present in the aromatic ring |
||
|
c. The rate of proton exchange between the solvent and the analyte |
||
|
d. The degree of resonance within the aromatic ring |
Ethers, esters, and alcohols all contain C-O stretching bands. How can an ether be distinguished from the other two compounds?
|
a. The absence of C=O and O-H bands eliminate esters and alcohols. |
||
|
b. Alcohols and esters have split C-O bands, while ethers show only one band. |
||
|
c. The C-O band of an ether appears in a different region than that of an alcohol or ester. |
||
|
d. Alcohols and esters have very broad C-O bands due to hydrogen bonding, while ethers have a very sharp band. |
Identify this compound.
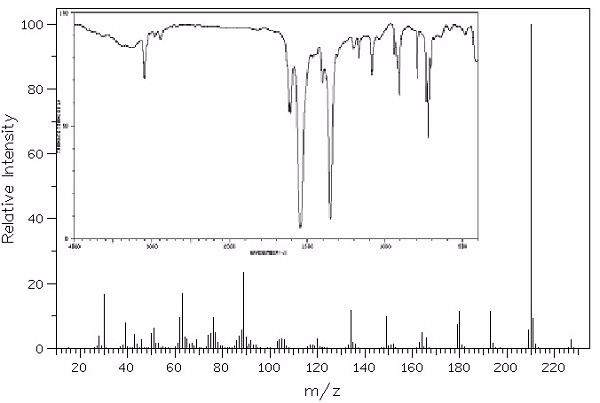
|
a. 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene |
||
|
b. 3-aminotoluene |
||
|
c. 2-aminostyrene |
||
|
d. p-nitrotoluene |
Identify this compound.
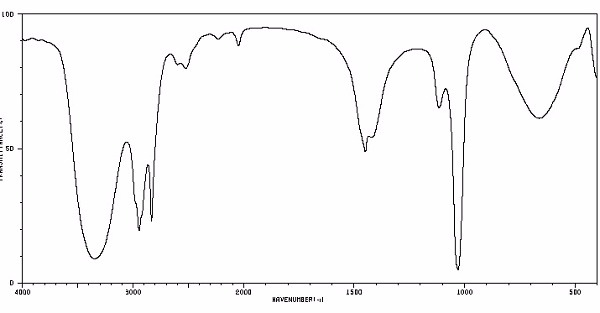
|
a. methanol |
||
|
b. methane |
||
|
c. formaldehyde |
||
|
d. acetone |
Identify this compound.
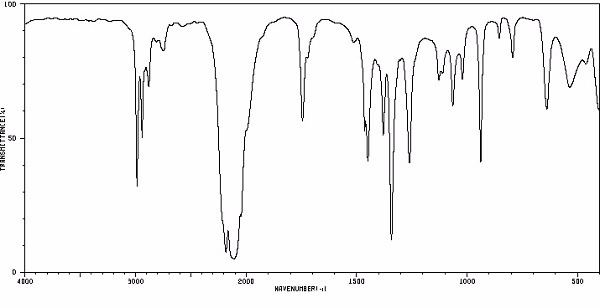
|
a. ethylisothiocyanate |
||
|
b. isoamyl alcohol |
||
|
c. propylene glycol |
||
|
d. ethylpropylether |
Identify this compound.
