1
A baker purchases some machinery for his bakery in period 1 for $1000 but decides to sell it in period 2 for $600. If the prevailing interest rate is 10% per year, what is the baker's opportunity cost of using the durable asset (the machinery) in period 1?
Choose one answer.
|
a. $500. |
||
|
b. $400. |
||
|
c. $100. |
||
|
d. $300. |
Question 2
A clothing company finds it cheaper to make clothes for adults and children in the same factory than producing each in separate plants. What would you describe this company's cost efficiency as?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The company possesses economies of scale. |
||
|
b. The company is located at a cheap location. |
||
|
c. The company is not paying its employees enough. |
||
|
d. The company possesses economies of scope. |
Question 3
A consulting company has been using a certain software for its products. The company has also invested substantial time and money in training its employees to use the latest version of the software. A new firm has come up with its own software and wants to lure the company into buying this new software. What should the firm do in order to ensure profitability in this market?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The new firm should compensate the company by offering better features than the software currently being used by the consulting firm. |
||
|
b. The new firm should ensure that the cost of the new software is greater than the cost of the other software, signaling better quality of the new product. |
||
|
c. Since the firm is new, it should not waste time or money in extensive promotion for fear of not being able to recoup these expenses. |
||
|
d. The new firm should pay the consulting company to try its new product. |
Question 4
A few firms, selling the same product in a market, decide to divide the geographical locations amongst themselves, so that each firm is allocated a unique location to sell its product and is not allowed to enter the other firms' location to sell the product. What kind of behavior are the firms engaging in?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Price Fixing. |
||
|
b. Explicit Collusion. |
||
|
c. Tacit Collusion. |
||
|
d. Bid Rigging. |
Question 5
A gardener has two helpers who are paid on a daily basis. Between both the helpers, the gardener can only spare $100 a day. If both come to work, the money is divided equally. If only one shows up, he gets the entire amount. The pay-offs for the two helpers are given in the table below. Which of the strategies is a Nash equilibrium?
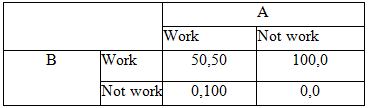
Choose one answer.
|
a. (Work, Work) |
||
|
b. (Work, Not Work) |
||
|
c. (Not Work, Work) |
||
|
d. (Not Work, Not Work) |
Question 6
A monopolist decides to produce a quantity at the level where its marginal revenue equals its marginal cost (MR=MC), charging a single price for every unit sold. Which of the following is true given the above information?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The amount of deadweight loss in this situation is almost negligible. |
||
|
b. The monopolist is producing an efficient amount of output. |
||
|
c. There is no consumer surplus in this situation. |
||
|
d. This is also referred to as linear pricing. |
Question 7
A person who has been using the wireless services of company A finds it costly and is aware of a new cellular phone company that offers lower cost services for the same quality of service that company A provides. However, because it has been with company A for a long time and is used to its features, he is unsure of giving it up. What kind of costs does this person have in mind?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Entry costs. |
||
|
b. Switching costs. |
||
|
c. Opportunity costs. |
||
|
d. Collusive costs. |
Question 8
According to the Coase theorem, if negative externalities exist, how can optimally social levels of production can be achieved?
Choose one answer.
|
a. If the perpetrator of the negative externalities is made legally liable or if the victim of the externality makes a payment to the perpetrator. |
||
|
b. Only if the perpetrator of the negative externalities is made legally liable to the victim of the externality. |
||
|
c. Only if the victim of the externality makes a payment to the perpetrator of the externality. |
||
|
d. It is impossible to achieve a socially optimal level of production in this case. |
Question 9
According to the Structure-Conduct-Performance paradigm, which of the following is the most efficient form of market structure?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An unregulated monopoly. |
||
|
b. Competition. |
||
|
c. Monopoly with governmental controls. |
||
|
d. The Structure-Conduct-Performance paradigm does not identify any kind of market structure as efficient. |
Question 10
An incumbent in an industry possesses extensive economies of scale. For an entrant to enter the industry, which of the following is a possibility? I. The entrant will potentially enter on a small scale with a relatively small effect on price but with high average costs, resulting in negative post-entry profits. II. The entrant will potentially enter on a cost-competitive basis, with significant market share and lowering prices, but making positive post-entry profits.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is correct. |
||
|
b. Only II is correct. |
||
|
c. Both I and II are correct. |
||
|
d. Neither I nor II are correct. |
Question 11
Apple Inc. has stipulated that all retailers selling their goods have a minimum price that is set by them for their products. Which of the following is not likely to occur under this "resale price maintenance?"
