1
About what percent of GDP was the 2009 budget deficit?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 5-10% |
||
|
b. 10-15% |
||
|
c. 15-20% |
||
|
d. 20-25% |
||
|
e. 25-30% |
Question 2
According to Milton Friedman, what tends to contribute to fast reductions in government spending?
Choose one answer.
|
a. When a Democrat is in the executive and Republicans control the legislature |
||
|
b. When there is a recession which results in a contraction in revenues |
||
|
c. When there is a demographic shift towards an “older society” |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 3
According to the Coase theorem, what prevents externality problems from being resolved by bargaining?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Legislation |
||
|
b. Weak property rights |
||
|
c. Common set of values |
||
|
d. Adequate institutions to regulate |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 4
According to the NMcbeth reading, what are some key components of interest group formation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Acquisition of goods/benefits incentives |
||
|
b. Patronage |
||
|
c. Group size |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 5
According to the Ramsey rule, which good represented in figure 5 should be taxed, the good in graph A or the good in graph B?
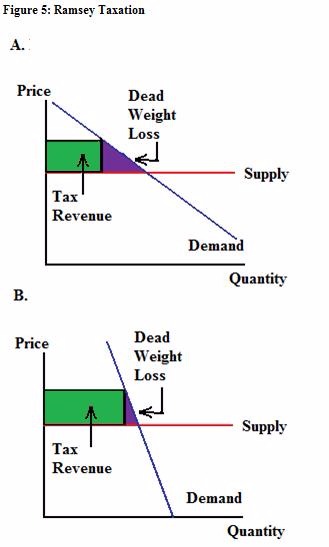
Choose one answer.
|
a. Graph A |
||
|
b. Graph B |
||
|
c. Both goods should be taxed. |
||
|
d. It is impossible to determine from the information given. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 6
According to the Rent Seeker Watch blog, what was the major opposition to providing the home mortgage interest deduction?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It is complicated to fill out the tax paperwork to benefit. |
||
|
b. Realtors claim most of the benefit in their fees. |
||
|
c. It is regressive, because the wealthy with very expensive homes benefit the most. |
||
|
d. It will not go into place until 2035. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 7
Agricultural and fishing subsidies make up about what percent of the EU budget?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 10-20% |
||
|
b. 20-30% |
||
|
c. 30-40% |
||
|
d. More than 40% but less than 80% |
||
|
e. More than 80% |
Question 8
By how much does the quantity of widgets demanded decrease when the tax was imposed, according to figure 4?
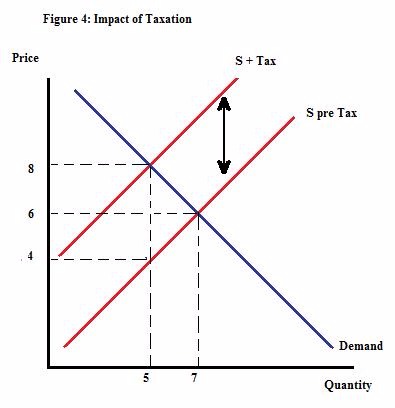
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0 |
||
|
b. 2 |
||
|
c. 5 |
||
|
d. 7 |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 9
Governments give subsidies for which of the following reasons?
Choose one answer.
|
a. To keep market prices down |
||
|
b. To boost demand for certain goods |
||
|
c. To maintain revenues of producers of certain goods |
||
|
d. To encourage a service or activity with a positive externality |
||
|
e. All of the above |
Question 10
How has the composition of California’s sources of revenue changed between 1966-1967 and 2006-2007?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The importance of personal income tax has decreased as a percent of the total budget. |
||
|
b. The importance of sales and use tax has increased as a percent of the total budget. |
||
|
c. Corporation tax has been eliminated. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 11
If the government proposes a tax rate higher than the one shown at point B in Figure 6, what would be the result, according to the Laffer curve idea?
