1
A Gini Coefficient of 0 represents which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. A country which does not have a service sector | ||
| b. Perfect inequality | ||
| c. A country whose GDP per capita growth is 0 | ||
| d. Perfect equality | ||
| e. A country that has a high GDP per capita growth |
Question
2
A multi-dimensional measure of poverty include includes which of the following elements?
Choose one answer.
| a. Health level | ||
| b. Education level | ||
| c. Vulnerability to natural events | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. C and D only |
Question
3
As defined by the 1987 UN World Commission on Environment and Development, which of the following best describes sustainable development?
Choose one answer.
| a. Development with a small carbon footprint | ||
| b. Development for which financial resources will be available over the medium and long term | ||
| c. Development strategies that can be easily replicated by other countries or regions | ||
| d. Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs | ||
| e. Development that threatens the needs of future generations |
Question
4
On Figure 1, which line on the Lorenz curve represents a country with the highest level of inequality?
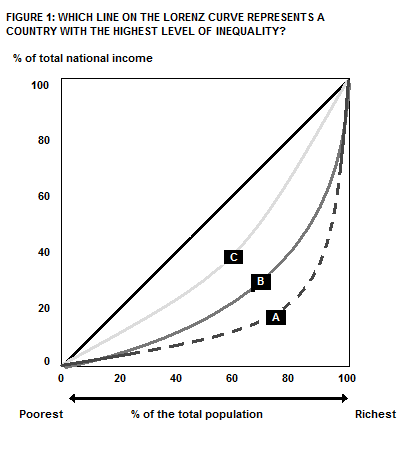
Choose one answer.
| a. Line A | ||
| b. Line B | ||
| c. Line C | ||
| d. Lines A and B | ||
| e. Lines B and C |
Question
5
On Figure 2, what is the name of Line D in the Lorenz curve model?
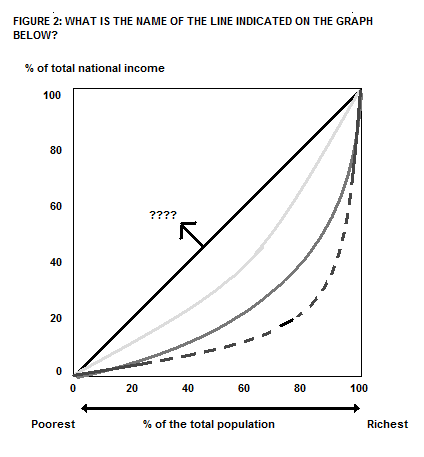
Choose one answer.
| a. Line of absolute equality | ||
| b. Line of development | ||
| c. Line of industrialization | ||
| d. Line of high growth | ||
| e. Line of absolute inequality |
Question
6
The Gini Coefficient for a country is 0.8. What can one conclude about the income distribution in this country?
Choose one answer.
| a. Income is equally distributed. | ||
| b. Income is nearly equally distributed. | ||
| c. Income is perfectly distributed. | ||
| d. Income is close to being imperfectly distributed. | ||
| e. Income is nearly perfectly distributed. |
Question
7
The Gini Coefficient is calculated by finding which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. The percentage of the population living on less than $1 a day | ||
| b. The area between a Lorenz curve and the line of absolute equality | ||
| c. The difference between the richest and poorest of the population | ||
| d. The proportion of the population with more than a primary education | ||
| e. The percentage of the population living on more than $1 a day |
Question
8
True or False. For any two countries, the one with the bigger per capita GDP will have a more equitable distribution of income.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
9
True or False. Population growth is higher in high income countries rather than in low income countries.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
10
True or False. Sustainability is principally a national issue and is not an international or global one.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
11
True or False. There is a strong positive correlation between economic growth and poverty.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
12
True or False. There is not enough food produced in the world to feed the world's population.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
13
What change in the economy is associated with postindustrialization?
Choose one answer.
| a. Transition to democracy | ||
| b. Improvement in the physical infrastructure | ||
| c. Increase of the service sector | ||
| d. Decrease in legal barriers to trade | ||
| e. Decrease of the service sector |
Question
14
What percentage of the world population does the developing world constitute?
Choose one answer.
| a. Less than 10% | ||
| b. More than 10% but less than 25% | ||
| c. More than 25% but less than 50% | ||
| d. More than 50% but less than 75% | ||
| e. More than 75% |
Question
15
Which of the following best represents Adam Smith's view of laissez faire?