Choose one answer.
|
a. Every retailer will price at the uniform minimum level. |
||
|
b. Retailers can earn enough profit to promote a brand or offer better service. |
||
|
c. Imposing minimum resale prices creates an incentive to cheat. |
||
|
d. Price-conscious customers will not be able to benefit from choosing one retailer over the other. |
Question 12
Assume that a monopolist has the following linear market demand function: P= 160-4Q, where P=price and Q=quantity demanded. The monopolist's average and marginal cost curves are constant, and both always equal to $40. If the firm wants to charge a single price for all units sold, what would be the firm's economic profits?
Choose one answer.
|
a. $900 |
||
|
b. $1500 |
||
|
c. $600 |
||
|
d. $15 |
Question 13
Assume that a monopolist has the following linear market demand function: P= 160-4Q, where P=price and Q=quantity demanded. The monopolist's average and marginal cost curves are constant, and both always equal to $40. The monopolist charges $120 to people who belong to a certain group (group1) and $60 to people who belong to another group (group2). What is the monopolist's economic profit?
Choose one answer.
|
a. $900 |
||
|
b. $1100 |
||
|
c. $2100 |
||
|
d. $2700 |
Question 14
Cournot described a market as “the entire territory of which parts are so united by the relations of unrestricted commerce that prices there take the same level throughout, with ease and rapidity.” Which of the following violates an implicit assumption in the above definition?
Choose one answer.
|
a. There is only a single homogenous product. |
||
|
b. The price of the product does not affect the price of products in other markets and vice versA. |
||
|
c. The products are differentiated. |
||
|
d. The firms in the market produce perfect substitutes. |
Question 15
Delite is a firm that produces light bulbs in a perfectly competitive market. The company owner wants to retire and decides to decrease production gradually. If Delite decides to produce less, what effect would the excess demand created by Delite have on the price of light bulbs?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The price of light bulbs would be higher than before. |
||
|
b. The firms are price takers and hence there would be no effect on the price of light bulbs. |
||
|
c. The price of light bulbs would be lower than before. |
||
|
d. Nothing can be said about prices without more information. |
Question 16
Figure 1 shows a perfectly competitive firm's supply and demand curves. What do the areas denoted by A and B signify?
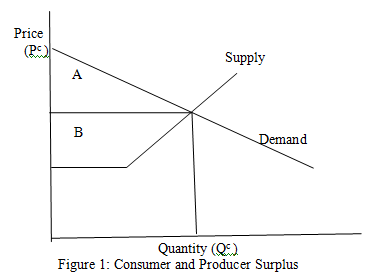
Choose one answer.
|
a. Aggregate consumer surplus |
||
|
b. Aggregate producer surplus |
||
|
c. Quasi-rents |
||
|
d. Sum of aggregate consumer and producer surplus |
Question 17
Firm A bought a piece of land and built a factory on it. The firm has to pay the mortgage on the land, and also has some overhead costs related to purchasing machinery, the purchase of raw materials, and labor. If the firm decided to close the production in the following year, which of the following costs would the firm be able to avoid?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The fixed costs, i.e. the cost of purchasing machinery. |
||
|
b. The sunk costs, i.e. the cost of buying the land and constructing the factory. |
||
|
c. The variable costs, i.e. the cost of purchasing materials and labor. |
||
|
d. The costs of purchasing labor only, the rest would still have to be incurred by the firm. |
Question 18
Firm A bought a piece of land and built a factory on it. After experiencing losses for a few years, it shut down the factory, and was also unable to sell it. Which of the following defines the cost borne by Firm A in purchasing the land and building the factory?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Avoidable cost. |
||
|
b. Sunk expenditure. |
||
|
c. Variable cost. |
||
|
d. Total expenditure. |
Question 19
Firm A is an incumbent and firm B is a new entrant. Which one of the following best describes the term "strategic accommodation?"
Choose one answer.
|
a. Firm A welcomes the entry of firm B with the intention of healthy competition. |
||
|
b. Firm A welcomes the entry of firm B knowing fully well that it has a loyal customer base. |
||
|
c. Firm A maximizes its positioning advantage in the market relative to the entrant through its strategic investment, but does not drive out the rival out of the market. |
||
|
d. None of the above. |
Question 20
Firm A is the sole provider of electricity in Standard city. Firm B is a potential entrant into the market. Which of the following factors should not matter to firm B in deciding to provide electricity to Standard city?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The average cost of production for firm A is lower than the average cost to firm B. |
||
|
b. The price charged by firm A to its customers is very high. |
||
|
c. Firm A has access to a superior factor of production. |
||
|
d. Entering the market requires substantial sunk investments that may or may not be recovered. |
Question 21
How do economists distinguish between short run and the long run?