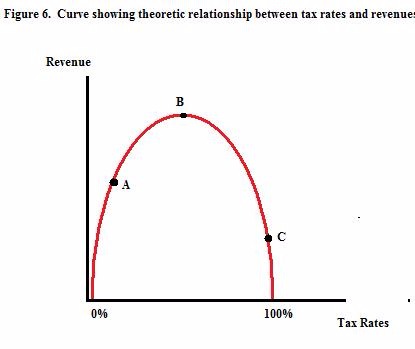
Choose one answer.
|
a. Tax revenues would increase. |
||
|
b. Tax revenues would decrease. |
||
|
c. Tax revenues would remain the same. |
||
|
d. It is impossible to detect based on the information given. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 12
If the total work and leisure allocation is 80 hours, what does the individual in Figure 9 choose to do in the presence of unemployment insurance?
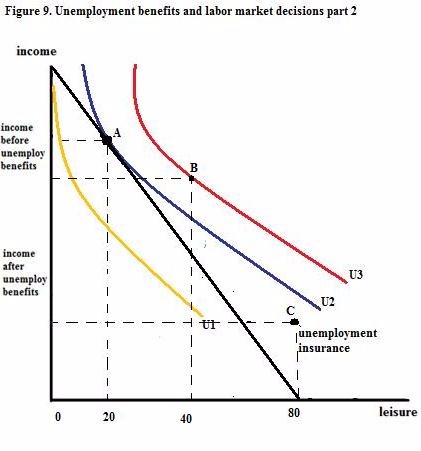
Choose one answer.
|
a. The individual will choose to work. |
||
|
b. The individual will choose not to work. |
||
|
c. The individual will work if his/her wage increases by $2. |
||
|
d. B and C only |
||
|
e. This is impossible to determine based on the information given. |
Question 13
If the total work and leisure allocation is 80 hours, how many hours of work will the individual in Figure 9 choose to work?

Choose one answer.
|
a. 0 |
||
|
b. 20 |
||
|
c. 40 |
||
|
d. 60 |
||
|
e. 80 |
Question 14
In 2006-2007, what are the two largest areas of California state spending?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Transportation and criminal justice |
||
|
b. Higher Education and criminal justice |
||
|
c. K-12 education and health and social services |
||
|
d. K-12 education and transportation |
||
|
e. Health and social services and higher education |
Question 15
In figure 3 of the Pigouvian tax model, what does the distance C represent?
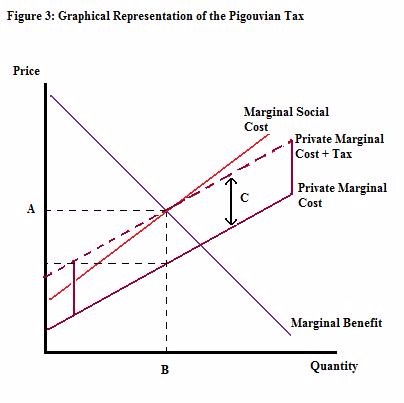
Choose one answer.
|
a. The social benefit of the provision of the good |
||
|
b. The tax required to compensate for the cost to society (negative externality) |
||
|
c. The excess profit for the producer |
||
|
d. The surplus for the consumers |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 16
In figure 3 of the Pigouvian tax model, what does point B represent?

Choose one answer.
|
a. Market clearing quantity |
||
|
b. Profit maximizing quantity for the producer |
||
|
c. Government mandated quantity |
||
|
d. Quota |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 17
In figure 3 of the Pigouvian tax model, what is the price marked by point A known as?

Choose one answer.
|
a. Positive externality price |
||
|
b. Market clearing price |
||
|
c. Socially efficient price |
||
|
d. Privately determined price |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 18
In figure 4, who bears most of the tax?

Choose one answer.
|
a. The producer |
||
|
b. The consumer |
||
|
c. The producer and the consumer bear the tax equally. |
||
|
d. This tax has no excess burden. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 19
In Figure 6, which point on the curve represents the maximum level of tax revenue?

Choose one answer.
|
a. Point A |
||
|
b. Point B |
||
|
c. Point C |
||
|
d. Both Point A and C |
||
|
e. All points are at the same level. |
Question 20
In figure 6, which point on the curve represents the highest tax rate?