Choose one answer.
| a. The accumulation of gold and silver by the state through increased exports and decreased imports | ||
| b. The accumulation of gold and silver through by the state through increased imports of goods and services | ||
| c. The consolidation of a single free market in Europe | ||
| d. The domination of other countries by discouraging their imports and encouraging their exports | ||
| e. The export of gold and silver to other countries in exchange for their raw materials ANSWER: A | ||
| f. Large markets are superior to small markets. | ||
| g. Markets are most effective at generating wealth when government intervention is limited. | ||
| h. Mercantilism is the most effective development strategy for a state. | ||
| i. Development should be led by a strong centralized state. | ||
| j. Markets are least effective at generating wealth when government intervention is limited. |
Question
16
Which of the following countries in the Americas is least developed?
Choose one answer.
| a. USA | ||
| b. Canada | ||
| c. Mexico | ||
| d. Guatemala | ||
| e. Brazil |
Question
17
Which of the following describes why income inequality is bad for economic development?
Choose one answer.
| a. Income inequality may threaten political stability, because people are dissatisfied with their economic situation and place blame on political authorities. | ||
| b. Income inequality reduces the pool of people with resources, such as education, to improve productivity. | ||
| c. Income inequality may increase distrust and deter commitment amongst people in the marketplace, making contracts enforcement difficult. | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
18
Which of the following factors tend not to lead to a decrease in population growth?
Choose one answer.
| a. When health conditions improve and parents no longer fear some of their children will die | ||
| b. When more women join the labor market and thus decide to have fewer children | ||
| c. When the population has access to modern contraception | ||
| d. When more women are educated | ||
| e. When men are more educated than women |
Question
19
Which of the following indicates a classification which does not determine a country's level of development?
Choose one answer.
| a. Level of industrialization | ||
| b. Level of income | ||
| c. Level of natural and human resources | ||
| d. GDP per capita | ||
| e. Population |
Question
20
Which of the following is a goal of economic development?
Choose one answer.
| a. Economic growth | ||
| b. Reduction of poverty | ||
| c. Improvement of human development (education, health, etc). | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. None of these answers |
Question
21
Which of the following statements best describes the social and political system of a feudal society?
Choose one answer.
| a. It is a decentralized system where serfs that are loyal to a single count provide services to the count in return for security and protection. | ||
| b. It is a highly centralized system in which upward mobility is determined by individual merit and entrepreneurship. | ||
| c. It is a centralized monarchic system where a king is the sole authority over a wide expanse of territory. | ||
| d. It is a system with a high level of democratic decision-making and grassroots participation in policy-making. | ||
| e. It is a decentralized system in which upward mobility is determined by individual merit and entrepreneurship. |
Question
22
According to neo-classical theory, what changes will lead to a shift out in long-run aggregate supply?
Choose one answer.
| a. Privatization of state-owned enterprises | ||
| b. Opening controls against foreign investment | ||
| c. Eliminating barriers to trade | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. None of these answers |
Question
23
According to the Neo-Marxists, what dynamic reinforces underdevelopment?
Choose one answer.
| a. The need to extract excess value from under-developed countries, particularly with raw materials | ||
| b. The effect of copyright laws on the ability of underdeveloped countries to develop a manufacturing sector | ||
| c. The institution of heavy trade barriers by developed countries against developing countries | ||
| d. The competitive nature of capitalism | ||
| e. The need for labor imports into the developed countries |
Question
24
According to the Romer model, if the stock of ideas increases by 15 %, by how much will output per worker increase, when all else is equal?
Choose one answer.
| a. 5% | ||
| b. 10% | ||
| c. 15% | ||
| d. 20% | ||
| e. 30% |
Question
25
Complete the following sentence. Marx believed that economic development should be led by:
Choose one answer.
| a. religious leaders. | ||
| b. capitalists. | ||
| c. individual entrepreneurs . | ||
| d. the state. | ||
| e. the bourgeoisie. |
Question
26
Complete the following sentence. The Romer model falls into a class of growth models in which the key determinants of economic growth are.
Choose one answer.
| a. implicit in the model. | ||
| b. explicit in the model. | ||
| c. exogenously determined. | ||
| d. not known. | ||
| e. the given saving and population growth rates. |
Question
27
Fill in the blanks. In the Solow model, if net investment is positive, then the economy is ___________ its steady state level, and output growth is
___________.
Choose one answer.
| a. above; negative | ||
| b. below; negative | ||
| c. above; positive | ||
| d. below; positive | ||
| e. above; neutral |
Question
28
For neo-classical theorists, economic under-development is the product of which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. Inappropriate economic policies and too much state interference in the economy | ||
| b. Barriers against free trade | ||
| c. Low prices for raw materials | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
29
For Rostow, which of the following constitute pre-conditions for take-off?