Choose one answer.
|
a. In the short run, all costs have to be accounted for but in the long run, the costs disappear. |
||
|
b. The short run is the period in which some of the firm's factors are fixed where as in the long run, all factors are variable. |
||
|
c. The short run is the period in which the firm's costs are greater than the costs in the long run. |
||
|
d. The short run is the period in which the firm begins its operations and the long run is the period when it has mastered its operations. |
Question 22
How does the structural approach to market definition use indirect evidence in order to infer the elasticity of demand?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Through shipment flows. |
||
|
b. Using qualitative criteriA. |
||
|
c. Through price correlations. |
||
|
d. All of the above. |
Question 23
How would you distinguish between the public interest theory and the economic theory of regulation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Under the public interest theory of regulation, regulation arises as a response to public's demands where as under the economic theory, regulation is needed for the government to make profits. |
||
|
b. Under the public interest theory of regulation, regulation arises as a response to market failure where as the economic theory of regulation, claims that regulation is needed because of demand for, and supply of, the government’s legal monopoly on coercion. |
||
|
c. Under the public interest theory of regulation, lawyers are recruited to make laws where as under the economic theory of regulation, economists are recruited to make laws. |
||
|
d. The public interest theory of regulation and the economic theory of regulation, are different terms implying the same case for regulation. |
Question 24
In defining an antitrust market, which of the following determines market power?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The cross-price elasticity of demand of a hypothetical monopolist. |
||
|
b. The own-price elasticity of demand of a hypothetical monopolist. |
||
|
c. The own-price elasticity of supply of a hypothetical monopolist. |
||
|
d. The cross-price elasticity of supply of a hypothetical monopolist. |
Question 25
In Galaxy town, there are a few stores that sell the same brand of binoculars but only one store offers a warranty for its products. If getting a warranty is preferable to all consumers, how would the store that offers warranty be characterized as?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The store offering a warranty would be seen as one with a differentiated product. |
||
|
b. The store offering a warranty would be seen as a monopolist. |
||
|
c. The store offering a warranty would be seen as one with a defective product. |
||
|
d. The store offering a warranty would be seen a price maker. |
Question 26
In making a strategic move, which of the following can alter your rival’s expectations regarding your future (optimal) behavior? I. Changing your pay-offs. II. Removing some actions from your future choice set.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is true. |
||
|
b. Only II is true. |
||
|
c. Both I and II are true. |
||
|
d. Neither I nor II are true. |
Question 27
In reference to the vertical relationship between two firms in sequence along the production process, which of the following describes a "downstream" firm?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A firm involved in the beginning of the production process. |
||
|
b. A firm that experiences some negative externalities because of the production of another firm. |
||
|
c. A firm that uses the product of an upstream firm to advance to the next level of production. |
||
|
d. A firm that cannot be located next to another firm because they are involved in the same production process. |
Question 28
Read-on limited is the forerunner in manufacturing electronic comic books tablet and has a market share of 85%. It's main competitor, Cosmos Inc., had a similar product but can be used either for kids' literature or newspaper comic strips. As a result, Read-on limited has sufficient latitude in raising prices above its marginal cost. If Read-on raises its price from the existing level and consumers react by substituting to Cosmos, what would this reflect?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Because products are not homogenous, this reflects supply substitution. |
||
|
b. Because products are not homogenous, this reflects demand substitution. |
||
|
c. Because products are close substitutes, this reflects supply substitution. |
||
|
d. Because products are sufficiently differentiated, this reflects supply substitution. |
Question 29
Suppose a government agency is planning to build a new office complex in a small town for which it needs to hire both an architect and a construction company. There is only one reputed architect and only one reliable construction company in town. It would be very expensive for the local government to hire workers from out of town, if the local architect and the local construction company decide not to take up the government project. Both the architect and the construction company are not allowed to interact with each other regarding their decision to work for the new office complex and are allowed to give their final decision only once. The table below shows the pay-offs, or the profits (in thousands), that each company will accrue if they decide to work or not for the government. What is the dominant strategy in this game?
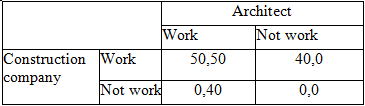
Choose one answer.
|
a. "Not work" for both the construction company and the architect. |
||
|
b. "Work" for the construction company, "not work" for the architect. |
||
|
c. "Work" for both the construction company and the architect. |
||
|
d. "Not work" for the construction company, "work" for the architect. |
Question 30
The 'maximin" strategy is a rational solution to which of the following games?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Nonconstant sum game. |
||
|
b. Sequential games. |
||
|
c. Dynamic games. |
||
|
d. Two-person zero sum game. |
Question 31
The employees of an office building in downtown Bethesda have access to only one parking garage which charges $2.75 for the first hour of parking and $1:25 for every additional hour parked. What is this pricing strategy referred to as?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Linear pricing. |
||
|
b. Price discrimination. |
||
|
c. Two-part tariff. |
||
|
d. Second-degree price discrimination. |
Question 32
The pay-offs for a certain game are given in the table below. Which of the following types of games best describes the game presented in the table?