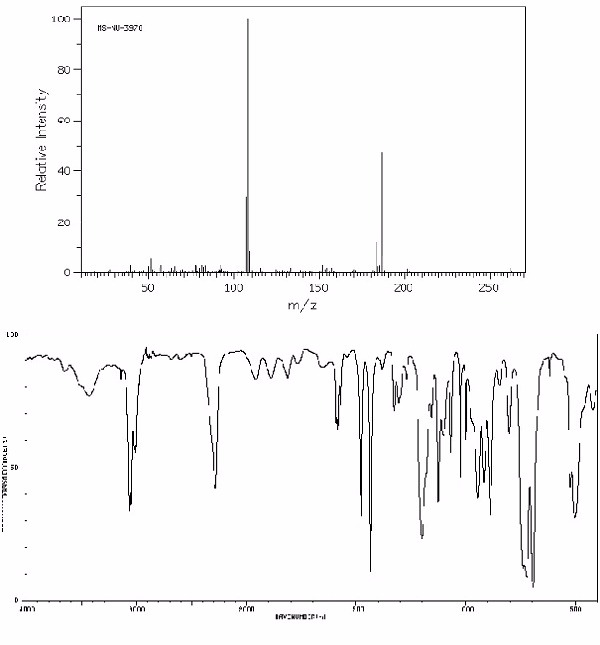
|
a. diphenylphosphine |
||
|
b. dihexyl ether |
||
|
c. benzoyl bromide |
||
|
d. hexafluorobenzene |
Identify this compound.
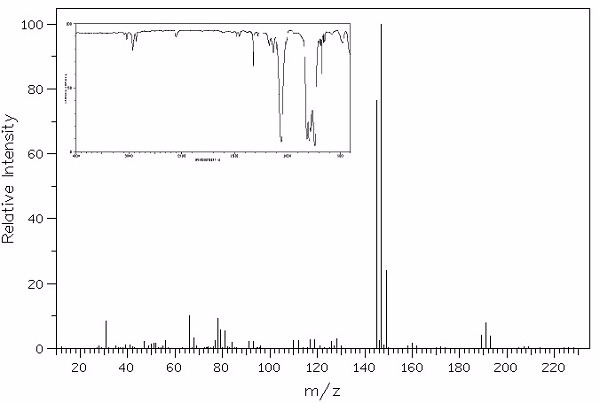
|
a. dibromochlorofluoromethane |
||
|
b. carbon tetrachloride |
||
|
c. bromochlorofluoroiodomethane |
||
|
d. methylene bromide |
The electromagnetic radiation used for NMR spectroscopy falls in which region?
|
a. Microwave |
||
|
b. X-ray |
||
|
c. Gamma ray |
||
|
d. Radio wave |
12C and 16O nuclei cannot be observed by NMR spectroscopy. Why?
|
a. They have zero spin and yield no signal. |
||
|
b. They have low natural abundance. |
||
|
c. They interact too strongly with the magnetic field. |
||
|
d. They cause complex spin-spin interactions, which cannot be interpreted. |
All of the following are I = ½ systems, except
|
a. 19F |
||
|
b. 13C |
||
|
c. 14 N |
||
|
d. 1H |
Nuclei with even masses and odd numbers of protons and neutrons
|
a. Have integral spins and can be observed by NMR. |
||
|
b. Have fractional spins and can be observed by NMR. |
||
|
c. Have integral spins and cannot be observed by NMR. |
||
|
d. Have fractional spins and cannot be observed by NMR. |
Which of the following is NOT a reason why tetramethylsilane (TMS) is often used for a reference in NMR spectroscopy?
|
a. It is chemically inert and miscible with organic solvents. |
||
|
b. It gives a single, sharp peak in a region where other organic molecules do not have signals. |
||
|
c. Its signal appears at the same frequency regardless of the applied magnetic field. |
||
|
d. It is easily removed from the sample after analysis. |
Which of the following would be a poor choice as a proton NMR solvent?
|
a. Acetone-d6 |
||
|
b. Deuterium oxide |
||
|
c. Carbon tetrachloride |
||
|
d. o-toluene |
What structural information does 1H-NMR spectroscopy NOT provide?