Choose one answer.
|
a. Point A |
||
|
b. Point B |
||
|
c. Point C |
||
|
d. Both Point A and C |
||
|
e. All points represent an equal tax rate. |
Question 21
In figure 7, what is the effect of the subsidy on the quantity of boxes of widgets demanded by consumers after the subsidy?
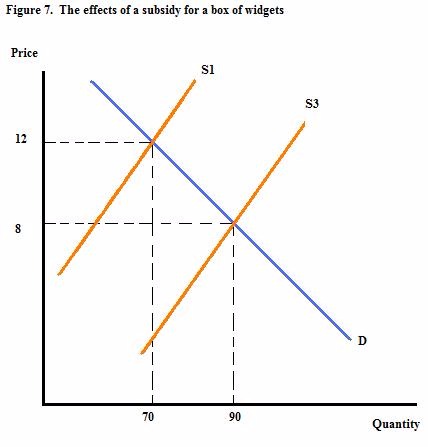
Choose one answer.
|
a. It increases by 70. |
||
|
b. It increases by 90. |
||
|
c. It increases by 20. |
||
|
d. It decreases by 70. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 22
In Figure 7, what is the effect of the subsidy on the price consumers pay for a box of widgets?

Choose one answer.
|
a. It falls by 12. |
||
|
b. It falls by 8. |
||
|
c. It falls by 5. |
||
|
d. It falls by 4. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 23
In which of the following areas does government commonly put into place public-private partnerships?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Provision of roads |
||
|
b. Development of pharmaceutical products |
||
|
c. Hospitals |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. A and B only |
Question 24
The Laffer curve is meant to demonstrate what idea?
Choose one answer.
|
a. People will pay very high taxes on goods for which they have inelastic demand. |
||
|
b. Luxury goods are the best goods to tax for equity reasons. |
||
|
c. Total taxes collected may fall when taxes are increased. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 25
The simplified version of the Ramsey rule states which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Taxes should be imposed on goods consumed predominantly by the rich. |
||
|
b. Taxes should be imposed on goods consumed by everyone. |
||
|
c. Tax rates on goods should be inversely related to their elasticity of demand. |
||
|
d. Tax rates on goods should be directly related to their elasticity of demand. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 26
U.S. Tobacco lobbying public officials enacted which policy change?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A subsidy for their stop smoking devices |
||
|
b. A per unit tax rather than usual ad valorem tax |
||
|
c. Lower oversight of their facilities |
||
|
d. Payment of carbon credits for their plantations on US soil |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 27
What action does Congressman Pence suggest to respond to the increasing size of the public debt?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Letting the Bush tax cuts expire |
||
|
b. Extending the retirement age for Social Security |
||
|
c. Imposing constitutional limits on spending |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 28
What are Holcombe’s arguments against common usage of the word “public good?”
Choose one answer.