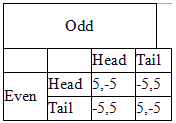
Choose one answer.
|
a. A prisoner's dilemma. |
||
|
b. A zero-sum game. |
||
|
c. A cooperative game. |
||
|
d. A sequential game. |
Question 33
Toothpaste Fresh is greatly valued by its customers and has been in the market for a long time. A new toothpaste Minty, has entered the market. However, the cross-price elasticity of demand between the two toothpastes is very high. In this situation, if the price of Minty is lower than the price of Fresh when it is introduced in the market, what can be one possible reaction from the firm that makes Fresh?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Fresh does not have to do anything because it has a loyal customer base. |
||
|
b. Fresh will experience losses and will ultimately exit the market. |
||
|
c. Minty can expect an aggressive price-competition from Fresh post-entry. |
||
|
d. Nothing can be said with the information provided. |
Question 34
Under resale price maintenance, if the retailers start to conspire to raise prices for a certain manufacturer's brand, which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The retailers must have sufficient market power to be able to do that. |
||
|
b. There is always an incentive to cheat. |
||
|
c. The retailers can ask the manufacturer to set a price that maximizes the retailers' joint profit. |
||
|
d. All of the above. |
Question 35
What are some of the vertical restraints experienced by downstream firms?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Exclusive territories. |
||
|
b. Exclusive dealing. |
||
|
c. Resale-Price maintenance. |
||
|
d. All of the above. |
Question 36
What are the factors that influence the size of dead weight loss for a monopolist?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The size of the deadweight loss depends on the Lerner index (which varies inversely with the elasticity of demand). |
||
|
b. The size of the deadweight loss depends on the quantity distortion (which varies directly with the elasticity of demand). |
||
|
c. The size of the deadweight loss depends on both the Lerner index (which varies directly with the elasticity of demand) and the quantity distortion with respect to the competitive quantity (which varies inversely with the elasticity of demand). |
||
|
d. The size of the deadweight loss depends on both the Lerner index (which varies inversely with the elasticity of demand) and the quantity distortion with respect to the competitive quantity (which varies directly with the elasticity of demand). |
Question 37
What the possible factors that are barriers to entry for an entrant firm?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Economies of scale. |
||
|
b. Product differentiation. |
||
|
c. Absolute cost advantages. |
||
|
d. All of the above. |
Question 38
Which of the answer choices best defines the following game, described as: "Sequential moves by players, having a partial idea of their rivals' actions"?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Static games of complete information. |
||
|
b. Dynamic games of complete information. |
||
|
c. Static games of incomplete information. |
||
|
d. Dynamic games of incomplete information. |
Question 39
Which of the following are possible scenarios for entry deterrence?
Choose one answer.
|
a. If the capacity investment of the incumbent in the first stage is a sunk expenditure, it becomes possible for the firm to the limit output if there is a potential entrant. |
||
|
b. An incumbent invests in excess capacity and holds it in reserve. If there is a possible entrant, the incumbent uses the capacity to meet demand and launch a price war. |
||
|
c. An incumbent overinvests in capacity and has a cost advantage because its marginal costs are less than the marginal costs of the entrant making it credible for it to produce to capacity—provided its marginal revenue is greater than its marginal costs. |
||
|
d. If the capacity investment of the incumbent in the first stage is a sunk expenditure, it becomes possible for the firm to the increase prices if there is a potential entrant. |
Question 40
Which of the following best describes an antitrust market?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An antitrust market is a group of products and a geographic area in which a single supplier has the ability to exert significant market power. |
||
|
b. A market where the emphasis is on identifying equilibrium price. |
||
|
c. A market where the firms do not trust each other. |
||
|
d. A market where the prices cannot be trusted. |
Question 41
Which of the following best describes the term "quasi-rents?"
Choose one answer.
|
a. Quasi-rents are the difference between total revenues and total costs in the long run. |
||
|
b. Quasi-rents are the difference between total revenues and avoidable costs in the long run. |
||
|
c. Quasi-rents are the difference between total revenues and avoidable costs in the short run. |
||
|
d. Quasi-rents are the difference between total revenues and sunk costs in the short run. |
Question 42
Which of the following best explains the terms "cooperative advertising" and "predatory advertising?"