|
a. The number of different types of hydrogens in a molecule. |
||
|
b. The relative numbers of different types of hydrogens. |
||
|
c. The electronic environment of different types of hydrogens. |
||
|
d. The relative abundance of different isotopes of hydrogen. |
The universal scale for reporting chemical shifts in NMR is
|
a. Hz |
||
|
b. ppm |
||
|
c. MHz |
||
|
d. nm |
An NMR spectrum is acquired by
|
a. Varying the magnetic field with a constant rf signal. |
||
|
b. Varying the rf signal with a constant external magnetic field. |
||
|
c. Varying the rf signal and the external magnetic field, simultaneously. |
||
|
d. Both a and b are correct. |
Which of the following appears the most lowfield?
|
a. Aldehydes |
||
|
b. Alcohols |
||
|
c. Alkanes |
||
|
d. Aromatics |
If a proton is more "shielded" it will appear
|
a. Lowfield, at a low ppm or Hz |
||
|
b. Highfield, at a low ppm or Hz |
||
|
c. Lowfield, at a high ppm or Hz |
||
|
d. Highfield, at a high ppm or Hz |
Which of the following correctly describes the relative intensities of splitting an NMR peak?
|
a. Triplet – 1:3:1 |
||
|
b. Quartet – 1:4:4:1 |
||
|
c. Pentet – 1:3:5:3:1 |
||
|
d. Sextet – 1:5:10:10:5:1 |
Adjacent protons can act as magnets and affect the amount of radiation required for proton resonance in NMR. This interaction causes
|
a. Rapid relaxation and unreliable integration results |
||
|
b. Spin-spin coupling, resulting in peak splitting |
||
|
c. Increased shielding, forcing the chemical shift to be lower |
||
|
d. Decreased shielding, forcing the chemical shift to be higher |
By irradiating two dissimilar nuclei, an increase in the difference in population between the “spin-aligned” and “spin-opposed” states occurs and increases the signal intensity. This is referred to as
|
a. Nuclear Overhauser Enhancement (NOE) |
||
|
b. Heteronuclear Correlation Spectroscopy (HETCOR) |
||
|
c. Correlation Spectroscopy (COSY) |
||
|
d. Distortionless Enhancement by Polarization Transfer (DEPT) |
Distortionless Enhancement by Polarization Transfer (DEPT) would allow which of the following NMR peaks to be distinguished from one another?
|
a. Methylene groups from methyl groups |
||
|
b. Hydroxyl groups from amine groups |
||
|
c. Ortho, meta, and para substituent groups on a benzene ring |
||
|
d. Aromatic carbons from aliphatic carbons |
In a COSY spectrum, the dark spots along the diagonal
|
a. Do not yield structural information because they correspond to the same peak on each coordinate axis. |
||
|
b. Allow distinctions to be made between heteronuclear coupling constants. |
||
|
c. Do not give any structural identification because they are too intense to be deconvoluted. |
||
|
d. Give the most structural information because they differentiate between different hybridizations. |
Analysis of two peaks in a proton NMR spectrum gives a 3:2 integration. This means that
|
a. There are three hydrogens on one carbon and two on another. |
||
|
b. The ratio between the two types of hydrogen environments is 3:2. |
||
|
c. One of the peaks is a methyl group and the other is a methylene group. |
||
|
d. The peaks belong to a straight chain aliphatic compound. |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is an application of NMR spectroscopy in which of the following ways?
|
a. It measures the distribution of hydrogen nuclei in the body. |
||
|
b. It measures the distribution of carbon nuclei in the body. |
||
|
c. It scans for unique nuclei within human tissues. |
||
|
d. It allows a non-invasive measure of bone density. |
Identify this compound.
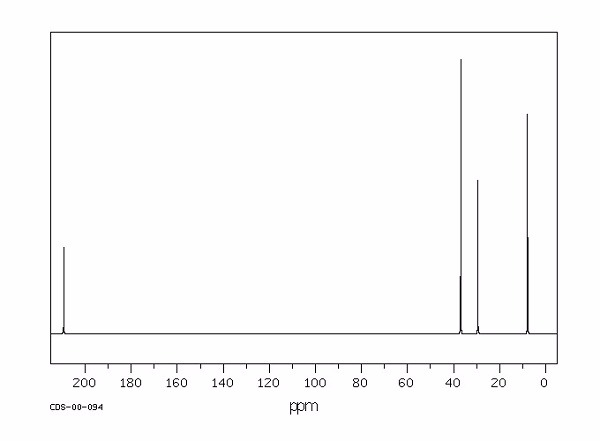
|
a. 2-butanone |
||
|
b. n-butanol |
||
|
c. butane |
||
|
d. 2-butene |
Identify this compound.