|
a. Many of these goods are successfully produced in the private sector, thus do not need to be produced by the government. |
||
|
b. Many goods provided by the government do not fit the definition of a public good. |
||
|
c. Most goods referred to as public goods are actually paid for by private individuals. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. None, Holcombe is a proponent of providing “public goods.” |
Question 29
What are some reasons for government failure?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Separation of powers |
||
|
b. Political self-interest |
||
|
c. Unintended consequences |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 30
What do critics of farm subsidies argue regarding the farm subsidies’ effects on developing countries?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They promote overeating in the developing world. |
||
|
b. They make developed countries uncompetitive with developing country. |
||
|
c. They lower world prices for crops, thus reducing the income of farmers in developing countries. |
||
|
d. They lead to freer markets for agricultural commodities. |
||
|
e. All of the above |
Question 31
What does California’s Proposition 13 state, with regards to public finance?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It limits the amount of property tax that can be levied. |
||
|
b. It limits state spending to no more than 10 percent of State GDP. |
||
|
c. It reformed state spending on social services. |
||
|
d. It increased the income tax rate on the highest income tax bracket. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 32
What economic concept do proponents of extending the Bush tax credits frequently cite?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Keynesian cross |
||
|
b. Laffer curve |
||
|
c. Prisoner’s dilemma |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 33
What findings of the CPO report does Dustin Ensinger cite regarding the effects of the stimulus spending?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It cost more than originally expected. |
||
|
b. In the second quarter of 2010, it helped create 3.3 million jobs. |
||
|
c. It did not create any jobs. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both A and C |
Question 34
What has been the most highly subsidized crop in recent U.S. history?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Corn |
||
|
b. Wheat |
||
|
c. Soy |
||
|
d. Cotton |
||
|
e. Dairy |
Question 35
What is a merit good?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A good one receives as a reward. |
||
|
b. A good that has positive externalities. |
||
|
c. A good which has a special symbolic place in society. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both A and C |
Question 36
What is a public subsidy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It is a payment of a private citizen or entity to the government. |
||
|
b. It is a payment from one private citizen or entity to another. |
||
|
c. It is a type of tax. |
||
|
d. It is a payment of the government to a private citizen or entity. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 37
What is Bruce Bartlett’s opposition to constitutional limits on spending?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It would give too much power to the Republicans. |
||
|
b. Discretionary spending is an increasingly small part of the budget. |
||
|
c. Tax loopholes can have an even bigger effect on the deficit. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 38
What is meant by the term “rent seeking?”
Choose one answer.
|
a. People who protest the increasingly high prices for rent in urban areas |
||
|
b. The equalization of rent in a city as people move to lower rent areas |
||
|
c. The lobbying of politicians to attempt to influence policy to gain subsidies or special benefits for a group |
||
|
d. The use of a tax system that taxes rich individuals at a higher rate than poor individuals |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 39
What is one major cause of California’s large revenue shortfalls in the state’s budget?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The stock market decline reduced returns to General Fund revenues. |
||
|
b. Tax receipts fell. |
||
|
c. New technologies failed to effectively collect revenues. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 40
What is Ron Paul’s opinion on stimulus spending?
Choose one answer.
|
a. He believes stimulus spending is correct in theory but was not properly administered. |
||
|
b. He believes that stimulus spending kept the economy from imploding. |
||
|
c. He believes that stimulus spending is ineffective and only serves to increase the national debt. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 41
What is Samuelson’s definition of a public good?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A good which, once it has been produced for a few consumers, can be consumed by additional consumers at no cost |
||
|
b. A good which is completely financed by the government |
||
|
c. A good that is distributed by the government |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 42
What is the amount of tax in figure 4?

Choose one answer.
|
a. 2 |
||
|
b. 4 |
||
|
c. 6 |
||
|
d. 8 |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 43
What is the area of excess burden in figure 4?

Choose one answer.
|
a. 0 |
||
|
b. 2 |
||
|
c. 4 |
||
|
d. 6 |
||
|
e. 8 |
Question 44
What is the cyclical component of the budget deficit?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The part attributable to a temporary dip in national output |
||
|
b. The part related to non-discretionary spending |
||
|
c. The part that remains even after a recession has ended |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 45
What is the definition of a change that is “pareto efficient?”
Choose one answer.