Choose one answer.
|
a. Cooperative advertising means that there would be an increase in demand for rival firms' products along with increase in its own products while predatory advertising leads to an increase in demand for the advertising firm only. |
||
|
b. Both increase demand for rival firms’ products as well as those of the advertising firm's products. |
||
|
c. Both terms mean that there would be an increase in demand for the advertising firm only. |
||
|
d. Cooperative advertising means that there would be an increase in demand for the advertising firm only while predatory advertising leads to an increase in demand for both rival firms' products along with an increase in its own products. |
Question 43
Which of the following can be a possible result of advertising as an instrument to deter entry? I. If advertising tends to create goodwill, it will decrease a potential entrant's profits. II. If advertising tends to lock in an incumbent's customers, its pricing response to entry will not be very harsh.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is true. |
||
|
b. Only II is true. |
||
|
c. Both I and II are true. |
||
|
d. Neither I nor II are true. |
Question 44
Which of the following definitions best describes "limit output?"
Choose one answer.
|
a. It refers to the minimum level of output for a firm beyond which it will yield negative profits. |
||
|
b. It refers to the minimum level of output for a firm that deters entry by another firm. |
||
|
c. It refers to the level of the limited level of output that a firm wishes to produce in order to keep its prices high. |
||
|
d. It refers to the minimum level of output that lets more than one firm profitable in the industry. |
Question 45
Which of the following describe problems associated with assessing efficiency on the basis of changes in total surplus?
Choose one answer.
|
a. In the presence of externalities, the demand and supply curves fail to reflect social costs when representing consumer and producer surplus. |
||
|
b. Consumer surplus is an exact measure of consumer welfare. |
||
|
c. When changes in total surplus are used to rank outcomes, distribution of the gains of trade is taken into account, which is irrelevant. |
||
|
d. Maximization of total surplus in one market is efficient only if surplus in other markets is not maximized. |
Question 46
Which of the following describe transaction costs as mentioned by Ronald Coase in his explanation of the transaction cost approach to the theory of the firm?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Search and information costs. |
||
|
b. Bargaining and decision costs. |
||
|
c. Policing and enforcement costs. |
||
|
d. All the answer choices are correct. |
Question 47
Which of the following describes a pareto optimal situation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It is not possible to make someone better off without making another person worse off. |
||
|
b. An outcome in which there are no unexploited gains from trade. |
||
|
c. An outcome in which total surplus is maximized. |
||
|
d. All of the choices define a pareto optimal situation. |
Question 48
Which of the following describes the relationship between the Lerner index and the elasticity of demand?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The Lerner Index and the elasticity of demand move together: higher the elasticity of demand, greater the Lerner index. |
||
|
b. The Lerner Index is equal to the elasticity of demand. |
||
|
c. The Lerner Index and the elasticity of demand are inversely related: higher the elasticity of demand, smaller the Lerner index. |
||
|
d. The Lerner Index and the elasticity of demand depend upon other factors as well which need to be taken into account, in order to determine their relationship. |
Question 49
Which of the following does NOT describe indivisibilities that create economies of scale?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Marketing and advertising expenses. |
||
|
b. Expenditures on research and development. |
||
|
c. Maintaining increasing amounts of inventory and back up with increasing levels of output. |
||
|
d. Specialized resources and division of labor. |
Question 50
Which of the following does NOT explain why a firm's elasticity of demand tends to be larger in the long run?
Choose one answer.
|
a. New entrants increase the elasticity of a firm's perceived demand curve, increasing reducing its market power. |
||
|
b. The long-run response of consumers to a price increase is often greater than their short-run response. |
||
|
c. It is illegal for any firm to maintain market power for too long, and in the long run the firm deliberately reduces it market power. |
||
|
d. Technological change can generate new products and services, and the introduction of these products reduces the market power of producers of established products. |
Question 51
Which of the following explains the relationship between the average cost function and the marginal cost function of a firm? I. If the marginal cost is below the average cost, the average cost function is falling. II. If the marginal cost is above the average cost, the average cost function is falling. III. At the level of output for which average cost is minimized, marginal cost is equal to average cost.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is true. |
||
|
b. Only II is true. |
||
|
c. II and III are true. |
||
|
d. I and III are true. |
Question 52
Which of the following is a suitable explanation of a "mixed strategy?”