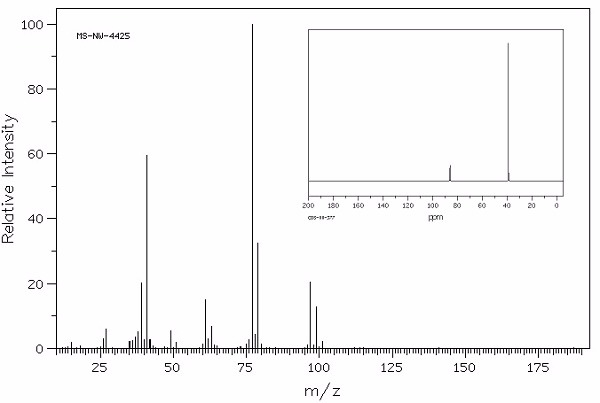
|
a. 2,2-dichloropropane |
||
|
b. 2,2-dibromopropane |
||
|
c. 2,2-dichloropropanol |
||
|
d. 2,2-dibromopropanol |
Identify this compound.
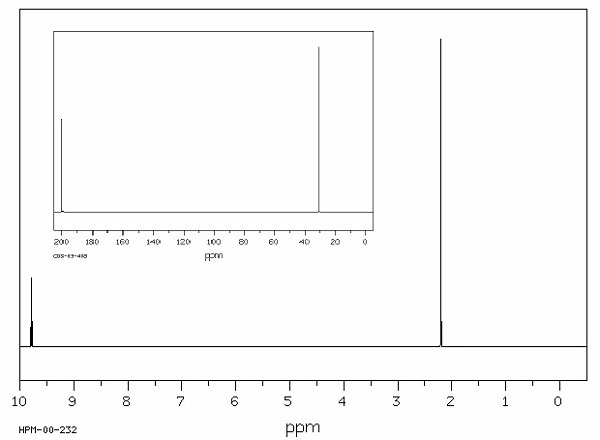
|
a. acetaldehyde |
||
|
b. acetic acid |
||
|
c. ethanol |
||
|
d. diethyl ether |
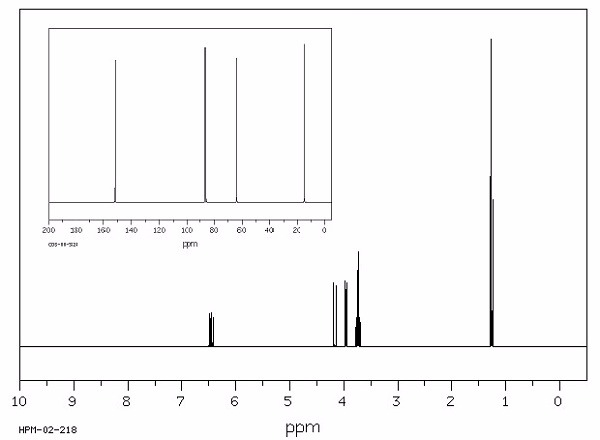
Identify this compound.