|
a. A change that maximizes total utility |
||
|
b. A change that minimizes the loss in utility |
||
|
c. A change that makes at least one person better without making anyone else worse off |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 46
What is the economic term for someone who enjoys the benefits of consumption of a good without paying for it?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A free rider |
||
|
b. A cheapskate |
||
|
c. A younger sibling |
||
|
d. A free loader |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 47
What is the effect of paying a subsidy on consumer surplus, for a normal good with moderately elastic demand?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It increases for consumers of the subsidized good. |
||
|
b. It decreases for consumers of the subsidized good. |
||
|
c. It does not change for consumers of the subsidized good. |
||
|
d. It is impossible to tell from the information provided. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 48
What is the fiscal dilemma, in the Citizendium reading about fiscal sustainability?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Whether to allow the private sector to supply certain goods or allow the government to do so |
||
|
b. Whether to increase the deficit to mitigate a recession or to reduce it to increase investor confidence |
||
|
c. Whether to allow spending to occur at the central or state level |
||
|
d. Whether to subsidize the use of merit goods |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 49
What is the most important element of Federal Spending?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Medicare |
||
|
b. Social Security |
||
|
c. Welfare |
||
|
d. Defense spending |
||
|
e. Education |
Question 50
What is the most important relationship between fiscal sustainability and investment markets?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Taxation of investors is a major driver of fiscal sustainability, and higher taxation of investment may lead to investment markets drying up. |
||
|
b. Investors are unconcerned with issues of fiscal sustainability. |
||
|
c. The government takes debt to finance deficit spending and investors may become intolerant to high borrowing. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 51
What is the name for a taxation that is equal to an individual’s willingness to pay for one more unit at the point when the marginal cost of supply is equal to the total willingness to pay for an additional unit of a good across society?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Lindahl tax |
||
|
b. Ramsey tax |
||
|
c. Coasian tax |
||
|
d. Laffer tax |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 52
What is the name of the parabola (in red) graphed in Figure 6?

Choose one answer.
|
a. The Keynesian cross |
||
|
b. The Laffer curve |
||
|
c. The Supply curve |
||
|
d. The IS/LM model |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 53
What is the term for the private sector consortium which participates in a public-private partnership?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Local organization |
||
|
b. Special purpose vehicle |
||
|
c. Decentralized agency |
||
|
d. Developmental agency |
||
|
e. Rent seeker |
Question 54
What term refers to a per-unit tax on a good generating a negative externality that is equivalent to the marginal externality at the socially efficient quantity?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Pigouvian tax |
||
|
b. Head tax |
||
|
c. Ramsey tax |
||
|
d. Lindahl tax |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 55
What term refers to the connection between Congress, interest groups, and the bureaucracy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The holy trinity |
||
|
b. The iron triangle |
||
|
c. Free-riders |
||
|
d. Faux amis |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 56
What trade-off might we face with regard to the extension of the Bush tax cuts, according to Jason Welker author of “Economics in plain English?”
Choose one answer.
|
a. Higher taxes now, or higher taxes and higher interests rates in the future |
||
|
b. Higher taxes now or higher spending now |
||
|
c. Lower taxes now or lower interest rates later |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 57
What was one major criticism of Keynesian theory?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Monetary policy has a much larger effect on aggregate demand than fiscal policy. |
||
|
b. Keynesianism was too strict on maintaining balanced budgets. |
||
|
c. Keynesianism did not consider the psychological effects of recessions on investors and consumers. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 58
What was the major purpose of the Gramm-Rudman-Hollings act?
Choose one answer.
|
a. To consider the funding of the public school system |
||
|
b. To simplify the tax code |
||
|
c. To impose automatic spending cuts in the case of large budget deficits |
||
|
d. To require the use of public voting on changes to social security |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 59
What was the major task of the Grace Commission?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Common means of tax evasion |
||
|
b. Waste and inefficiency in the U.S. government |
||
|
c. Regressivity of excise tax |
||
|
d. Most efficient way to fund highway costs |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 60
What well known theorem holds that bargaining can generally resolve problems of externalities?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Coase theorem |
||
|
b. Pareto theorem |
||
|
c. Tiebout theorem |
||
|
d. Median voter theorem |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 61
What were the two most important sources of revenues for the Federal Government in 2010?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Individual income tax and Social Security tax (and other payroll tax) |
||
|
b. Corporate income tax and individual income tax |
||
|
c. Corporate income tax and Social Security tax (and other payroll tax) |
||
|
d. Individual income tax and estate taxes |
||
|
e. Custom duties and property taxes |
Question 62
When does government failure occur?