Choose one answer.
|
a. When a player in a game chooses among two or more strategies at random according to specific probabilities, he is using a "mixed strategy." |
||
|
b. When a player in a game chooses the same strategy irrespective of the strategy of the other player, he is using a "mixed strategy." |
||
|
c. When a player chooses the strategy opposite to that of the other player, he is using a "mixed strategy." |
||
|
d. When a player mixes up his strategy depending upon the choice his opponent makes, he is using a "mixed strategy." |
Question 53
Which of the following is not a possible strategy adopted by incumbents in a market to increase the barrier to entry?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An incumbent firm may strategically raise its rivals costs putting them at a disadvantage. |
||
|
b. An incumbent firm may engage in aggressive post-entry behavior by reducing its marginal costs after a new firm has entered the market. |
||
|
c. Incumbent firms can strategically reduce the revenue of a potential entrant by reducing the demand for their product. |
||
|
d. Incumbent firms can strategically buy all factors of production and not let the new entrants access to any of it. |
Question 54
Which of the following is not a true characteristic of the model described?
Choose one answer.
|
a. In the Cournot duopoly model, the strategic choice of the firms is the output level. |
||
|
b. In the Bertrand duopoly model, the strategic choice of the firms is the price level. |
||
|
c. In the Stackelberg duopoly model, both firms act at the same time. |
||
|
d. The best response functions of the Cournot model are negatively sloped. |
Question 55
Which of the following is not a valid statement with respect to market power?
Choose one answer.
|
a. In economics, if price is sufficiently above marginal cost, a firm is said to have market power. |
||
|
b. A firm with an upward sloping demand curve is said to have market power. |
||
|
c. A firm with a downward sloping demand curve is said to have market power. |
||
|
d. The market power of a firm is based on its elasticity of demand. |
Question 56
Which of the following is not required for an action to be strategic?
Choose one answer.
|
a. You should be able to move before the other players make their final move. |
||
|
b. The rivals should be aware of your action or move before they make a move. |
||
|
c. You must not change your incentives or choices in the future. |
||
|
d. Your strategic behavior should result in the rivals' behavior increasing your payoff. |
Question 57
Which of the following is not true about cartels?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Cartels tend to monopolize the market by raising prices and restricting quantities. |
||
|
b. Firms tend to cartelize when there are no government restrictions. |
||
|
c. In order to be an effective cartel, the firms in a cartel must prevent entry of new firms. |
||
|
d. A firm in a cartel, would never have any incentive to cheat other members of the cartel. |
Question 58
Which of the following is not true about predatory pricing?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A firm involved in predatory pricing prices its products below marginal cost in order to hurt the rival firms and pushing them to exit the industry. |
||
|
b. Predatory pricing may lead the predator firm in becoming a monopolist after the rival has exited the industry. |
||
|
c. Predatory pricing leads to a pricing war between the predator firm and the rival firm. |
||
|
d. Predatory pricing usually does not lead to a pricing war between the predator firm and the rival firm because the rival firm cannot afford to compete and thus exits the market. |
Question 59
Which of the following is not true about regulating a natural monopoly?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A strong natural monopoly exists if economies of scale are exhausted where price equals average cost. |
||
|
b. A single firm may be cost efficient by minimizing industry average costs but this would be at the cost of it having monopoly power. |
||
|
c. Regulation of a natural monopolist may not be the most efficient governance instrument. |
||
|
d. Natural monopoly is one of the main sources that justify price and entry regulation. |
Question 60
Which of the following is NOT true about the extensive form game?
Choose one answer.
|
a. In an extensive form game, one can identify when each player can move or make a decision. |
||
|
b. In an extensive form game, each player has information about the previous actions taken by his/her opponents. |
||
|
c. In an extensive form game, it is difficult to identify all possible outcomes of the game. |
||
|
d. In an extensive form game, a player can identify what choices are available to him/her when it is his/her turn to move. |
Question 61
Which of the following is NOT true of a monopolist?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A monopolist's profits depend upon the behavior of the consumers, its cost function, and its price or output. |
||
|
b. Monopoly pricing is inefficient because the monopolist produces too little output. |
||
|
c. The cross price elasticities of demand between the product of the monopolist and other products are large. |
||
|
d. Under monopoly power, there is a transfer of surplus from consumers to the firm as profits. |
Question 62
Which of the following is not true of the two player Stackelberg game with linear demand and constant marginal costs?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The firm that is the leader has greater profits than the follower firm. |
||
|
b. The two firms in the game do not move sequentially. |
||
|
c. The aggregate output in the Stackelberg game is more than the aggregate output in the Cournot game. |
||
|
d. The aggregate price in the Stackelberg game is more than the aggregate price in the Cournot game. |
Question 63
Which of the following is NOT true with regards to a firm's market power?