Choose one answer.
| a. Investment rate of at least 10% of GNP | ||
| b. Universal primary education | ||
| c. Development of one or more manufacturing sectors with a high growth rate | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
30
Given constant returns to labor, if 2 workers produced 14,000 bales of hay, how many bales of hay would 5 workers produce?
Choose one answer.
| a. 14,000 | ||
| b. 25,000 | ||
| c. 35,000 | ||
| d. 50,000 | ||
| e. 65,000 |
Question
31
How might a government try to increase output, if the government is to follow the suggestions of the Harrod-Domar model?
Choose one answer.
| a. By encouraging savings | ||
| b. By beginning to use state-owned enterprises | ||
| c. By promoting technologies which help firms to produce more output with less capital (lowering the capital to output ratio) | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
32
How would Lewis describe the traditional agricultural sector?
Choose one answer.
| a. A sector which might help to elevate the livelihoods of the people involved | ||
| b. A sector with low productivity, high unemployment, low incomes, and low savings | ||
| c. A sector from which people cannot transition into other sectors | ||
| d. A sector with highly educated but low productivity labor | ||
| e. A sector with full employment and therefore producing at the full employment output |
Question
33
If $20 worth of capital equipment produces each $5 of annual output, then what is the capital to output ratio?
Choose one answer.
| a. 1 to 4 | ||
| b. 4 to 1 | ||
| c. 1 to 2 | ||
| d. 2 to 1 | ||
| e. 4 to 4 |
Question
34
If you double the inputs K and L, what will happen to the output Y?
Choose one answer.
| a. The output Y will increase but at a diminishing rate. | ||
| b. The output Y will increase at an increasing rate. | ||
| c. The output Y will decrease but at a diminishing rate. | ||
| d. The output Y will remain the same. | ||
| e. The output Y will double. |
Question
35
Important beliefs of the structuralist school include which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. The northern developed countries do not share the wealth generated from productivity enhancing technological improvements due to problems in the political structure. | ||
| b. A completely free market approach will always yield the most efficient and equitable outcome. | ||
| c. One way for southern countries to develop is to substitute imported industrial goods with domestically produced ones. | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
36
In the Lewis model, what does the term "surplus labor" refer to?
Choose one answer.
| a. An amount of labor that is so high that it deflates wages throughout the economy | ||
| b. Labor that does not have at least a primary level education | ||
| c. Labor that can be withdrawn from the low productivity agricultural sector without a decrease in the total production | ||
| d. Labor that is exploited by the capitalist class | ||
| e. Labor that can be withdrawn from the industrial sector without a decrease in the total production |
Question
37
In the Lewis model, what will cause an expansion in modern sector employment?
Choose one answer.
| a. A reinvestment of profits by capitalists that allows production to expand | ||
| b. Interventions by the State to expand employment | ||
| c. An increase in technology | ||
| d. An increase in the surplus labor | ||
| e. An increase in wages in the traditional agricultural sector |
Question
38
In the resource constraint equation (see Figure 4), what does Lat signify?
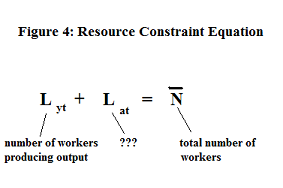
Choose one answer.
| a. The number of unemployed workers | ||
| b. The number of workers producing ideas or new technologies | ||
| c. The number of workers saving money | ||
| d. The number of workers working abroad | ||
| e. The number of workers producing output |
Question
39
In the Solow Growth model, if we start from a steady state and there is no change in savings/investment, then what will result from a permanent increase in
the rate of depreciation?
Choose one answer.
| a. Output growth will rise permanently, and the new steady state level of GDP will be higher than the old one. | ||
| b. Output growth will rise temporarily, and the new steady state level of GDP will be lower than the old one. | ||
| c. Output growth will fall temporarily, and the new steady state level of GDP will be higher than the old one. | ||
| d. Output growth will fall temporarily, and the new steady state level of GDP will be lower than the old one. | ||
| e. The result is ambiguous; we cannot be certain. |
Question
40
In the Solow model, how might we express the economic meaning of the vertical gap between the investment curve and the depreciation curve as indicated in
Figure 3?