Choose one answer.
|
a. When government cannot pass a new budget |
||
|
b. When government is unable to make compromises and enact new policies |
||
|
c. When policy leads to a deepening of the market failure or a new failure |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. A and B only |
Question 63
Which of the following are classified in the U.S. Federal Budget as mandatory spending?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Social Security |
||
|
b. Interest on the national debt |
||
|
c. Defense spending |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 64
Which of the following are negative externalities?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A college student whose loud music prevents other students from studying |
||
|
b. A factory which leaks toxic waste into the adjacent river |
||
|
c. A person who hurts himself running laps |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. A and B only |
Question 65
Which of the following benefits is associated with personal income taxes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Personal income taxes tend to be progressive. |
||
|
b. Personal income taxes perform well in terms of horizontal equity. |
||
|
c. Personal income taxes are very stable. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 66
Which of the following best describes a problem with property taxes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Property taxes are complicated to implement, because the value of houses is difficult to determine and thus the taxes are difficult to collect. |
||
|
b. Property taxes are unstable, because the value of property fluctuates dramatically every year. |
||
|
c. Property taxes are not always fair, because they are usually set for small areas; thus, areas with low value property have a difficulty mobilizing revenue, and poor people pay a large percentage of their total incomes in property taxes. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both A and C |
Question 67
Which of the following best describes an automatic stabilizer?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A type of tax that falls during a recession, such as a tax on luxury goods |
||
|
b. Spending on growth inducing areas, such as science and economic infrastructure, which leads to an increase in economic growth |
||
|
c. A type of government spending that increases automatically in a recession, such as unemployment insurance |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 68
Which of the following describes a common rationale for economic regulation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Consumer protection |
||
|
b. Industry protection |
||
|
c. New job creation |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 69
Which of the following describes the budget approval process in the state of California?
Choose one answer.
|
a. After the recommendations of the state senate and assembly, the budget is sent to the governor. |
||
|
b. After the recommendations of the subcommittees of state senate and assembly, the senate and assembly must pass the budget by 2/3 vote. |
||
|
c. A joint committee of the state senate and assembly iron out differences in their respective versions of the bill. |
||
|
d. The state senate and assembly must agree with a 2/3 vote to restore measures eliminated by the governor. |
||
|
e. All of the above |
Question 70
Which of the following is a major strength of the sales tax?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It is a stable tax that does not decline significantly in recessions. |
||
|
b. It is a progressive tax. |
||
|
c. It is charged evenly to internet vendors and local venders. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. Both A and C |
Question 71
Which of the following is an argument against subsidies?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Subsidies distort market prices. |
||
|
b. Decisions on who receive subsidies are often arbitrary. |
||
|
c. Financial cost of subsidies falls on tax payers, who may not receive any benefit in return. |
||
|
d. Subsidies may protect inefficient firms. |
||
|
e. All of the above |
Question 72
Which of the following is an example of semi-public goods?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Highways |
||
|
b. Garbage collection |
||
|
c. Personal cell phone |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 73
Which of the following is not a standard criterion for the evaluation of taxes and tax systems?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Fairness |
||
|
b. Simplicity |
||
|
c. Efficiency |
||
|
d. Adequacy |
||
|
e. Mandatory |
Question 74
Which of the following is true of excise taxes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Excise taxes are imposed on internationally traded goods. |