Choose one answer.
|
a. If a firm has market power, the elasticity of demand for the firm’s demand curve will always be more elastic than the elasticity of market demand. |
||
|
b. A firm's market power reduces if there are large numbers of firms in the industry. |
||
|
c. The more a firm differentiates its product from its competitors, the less market power it has. |
||
|
d. Firms can interact collusively to set prices and increase their market power. |
Question 64
Which of the following is true about regulatory risk? I. It refers to the potential for the regulator to holdup the firm before it has made its sunk investments. II. An important objective in designing regulatory institutions and enabling legislation is to minimize regulatory risk.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is true. |
||
|
b. Only II is true. |
||
|
c. Both I and II are true. |
||
|
d. Neither I nor II are true. |
Question 65
Which of the following is true about tacit collusions?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Since antitrust policies prevent industries from legally colluding, most industries engage in tacit collusions by covertly keeping their prices above non-cooperative levels. |
||
|
b. Differences in interests amongst firms, or large number of firms in an industry, may be factors that inhibit industries from coordinating high prices. |
||
|
c. Price leadership is a form of tacit collusion. |
||
|
d. All of the answers are correct. |
Question 66
Which of the following kinds of mergers describe the following statement? "Merger of firms involved in different parts of the production process of a good."
Choose one answer.
|
a. Vertical Merger. |
||
|
b. Horizontal Merger. |
||
|
c. Conglomerate Merger. |
||
|
d. None of the above. |
Question 67
Which of the following may be possible explanations for a government to grant franchises and create a potential barrier to entry? I. The government may grant exclusive production rights to a firm so that it can share the monopoly profits with the firm. II. The government may use legal restrictions on entry so as to create and redistribute monopoly profits. III. Governments grant patents and copyrights, thereby creating barriers to entry in order to encourage creation of new ideas and promote innovation.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is correct. |
||
|
b. Only II is correct. |
||
|
c. Only III is correct. |
||
|
d. All the choices are correct. |
Question 68
Which of the following provides a valid rationale for a colluding firm to cooperate and not cheat?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The firm intending to cheat would be considered a weak player. |
||
|
b. The present discounted value of income earned in the long run by cooperating is greater than the present discounted value of income earned in the short run by cheating. |
||
|
c. It would be considered unethical to cheat. |
||
|
d. The cooperating firms are benevolent and fair. |
Question 69
Which of the following scenarios best explains the situation of firms where constant returns to scale exist and where market price is above long run average cost?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The incumbent firms will have no incentive to expand or contract. |
||
|
b. The incumbent firms will experience positive economic profits and expand, inviting entry of new firms until the profits are driven away and prices return to long run average costs. |
||
|
c. The incumbent firms will experience negative economic profits and contract, making firms exit the industry and increasing prices until they equal long run average costs. |
||
|
d. The equilibrium market structure depends upon the relationship between the minimum efficient scale and the size of the market. |
Question 70
Which of the following statement is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The results of R&D efforts which determine the technology and characteristics of products for firms, are strategic decisions. |
||
|
b. The results of R&D efforts which determine the technology and characteristics of products for firms, are tactical decisions. |
||
|
c. Short run decisions of a firm, regarding pricing and output, are strategic decisions for the firms. |
||
|
d. Strategic decisions cannot have any impact on the marginal cost or marginal revenue of the rival firms. |
Question 71
Which of the following statements best describes economies of scale?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Long-run average cost increases as the rate of output increases. |
||
|
b. Long-run average cost stays constant as the rate of output increases. |
||
|
c. Long run average cost is at its minimum as the rate of output increases. |
||
|
d. Long-run average cost declines as the rate of output increases. |
Question 72
Which of the following statements is generally true when it comes to research and development activities undertaken by firms, resulting in a new invention?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The social value of an invention is usually smaller than the gain to a monopolist or a competitor. |
||
|
b. Inventions are rare because it is not easy to get patents. |
||
|
c. Any invention that is patented decreases the social value at large. |
||
|
d. The social value of an invention is usually larger than the gain to a monopolist or a competitor. |
Question 73
Which of the following statements is NOT a characteristic of firms in an oligopolistic market?
Choose one answer.
|
a. In an oligopoly, there is mutual interdependence between firms. |
||
|
b. In an oligopoly, there is repeated interaction between firms. |
||
|
c. In an oligopoly, only a few firms dominate the market. |
||
|
d. In an oligopoly, firms are price takers. |
Question 74
Which of the following statements is NOT true of the relationship between economies of scale and seller concentration?