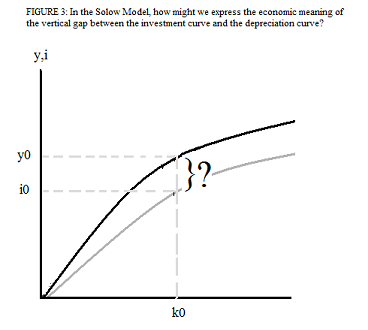
Choose one answer.
| a. Capital stock | ||
| b. GDP per capita | ||
| c. Consumption | ||
| d. Investment | ||
| e. Savings |
Question
41
In the Solow model, if a country is in the steady state, an earthquake causes wide-spread destruction of the capital stock, and there is no change in the
level of savings or depreciation, then this will result in which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. The growth rate of output will drop, and the country will end up at a lower steady state. | ||
| b. The growth rate of output will increase, and the country will end up at a higher steady state. | ||
| c. The growth rate of output will increase, and the country will end up at the original steady state. | ||
| d. The growth rate of output will increase, and the country will end up at a lower steady state. | ||
| e. The result is ambiguous; we cannot be certain. |
Question
42
In the Solow model, if an economy experiences an increase in the investment rate and an increase in the depreciation rate at the same time, then what will
be the result?
Choose one answer.
| a. Output will rise. | ||
| b. Output will fall. | ||
| c. Capital per worker will rise. | ||
| d. Capital per worker will fall. | ||
| e. The result is ambiguous; we cannot be certain. |
Question
43
In the steady state, which country will have the higher per capita consumption, and why?
Choose one answer.
| a. B will have the higher per capita consumption, because it is devoting more of its output to consumption and less to saving. | ||
| b. B will have the higher per capita consumption, because it will have a higher capital stock per worker, a higher output per worker, and thus a higher consumption per worker. | ||
| c. A will have the higher per capita consumption, because it will have a higher capital stock per worker, a higher output per worker, and thus a higher consumption per worker. | ||
| d. A will have the higher per capita consumption, because it will have a lower capital stock per worker, a lower output per worker, and thus a higher consumption per worker. | ||
| e. Both A and B will have the same consumption per worker, because they both have equal capital stock per worker, output per worker, and consumption per worker. |
Question
44
The Dependencia theory has its roots in what region of the world?
Choose one answer.
| a. Southeast Asia | ||
| b. North America | ||
| c. Latin America | ||
| d. The Middle East | ||
| e. Sub-Saharan Africa |
Question
45
The faster the population grows, the more labor there will be to produce goods and services, so faster population growth is good for economic growth. Why
may this not be true according to the Solow model?
Choose one answer.
| a. There will be too many people to feed and this may not be good. | ||
| b. What matters is per capita GDP; an increase in GDP may not translate to higher per capita GDP. | ||
| c. In the Solow model, what matters is capital stock per worker. If the additional population is not equipped with additional capital, output per worker will fall even though GDP is increasing. | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. B and C only |
Question
46
The Harrod-Domar growth model is based on the relationship of what two economic elements?
Choose one answer.
| a. Raw materials and technology | ||
| b. Savings and investment | ||
| c. Educational enrollment and number of teachers | ||
| d. Tariff and tax levels | ||
| e. Population and economic development |
Question
47
The Lewis model works as long as which of the following holds true?
Choose one answer.
| a. The wage rate in the modern sector is higher than in the traditional agricultural sector. | ||
| b. The modern sector grows fast enough to absorb labor from the traditional agricultural sector. | ||
| c. The traditional agricultural sector remains unproductive and thus able to release workers without reducing agriculture output. | ||
| d. The workers released from the agricultural sector can be quickly retrained to fit into the modern sector. | ||
| e. All of these answers |
Question
48
True or False. Import-substitution led to the development of many highly competitive industries in the countries which implemented it.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
49
True or False. Lenin believed that imperialism would delay the final crisis that will cause capitalism to collapse.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
50
True or False. Neo-classical economists believe that government-led development is the most effective path.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
51
True or False. The Neo-Marxists believed that developing countries must pass through advanced capitalism before moving on to socialism.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
52
True or False. The structuralists did not support capitalism.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
53
Using the formula in Figure 5 for the idea production function, if z = 0.01, l = 0.10, and N = 25, what is the growth rate of the stock of ideas?

Choose one answer.
| a. 1% | ||
| b. 2.5% | ||
| c. 5% | ||
| d. 25% | ||
| e. 30% |
Question
54
What are the three stages in Fisher Clark's theory of structural change?