||
|
b. Excise taxes are levied for a temporary time period. |
||
|
c. Excise taxes are collected on the sale of a particular class or category of items. |
||
|
d. Only the rich pay excise taxes. |
||
|
e. None of the above statements are true. |
Question 75
Which of the following is true of neutral tax?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It is defined by each citizen’s ability to pay. |
||
|
b. It is a taxation that will alter the incentives in the market. |
||
|
c. It is proportional to income. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 76
Which of the following is true of the median voter theorem?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Voting usually leads to inefficient solutions. |
||
|
b. Voting maximizes the preference of the median voter. |
||
|
c. The median voter is never satisfied for voting outcomes. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both A and C |
Question 77
Which of the following might be an example of a positive externality?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Vaccination campaigns reduce the chance of epidemics for everyone. |
||
|
b. Education leads to better informed voters who vote for better politicians. |
||
|
c. A neighbor’s mean dog scares away robbers for the surrounding houses. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. A and B only |
Question 78
Which of the following situations best reflects John Maynard Keynes’s philosophy on economic policy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It is the responsibility of government to promote equality. |
||
|
b. Fiscal policy can be a useful tool to stimulate consumer spending in times of recession. |
||
|
c. Monetary policy is the only means of providing economic stimulus. |
||
|
d. The invisible hand will always lead to an optimal economic outcome. |
||
|
e. None of the above. |
Question 79
Which of the following statements are true about the U.S. taxation system?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The income tax system is regressive. |
||
|
b. There are no Federal excise taxes. |
||
|
c. All states have the same general sales taxes. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 80
Which of the following statements is characteristic of a public good?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It is non-excludable. |
||
|
b. It is rejectable. |
||
|
c. It is non-rival. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both A and C |
Question 81
Which of the following statements is false?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The private sector can provide public goods. |
||
|
b. One argument for the provision of public goods is efficiency. |
||
|
c. A public good is one that is excludable. |
||
|
d. Providing a public good helps to overcome the problem of free riders. |
||
|
e. All of the above |
Question 82
Which of the following statements is true about the relationship between taxes and labor supply?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Taxes on labor may increase the amount of labor supplied. |
||
|
b. Taxes on labor may decrease the amount of labor supplied. |
||
|
c. The effect of taxes on labor depends on a person’s preferences regarding leisure and income. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 83
Which of the following terms of decentralization refers to the method by which subnational officials are selected? (Hint: From the IMF paper)
Choose one answer.
|
a. Structural decentralization |
||
|
b. Decision decentralization |
||
|
c. Resource decentralization |
||
|
d. Electoral decentralization |
||
|
e. Institutional decentralization |
Question 84
Which of the following type of goods might be considered “merit goods?”
Choose one answer.
|
a. Cigarettes |
||
|
b. Vaccinations |
||
|
c. Education |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 85
Which of the graphs in figure 5 has a more elastic demand?

Choose one answer.
|
a. Graph A |
||
|
b. Graph B |
||
|
c. Both graphs are equal. |
||
|
d. It is impossible to determine based on the information given. |
||
|
e. None of the above |
Question 86
Which of the points on figure 2 is “pareto optimal?”
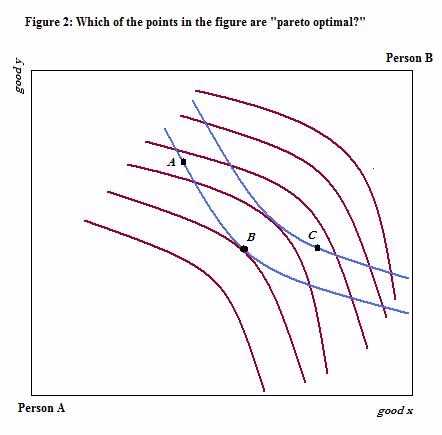
Choose one answer.
|
a. Point A |
||
|
b. Point B |
||
|
c. Point C |
||
|
d. All of the above |
||
|
e. Points A and C only |
Question 87
Which point represents the choice of the individual in Figure 9, given their budget constraint and map of preferences?

Choose one answer.
|
a. Point A |
||
|
b. Point B |
||
|
c. Point C |
||
|
d. None of the above |
||
|
e. It is impossible to determine from the information given. |
Question 88
Which point will the person described in Figure 8 choose if unemployment insurance is available?