Choose one answer.
|
a. When there are constant returns to scale, a firm has an advantage in producing more output. |
||
|
b. When there are diseconomies of scale a firm has a cost disadvantage in producing more than one unit of output. |
||
|
c. When there are economies of scale there is an obvious advantage to a firm to being large. |
||
|
d. If a firm has a U-shaped cost curve, the equilibrium market structure depends upon the relationship between the minimum efficient scale and the size of the market. |
Question 75
Which of the following statements is true about collusion amongst oligopolists? I. A collusive outcome is not a Nash equilibrium. II. The government has no law that prevents firms from colluding.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is true. |
||
|
b. Only II is true. |
||
|
c. Both I and II are true. |
||
|
d. Neither I nor II are true. |
Question 76
Which of the following, if true, would lead to a different outcome than what is expected in a prisoner's dilemma game?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The prisoner's dilemma is extended from its two-person representation to many person interactions. |
||
|
b. The players in a prisoner's dilemma game are allowed to communicate with each other. |
||
|
c. The players in a prisoner's dilemma game are allowed to act only once. |
||
|
d. The players in a prisoner's dilemma act in their best interests. |
Question 77
Which of the two explanations is correct for the following statement? According to Ronald Coase, the existence of an organization is to reproduce the conditions of a competitive market for its factors of production at a lower cost. However, despite the existence of organizations, there will still be market transactions because: I. costs of organizing additional transactions rise with scale and may be the same as that in the market II. the firms may not be able to reproduce the effects of market conditions.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is correct. |
||
|
b. Only II is correct. |
||
|
c. Both I and II are correct. |
||
|
d. Neither I nor II is correct. |
Question 78
Which term best describes the following situation? "A monopolist has less to gain than a competitive firm from a new patented innovation that competes with its preexisting monopoly rents."
Choose one answer.
|
a. Efficiency effect. |
||
|
b. Replacement effect. |
||
|
c. Complacent effect. |
||
|
d. Predatory effect. |
Question 79
Suppose that the cost function (the minimum cost of producing q units of output) in a firm is given by C(q) and the total revenue, determined by the output of the firm is given by R(q). What would be the firm's profit maximizing rule if it wants to stay in business?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The firm will produce at that level of output where marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue. |
||
|
b. The firm will produce at that level of output where total cost is equal to total revenue. |
||
|
c. The firm will produce at that level of output where the difference between marginal revenue and marginal cost is the highest. |
||
|
d. The firm will produce at that level of output where the difference between total revenue and total cost is the highest. |
Question 80
Suppose the cost function of a firm showing the minimum cost of producing q units of output is given by C(q). Which of the following intuitively explains the cost function? I. The cost function summarizes the economically relevant production possibilities of the firm. II. The cost function incorporates both technological efficiency (using no more inputs than necessary to produce q) and opportunity cost of inputs.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Only I is true. |
||
|
b. Only II is true. |
||
|
c. Both I and II are true. |
||
|
d. Neither I nor II are true. |
Question 81
What are the components that make up an economic market?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A set of products. |
||
|
b. A set of buyers and sellers. |
||
|
c. A geographic region in which buyers and sellers interact to set prices. |
||
|
d. All of the above. |
Question 82
What are the elements of a market failure test that justify regulation in the interest of the public? I. A determination of the feasibility of intervention to correct market inefficiencies. II. The benefits of regulation outweigh the costs associated with regulation.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Both I and II are correct. |
||
|
b. Only I is correct. |
||
|
c. Only II is correct. |
||
|
d. Neither I nor II is correct. |
Question 83
Which of the following best describes a strategic move?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Strategic moves are those that influence the choice of your opponent in your favor so that your rivals' expectations of how you will behave in the future is affected. |
||
|
b. Strategic moves are those that that involve a penalty on the rivals' actions. |
||
|
c. Strategic moves are those that confer a reward on the rivals' actions. |
||
|
d. Strategic moves are those that influence the choice of your opponent in both your and the opponent's favor. |
Question 84
Which of the following does not describe a game-theoretic situation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Reader, a monopolist book seller in a certain area, decides to raise the prices of the maps that it sells. |
||
|
b. Comcast, a cable TV provider, decides to cut down its rate on basic television channels when a new cable provider entered the market. |
||
|
c. Coke introduces a new beverage called Coke-Zero at the same time Pepsi launches it new product, Pepsi-Max. |
||
|
d. Yahoo and Google decide to collaborate and charge the same price to its advertisors. |
Question 85
Which of the following is true if a firm enjoys market power?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A firm with market power sets its price equal to its marginal cost. |
||
|
b. A firm with market power sets its price below marginal cost. |
||
|
c. A firm with market power has a demand function that is less elastic than its competitors. |
||
|
d. A firm with market power has a demand function that is more elastic than its competitors. |
Question 86
Which of the following statements is NOT true about the field of industrial organization?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Industrial organization neglects to study the behavior of firms and their effect on market performance. |
||
|
b. Amongst other things, industrial organization seeks to study how market structures affect price and output determination. |
||
|
c. A major area of research in industrial organization is the theory of oligopoly. |
||
|
d. Amongst other things, industrial organization is based on empirical work, based on models of firm behavior. |