Choose one answer.
| a. Primal organization, medieval organization, and industrial organization | ||
| b. Tribal order, preparation for take-off, and take-off | ||
| c. Primary production, secondary production, and tertiary production | ||
| d. Primary production, industrial production, and take-off production | ||
| e. Industrial organization, tribal organization, and primal organization |
Question
55
What does it mean in the Romer model when it says that there are constant returns to labor?
Choose one answer.
| a. Production of output will increase by the same marginal amount for every additional worker. | ||
| b. Workers can never become more productive. | ||
| c. Production of output is the same as in other countries. | ||
| d. Doubling inputs doubles output. | ||
| e. Doubling inputs doubles labor's output. |
Question
56
What does the Romer model include that allows an economy to sustain growth over time (holding savings constant) that the Solow model does not?
Choose one answer.
| a. Infrastructure | ||
| b. Discovery of raw materials | ||
| c. Technology | ||
| d. Investment | ||
| e. Savings |
Question
57
Which of the following accurately describes a criticism of the Lewis model?
Choose one answer.
| a. Urbanization in poor countries happens more quickly than the modern sector can create jobs, leading to problems of unemployment. | ||
| b. Capital might be plowed into labor saving technologies, which might in fact reduce employment in the modern sector. | ||
| c. Skilled labor is likely to immigrate abroad. | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
58
Which of the following accurately describes a criticism of the Harrod-Domar model?
Choose one answer.
| a. Economic growth does not necessarily result in economic development. | ||
| b. People in poor countries may be stuck in a poverty trap and unable to invest. | ||
| c. State owned enterprises tend to be less efficient than their privately owned competitors. | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
59
Which of the following accurately describes a criticism of Rostow's stages of development model?
Choose one answer.
| a. The model does not take into account technological changes. | ||
| b. The model is not relevant in a globalized world. | ||
| c. The model assumes that LDCs are just like DCs, except for differences in savings and investment. | ||
| d. The model is dynamic; it describes the process of how one stage ushers in the next. | ||
| e. The model's linearity is its strongest proof of its validity. |
Question
60
Which of the following accurately describes the belief of the Dependencia school regarding the effect of trade on developing countries?
Choose one answer.
| a. Free trade is the best and only means to promote development. | ||
| b. Export-led growth holds the key to industrialization and development. | ||
| c. Developing countries should protect domestic industry from competition and pursue a policy of import-substitution. | ||
| d. Developing countries are not integrated into the world system of trade. | ||
| e. Developing countries could not import capital to produce manufactured goods. |
Question
61
Which of the following accurately describes the economic reasons behind industrialization?
Choose one answer.
| a. As incomes rise, people's demands for food reach a limit and the demand for manufactured goods rises. | ||
| b. As the agricultural sector becomes more productive, labor can move to the industrial sector. | ||
| c. There is a change in interest rates. | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
62
Which of the following is a criticism against the neo-classical school?
Choose one answer.
| a. The model does not consider the potential for inequality. | ||
| b. The model has too large of a role for the government. | ||
| c. Market failures are not addressed. | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
63
Which of the following is a stage in Rostow's stages of development theory?
Choose one answer.
| a. Tribal | ||
| b. Communal | ||
| c. Metropolitan | ||
| d. Capitalist | ||
| e. Age of high mass consumption |
Question
64
Which of the following is a tactic suggested by the structuralist school to promote economic growth and development?
Choose one answer.
| a. Tariffs on imported industrial goods to help domestic producers to develop | ||
| b. State-owned enterprises | ||
| c. Import-substitution industrialization | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
65
Which of the following is central to Marx's economic theory of labor?
Choose one answer.
| a. Workers become more effective as education in the country increases. | ||
| b. Strong population growth is necessary to continue to increase national production. | ||
| c. Workers, or the proletariat, are being robbed of their labors by the owners of capital, or the bourgeoisie. | ||
| d. Without capital, labor has no value. | ||
| e. As capital becomes plentiful, labor loses its value. |
Question
66
Which of the following is not a tenet of the Dependencia school?
Choose one answer.
| a. According to some Latin American economists, capitalism will not give workers the chance for them to move upward. | ||
| b. Poor nations provide natural resources to the wealthy nations and are destinations for manufactured products. | ||
| c. Poor nations have been integrated into the world economy in such a way that it makes them dependent on the wealthy countries. | ||
| d. As long as the poor remain producers of primary products, they can never become developed. | ||
| e. As long as developing countries trade with the developed countries, they are bound to develop. |
Question
67
Which of the following schools was a proponent of import-substitution industrialization?