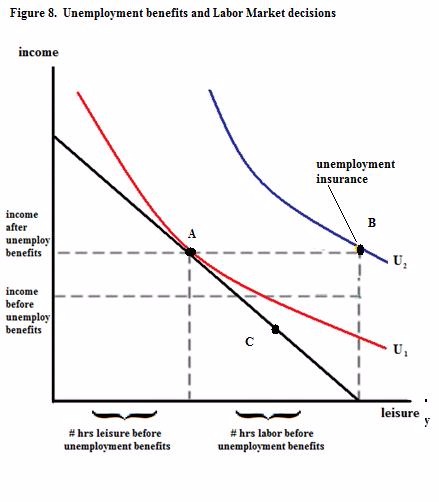
Choose one answer.
|
a. Point A |
||
|
b. Point B |
||
|
c. Point C |
||
|
d. Both Points A and C |
||
|
e. It is impossible to determine from the information given. |
Question 89
Which theory suggests that people will tend to move to those neighborhoods or cities which best fit their preferences for provision of public goods and payment of taxes?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Median Voter Theorem |
||
|
b. Pythagorean Theorem |
||
|
c. Tiebout Theorem |
||
|
d. Coase Theorem |
||
|
e. Samuelson Theorem |
Question 90
Which U.S. President instated the first Federal Income Tax?
Choose one answer.
|
a. George Washington |
||
|
b. Andrew Jackson |
||
|
c. Abraham Lincoln |
||
|
d. Grover Cleveland |
||
|
e. Theodore Roosevelt |
Question 91
Which U.S. President introduced the first progressive system of taxation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. George Washington |
||
|
b. Andrew Jackson |
||
|
c. Abraham Lincoln |
||
|
d. Grover Cleveland |
||
|
e. Theodore Roosevelt |
Question 92
Which U.S. president tried to apply Keynesian theory to his fiscal policy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Andrew Johnson |
||
|
b. Theodore Roosevelt |
||
|
c. Franklin D Roosevelt |
||
|
d. Ronald Regan |
||
|
e. All of the above |
Question 93
Who are the “losers” from the payment of a producer subsidy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. General tax payers |
||
|
b. Producers of the good subsidized |
||
|
c. Producers of the good not subsidized |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both A and C |
Question 94
Who are the “winners” from the payment of a producer subsidy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. General tax payers |
||
|
b. Producers of the good subsidized |
||
|
c. Consumers of the good subsidized |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 95
Why does political economy reason make the closure of military bases so difficult?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Because the Congress opposes it on grounds of military readiness |
||
|
b. Because the military is a sensitive topic due to strong patriotism in the communities with military bases |
||
|
c. Because military bases have long leases on the land where they have their facilities |
||
|
d. Because the military base creates many jobs in the areas where they are built |
||
|
e. Because there is not a law that supports the closure of such military bases |
Question 96
Why is rent seeking a difficult problem to resolve?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Individual consumers who are hurt by rent seeking are dispersed and difficult to organize, while those who benefit are concentrated and easier to organize. |
||
|
b. Rent price reflect competitive market outcomes and black markets for housing will emerge if politicians attempt to control prices. |
||
|
c. The zoning regulations in an area make it difficult to change business use into residential use, creating some rigidity in the market. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 97
Why might a politician choose to privatize the provision of a public good?
Choose one answer.
|
a. To improve efficiency |
||
|
b. To expand the size of government |
||
|
c. To improve government finance |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 98
Why might decentralization help to improve the quality of government?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Local officials are better remunerated on average than officials at the central levels. |
||
|
b. Citizens can select a locality which has the mix of public services and taxation they prefer. |
||
|
c. Politicians are closer to the people. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 99
Why were charter schools so controversial in New Orleans?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Schools have selected admission policies, which mean some students can be excluded. |
||
|
b. Charter schools have hidden agendas for religious indoctrination. |
||
|
c. The schools have a hidden set of tuition charges. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
||
|
e. Both B and C |
Question 100
How large is the consumer surplus in Figure 1?
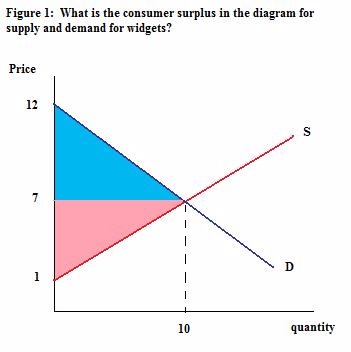
Choose one answer.
|
a. 50 |
||
|
b. 60 |
||
|
c. 25 |
||
|
d. 30 |
||
|
e. None of the above |