|
a. ethanethiol |
||
|
b. ethanethiolate |
||
|
c. acetone |
||
|
d. isoamyl acetate |
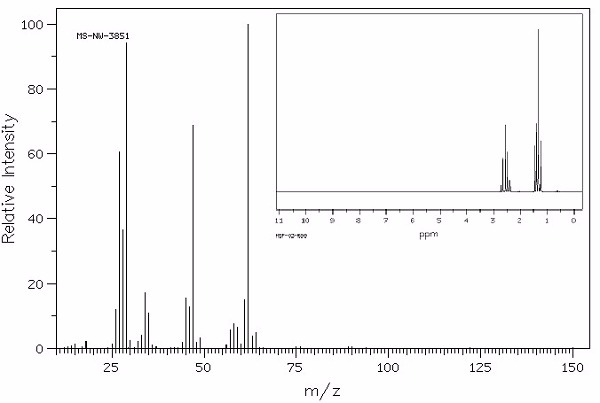
Identify this compound.
|
a. ethylvinyl ether |
||
|
b. isopropyl ether |
||
|
c. t-butylacetate |
||
|
d. butyric acid |
Identify this compound.
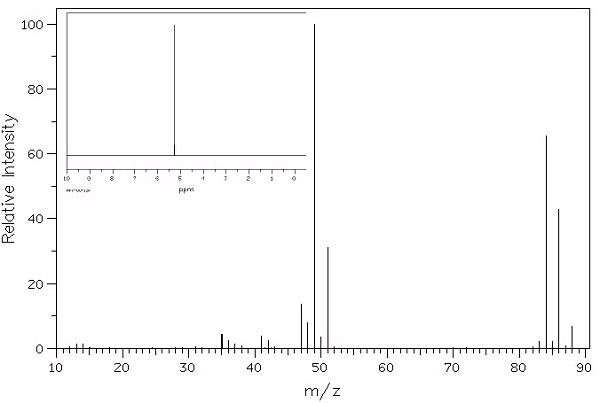
|
a. methylene chloride |
||
|
b. 1,1-dicholoroethane |
||
|
c. carbon tetrachloride |
||
|
d. dibromomethane |
Identify this compound.
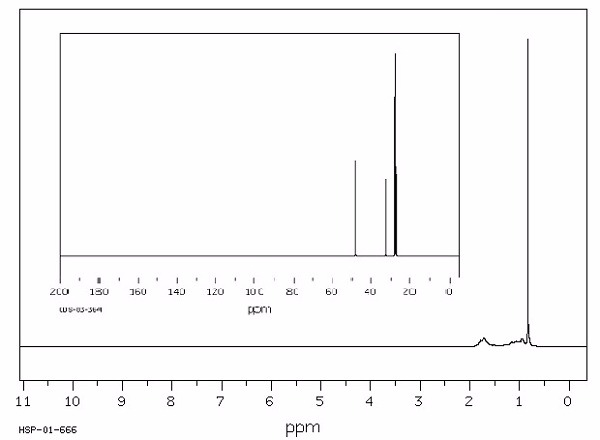
|
a. t-butylcyclohexane |
||
|
b. t-butylbenzene |
||
|
c. t-butylhexanol |
||
|
d. t-butylcyclohexanone |
Identify this compound.
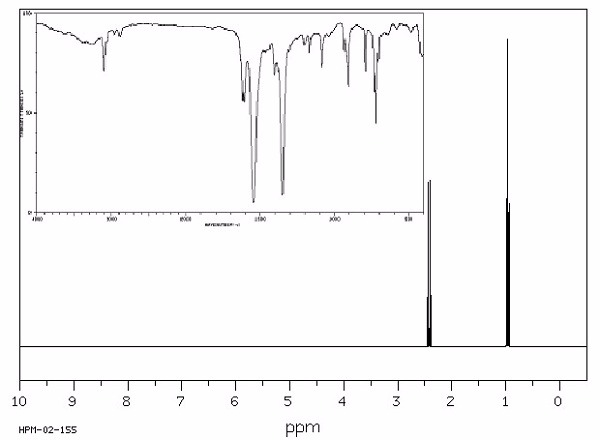
|
a. triethylamine |
||
|
b. tributylamine |
||
|
c. dinitroethane |
||
|
d. ammonium acetate |