Choose one answer.
| a. Marxist | ||
| b. Harrod-Domar | ||
| c. Keynesian | ||
| d. Dependencia | ||
| e. Structuralist |
Question
68
Which school of thought believes that a major impediment to development comes from the dualistic nature of underdeveloped economies (where a modern sector
dependent on developed countries for technology exists side by side with a traditional sector)?
Choose one answer.
| a. Neo-liberal | ||
| b. Structuralist | ||
| c. Marxist | ||
| d. Keynesian | ||
| e. Neo-Marxist |
Question
69
Why is it difficult for developing countries to join the "knowledge revolution"?
Choose one answer.
| a. Developing countries have relatively few scientists. | ||
| b. Information technology tools are less prevalent. | ||
| c. People in developing countries do not have useful applications for the technologies. | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
70
According to Fukuyama, the "radius of trust" can be which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. Limited to the number of people an individual can directly supervise and can therefore trust | ||
| b. Defined as the circle of people among whom cooperative norms function | ||
| c. As small as a group of friends or as large as an NGO or religious group | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
71
According to the earlier proponents of the big push strategy for development, a "big push" in investment is necessary in developing countries because of
which of the following reasons?
Choose one answer.
| a. In a traditional economy, people do not have the required habits for a profitable industrial society and therefore need a push. | ||
| b. The lack of modern technology requires a large investment in education. | ||
| c. Poor economies do not grow because complementary industries fail to cooperate; a "big push" is required to get these industries to develop simultaneously. | ||
| d. Poor economies must resolve pressing health and education challenges before they can industrialize. | ||
| e. Investment can only come in big lumps; smaller lumps are not profitable. |
Question
72
According to the World Bank, why is social capital so important for the poor?
Choose one answer.
| a. The poor rely on their friends, families, and neighbors to help them in the case of disaster (bad health, inclement weather, etc.). | ||
| b. The poor pool their resources to start up enterprises. | ||
| c. The poor cooperate to assure that child care needs are met. | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. None of these answers |
Question
73
According to Williamson's Hierarchy of Institutions (in the New Institutional Economics School), which of the following can be considered to be
institutions?
Choose one answer.
| a. Human motivations | ||
| b. Social structure | ||
| c. Political institutions | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. B and C only |
Question
74
Complete the following sentence. According to Francis Fukuyama, social capital can be defined as:
Choose one answer.
| a. a capital good that promotes communication between people. | ||
| b. an informal norm that promotes cooperation between two or more individuals. | ||
| c. an institution that forces people to come together that would not normally come together. | ||
| d. a formal structure that relinquishes power from one individual to another. | ||
| e. a capital good that deters communication between people. |
Question
75
Complete the following statement. According to Sen, South Korea is more developed than North Korea, because South Koreans have:
Choose one answer.
| a. political freedoms, economic facilities, social opportunities, transparency guarantees, and protective securities. | ||
| b. economic freedoms, religious freedoms, freedom of expression, freedom of movement, and free association. | ||
| c. free movement of goods and services, freedom from oppression by the government, freedom to start and close a business, freedom from undue taxation, and freedom from over-regulation. | ||
| d. political restrictions, religious restrictions, and social restrictions. | ||
| e. economic freedoms, social freedoms, and political restrictions. |
Question
76
How does Fukuyama suggest that social capital is formed?
Choose one answer.
| a. By repeated interactions between people and groups that show that cooperation pays off | ||
| b. By shared historical experience | ||
| c. By state intervention to create a large bureaucracy capable of monitoring and enforcing contracts | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
77
How does Mohammad Younis' microfinance scheme respond to adverse selection problems in microfinance?
Choose one answer.
| a. By implementing the requirement that borrowers put up collateral, such as motor bikes or livestock | ||
| b. By the use of specialized training to help the members of the bank to become better informed of savings and investment strategies | ||
| c. By placing borrowers in groups of people who know each other and giving the groups control over who receives loans, which results in the groups selecting those members most likely to pay back loans | ||
| d. By requiring collateral of all borrowers which is some fraction of how much the group borrowed | ||
| e. By requiring a lengthy disclosure of all pertinent information about borrowers and their associates |
Question
78
How does Sen define poverty?
Choose one answer.
| a. The lack of material well-being | ||
| b. The deprivation of basic capabilities for an individual | ||
| c. The lack of supportive social institutions to ensure ones basic livelihood | ||
| d. The lack of a cultural or religious identity | ||
| e. The need to supplement luxuries for an individual |
Question
79
In New Institutional Economics, what is meant by the principal-agent problem?
Choose one answer.
| a. The difficulty of finding a well-trained employee | ||
| b. The difficulty of motivating an agent to take an action, when the action is not directly observable | ||
| c. The difficulty of replicating good results in repeat projects | ||
| d. The difficulty of motivating an agent to take no action, when this is the best reward | ||
| e. The difficulty of identifying the principal results of a project |
Question
80
In New Institutional Economics, which of the following is an example of "transaction costs," which institutions can help to resolve?
Choose one answer.
| a. Uncertainty about the trustworthiness of sellers and buyers | ||
| b. The risk for a bank that lenders will not pay back | ||
| c. The high costs of constructing a public highway | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
81
In the model presented by Sachs et al., what was the effect of adding share of imported intermediate inputs in final demand?
Choose one answer.
| a. Countries which import an important part of their final production are very dependent on the rich, developed northern countries, and these countries should pursue import substitution industrialization. | ||
| b. Having a high share of imported intermediate inputs creates a high risk for a country in the event of a future exchange rate crisis. | ||
| c. The production of intermediate inputs tends to generate more employment than final goods; thus, countries with a high share of imported intermediate inputs will not produce as many jobs as they could otherwise. | ||
| d. When a country has to import a large value of intermediate inputs (relative to total production), even small transport costs can have important effects on output and growth. | ||
| e. There is no economic impact on importing intermediate inputs as long as the inputs are from a reliable source. |
Question
82
More recent calls for a "big push" strategy are concerned with which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. A big increase in foreign aid | ||
| b. A simultaneous increase in investment in many different sectors, as well as complementary policy changes and technical interventions | ||
| c. A national plan with an administrative structure to direct investments, technical intervention, and policy changes | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. None of these answers |
Question
83
True or False. There is a clear positive relationship between population density and per capita income.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
84
What economic function does social capital play?
Choose one answer.
| a. Social capital reduces the transaction costs related with contracts, hierarchies, and bureaucracy. | ||
| b. Social capital allows for coordination based on informal norms. | ||
| c. Social capital enables more efficient forms of industrial organization due to increased trust between workers and managers. | ||
| d. Social capital facilitates the free flow of information. | ||
| e. All of these answers |
Question
85
What is meant by the term "neighborhood effects," in the 2009 World Development report?
Choose one answer.
| a. The creation of functioning, pro-development neighborhoods on a city or village level can promote economic growth and development on a national level. | ||
| b. A country can experience either positive or negative spill-overs from countries in its region. | ||
| c. Countries in which neighbors live closer together tend to have higher social capital, leading to better development outcomes. | ||
| d. If two countries are close to each other, then it is more likely that they are both developed. | ||
| e. A poor country closer to a richer country will always be dominated by the richer country and remain poor. |
Question
86
What is the most important contribution to economic growth theory offered by New Institutional Economics?
Choose one answer.
| a. New Institutional Economics rejects the neo-classical theory and replaces it with an emphasis on institutions. | ||
| b. New Institutional Economics rejects the notion of market equilibrium determining prices and allocating resources. | ||
| c. New Institutional Economics includes the role of institutions in furthering or retarding economic growth. | ||
| d. New Institutional Economics rejects the role of laws, rules, customs, and norms in economic growth. | ||
| e. New Institutional Economics claims that institutions do not have a role in furthering or retarding economic growth. |
Question
87
What problem does the New Institutional Economics school suggest can arise when performance based measures are implemented (such as rewarding teachers for
high test scores) to resolve the principal-agent problem?
Choose one answer.
| a. The agent will game the system in order to gain the benefit, often through manipulating the performance based measure through cheating or fraud. | ||
| b. The reward system can often become too expensive. | ||
| c. The system can be too confusing for the agent to understand, and it will be impossible to get an accurate measure of performance on the ground. | ||
| d. Performance will not improve, harming both agent and principal. | ||
| e. The principal will not be able to monitor the behavior of the agent . |
Question
88
What variable do Sachs et al. add to the Harrod-Domar model to look at the relationship between income growth and geography?
Choose one answer.
| a. Transport costs | ||
| b. Population density | ||
| c. Elevation | ||
| d. Size of the country | ||
| e. GPD |
Question
89
What "poverty trap" or "vicious circle of poverty" did Nurkse famously describe in 1953?
Choose one answer.
| a. People in poor countries are too poor to save, which means that they cannot invest in capital to increase their productivity, which means they remain poor. | ||
| b. Women in poor countries are uneducated, which tends to result in high fertility rates, which means households do not have enough money to send girls to school. | ||
| c. Social structures in developing countries tend to limit the options available to the poor. | ||
| d. The poor tend to live far away from physical infrastructure, which limits their possibilities for accessing markets. | ||
| e. Workers in poor countries are fatalistic and accept poverty as their lot, so they remain poor. |
Question
90
What, according to Amartya Sen, is the principal end of development?
Choose one answer.
| a. Increased incomes | ||
| b. Freedom | ||
| c. Movement to industrial forms of organization | ||
| d. Democracy | ||
| e. Increased education |
Question
91
Which of the following behaviors is evidence of social capital?
Choose one answer.
| a. Honesty | ||
| b. Keeping commitments | ||
| c. Reciprocity | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. None of these answers |
Question
92
Which of the following benefits might social capital provide to political development?
Choose one answer.
| a. Social capital allows people in an individualist democratic system to form associations and organize for common causes. | ||
| b. Social capital allows for the organization of a civil society which protects against the power of the state. | ||
| c. Social capital leaves the responsibility to each individual to work for their own individual self interest. | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
93
Which of the following is a problem that some critics have with Sen's capability approach?
Choose one answer.
| a. Sen's capability approach does not clearly provide for individual freedoms, focusing too much on the overall social good of society. | ||
| b. Sen's capability approach does not consider the right to education, which is an important social good. | ||
| c. Sen's capability approach focuses too narrowly on economic development, defined as income per capita. | ||
| d. Sen's capability approach relies on a mix of capitalism and good values but cannot explain how good values might be developed. | ||
| e. Sen's capability approach does not take political freedoms into consideration. |
Question
94
Which of the following is included in the three dimensions of geographical transformations for economic development, as defined in the 2009 World
Development Report?
Choose one answer.
| a. Density, distance, and division | ||
| b. Productivity, power, and populism | ||
| c. Region, mineral richness, and roads | ||
| d. Education, history of dominance, and diversity | ||
| e. Power, education, and diversity |
Question
95
Why does Fukuyama argue that social capital can have negative externalities?
Choose one answer.
| a. Social networking sites, such as Facebook, waste productive time at work. | ||
| b. Strong social networks may work for their internal interest, which might be counter to that of society as a whole. | ||
| c. Socializing is a waste of time, and that time that would be better used to produce goods and services. | ||
| d. Too much social capital, like physical capital, can have diminishing marginal returns. | ||
| e. All of the studies on social capital show that it decreases productivity. |
Question
96
China's economic development progress can accurately be described by which economic development model?
Choose one answer.
| a. Harrod-Domar model | ||
| b. Solow Growth model | ||
| c. A. Lewis model | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. None of these answers |
Question
97
Fill in the blanks. Economic development is a(n) __________ process which can at best be explained by ____________.
Choose one answer.
| a. complex; several factors | ||
| b. linear process; specific factors | ||
| c. government controlled; institutional factors | ||
| d. external; factors outside the control of any country | ||
| e. internal; limited factors |
Question
98
Fill in the blanks. Many economic development theories focus on quantifiable factors such as ________, which are necessary for economic development but not
________. This suggests that there are some other important non-easily quantifiable factors such as __________, which are often ignored.
Choose one answer.
| a. savings; sufficient; capital | ||
| b. savings; sufficient; social capital | ||
| c. institutions; important; labor | ||
| d. institutions; important; capital | ||
| e. savings; insufficient; social capital |
Question
99
In the Mozambique study on achieving shared growth, which of the following are cited as key factors of success?
Choose one answer.
| a. The use of state-run industries to replace imported goods with domestically produced ones | ||
| b. The use of price controls to make sure that farmers receive at least a minimum level of income | ||
| c. The printing of extra money to finance a heightened level of public investment in infrastructure | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. None of these answers |
Question
100
True or False. It is only after a country has developed that the factors that led to development can be clearly delineated.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
101
Which of the following major risks was cited in the Sierra Leone case study on rebuilding local governments?
Choose one answer.
| a. The lack of significant local resources at the local level | ||
| b. Weak political commitment to real decentralization | ||
| c. National officials possibly feeling challenged by the rising power of local officials | ||
| d. All of these answers | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
102
Which of the following were success factors of the Mali rural electrification case study?
Choose one answer.
| a. The use of a highly centralized government led strategy | ||
| b. The use of women associations as energy providers in rural areas | ||
| c. The development of public private partnerships with local private operators | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |