1
10. If the tilt of the Earth was 90 degrees rather than 23.5 degrees (that is, no tilt), then how many seasons would the Earth have? (Hint: it may be
helpful to draw a picture.)
Choose one answer.
| a. One | ||
| b. Two | ||
| c. Three | ||
| d. Four | ||
| e. Five |
Question
2
Due to the rain shadow effect, which of the following will occur?
Choose one answer.
| a. More solar radiation will reach the windward side of a mountain range. | ||
| b. More solar radiation will reach the leeward side of a mountain range. | ||
| c. There will be drier conditions on the windward side of a mountain range. | ||
| d. There will be drier conditions on the leeward side of a mountain range. | ||
| e. There will be wetter conditions on the leeward side of a mountain range. |
Question
3
Fill in the blank. As countries move from an agricultural to a(n) ____ economy, there tends to be a shift in population from rural to urban settings.
Choose one answer.
| a. industrial | ||
| b. capitalistic | ||
| c. socialistic | ||
| d. communistic | ||
| e. socialistic and communistic |
Question
4
Fill in the blank. Deforestation results in less ____ being removed from the atmosphere. When this occurs, heat radiation is less able to radiate out of
the atmosphere and into space.
Choose one answer.
| a. oxygen | ||
| b. carbon dioxide | ||
| c. nitrogen | ||
| d. water vapor | ||
| e. methane |
Question
5
Fill in the blank. Fertility rate is the average number of children a woman in a particular country has in her lifetime. If a fertility rate for a given
country is less than ____, then the replacement level (the population of that country) is in decline (unless there is significant immigration).
Choose one answer.
| a. 2 | ||
| b. 1.5 | ||
| c. 2.1 | ||
| d. 1.7 | ||
| e. 3.5 |
Question
6
Fill in the blank. The main methods countries use to gain national wealth are based on sustainable ____ models and value-added principles.
Choose one answer.
| a. agricultural | ||
| b. national income | ||
| c. manufacturing | ||
| d. industrial | ||
| e. capitalistic |
Question
7
Fill in the blank. When one begins to understand the ____, it is easier to understand why people move from periphery to core.
Choose one answer.
| a. monetary rates | ||
| b. manufacturing needs | ||
| c. geopolitics | ||
| d. global economy | ||
| e. infrastructure |
Question
8
Geographers use Population Pyramids when describing the general trends in population growth for a particular region. Population can either be rapidly
expanding, expanding, stationary, or contracting. Which of the following population pyramids represents a rapidly expanding population growth?
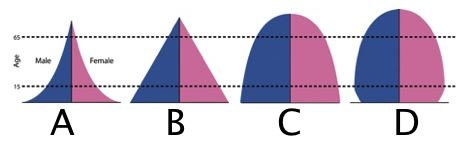
Choose one answer.
| a. A | ||
| b. B | ||
| c. C | ||
| d. D | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
9
If it is 4 pm in San Francisco, CA, what time is it in London, England?
Choose one answer.
| a. 7 pm | ||
| b. 7 am | ||
| c. Midnight | ||
| d. Noon | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
10
If the tilt of the Earth was 0 degrees rather than 23.5 degrees (that is, no tilt), then how many seasons would the Earth have? (Hint: it may be helpful to
draw a picture.)
Choose one answer.
| a. One | ||
| b. Two | ||
| c. Three | ||
| d. Four | ||
| e. Five |
Question
11
On the date of the June Solstice (known as the "summer solstice" in the northern hemisphere), which of the following locations has the greatest amount of
daylight hours?
Choose one answer.
| a. Murmansk, Russia (69° north latitude) | ||
| b. Montevideo, Uruguay (35° south latitude) | ||
| c. Kontiala, Mali (12.5° north latitude) | ||
| d. Omaha, Nebraska (41° north latitude) | ||
| e. Both C and D |
Question
12
There are 24 time zones in the world. How many degrees of longitude is each time zone?
Choose one answer.
| a. 20 degrees | ||
| b. 40 degrees | ||
| c. 30 degrees | ||
| d. 15 degrees | ||
| e. 60 degrees |
Question
13
True or False. Along convergent zones, volcanoes and earthquakes may occur.
Choose one answer.
| a. True | ||
| b. False |
Question
14
What are the two main areas of focus in the discipline of geography?
Choose one answer.
| a. Physical geography and human geography | ||
| b. Physical science and chemistry | ||
| c. Math and economics | ||
| d. Political geography and religion | ||
| e. Human geography and geology |
Question
15
What does the term "ethnicity" mean?
Choose one answer.
| a. Traits people are born with, including genetic backgrounds or physical features | ||
| b. Traits people learn after they are born, including language or religion | ||
| c. Physical characteristics that indicate a person's race | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
16
What locational information does latitude and longitude provide?
Choose one answer.
| a. Longitude = north and south; Latitude = east and west. | ||
| b. Longitude = north and east; Latitude = south and west. | ||
| c. Longitude = east and west; Latitude = north and south. | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
17
What type of religion is Christianity?
Choose one answer.
| a. Universal (or universalizing) | ||
| b. Ethnic (or cultural) | ||
| c. Tribal (or traditional) | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
18
Which of the following accurately describes demographic transition?
Choose one answer.
| a. The transition from high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system | ||
| b. The transition from low birth and death rates to high birth and death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system | ||
| c. The transition from high birth rates and low death rates to low birth rates and high death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system | ||
| d. The transition from low birth rates and high death rates to high birth rates and low death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
19
Which of the following climate types predominates the Mediterranean Sea?
Choose one answer.
| a. Type A: Tropical or equatorial climates | ||
| b. Type B: Dry or arid climates | ||
| c. Type C: Moderate or temperate climates | ||
| d. Type D: Cold or continental climates | ||
| e. Type E: Polar or extreme climates |
Question
20
What is the primary tool of the geographer?
Choose one answer.
| a. The compass | ||
| b. The map | ||
| c. The sundial | ||
| d. The telescope | ||
| e. The computer |
Question
21
Due in large part to its physical geography, which of the following European regions possess excellent farmlands?
Choose one answer.
| a. Northern Lowlands | ||
| b. Western Highlands | ||
| c. The Central Uplands | ||
| d. Alpine region | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
22
Fill in the blank. European colonialism was fueled by the economic concept of ____ that included the drive of governments to control trade and promote the
acquisition of wealth by the quick gain of gold or silver from their colonies.
Choose one answer.
| a. revolution | ||
| b. mercantilism | ||
| c. devolution | ||
| d. capitalism | ||
| e. socialism |
Question
23
Is ethnicity a positive, negative, or neutral cultural force?
Choose one answer.
| a. Ethnic unity can be a positive force, bringing people together. | ||
| b. Ethnic division can be a negative, divisive force, pulling people apart. | ||
| c. Ethnicity is always neutral; it is neither centripetal nor centrifugal. | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
24
IV. the concept of mass production
Choose one answer.
| a. the shift of coal for energy | ||
| b. I. | ||
| c. II. | ||
| d. III. | ||
| e. IV | ||
| f. All of the above |
Question
25
The region of Western Europe includes which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. Northern Europe | ||
| b. Southern Europe | ||
| c. Central Europe | ||
| d. The British Isles | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
26
What did the Roman Empire introduce to Europe?
Choose one answer.
| a. A common infrastructure | ||
| b. Specialization of goods | ||
| c. A currency system | ||
| d. Tools for exploration | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
27
What does the term "nation-state" refer to?
Choose one answer.
| a. A homogeneous group of people with a common heritage | ||
| b. A homogeneous group of people with a common language | ||
| c. A homogeneous group of people with a common religion | ||
| d. A homogenous group of people with a common political ambition | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
28
What key element has the northern European countries taken advantage of to expand their economies?
Choose one answer.
| a. Their social welfare system | ||
| b. Their diverse population | ||
| c. Their natural resources | ||
| d. Their advantageous geographic locations | ||
| e. Their vast land areas |
Question
29
What two forces are Europeans caught between with regards to forging a unified Europe?
Choose one answer.
| a. Holding on to cultural heritage and moving forward economically in a global economy | ||
| b. Struggling with internal conflicts based upon language and maintaining religious freedom | ||
| c. Facing language barriers with other countries of the world and maintaining religious differences | ||
| d. Both B and C | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
30
When was the Marshall Plan implemented in Europe, and what was its purpose?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Marshall Plan was implemented from 1918 to 1922 (after World War I) and was designed to help rebuild war-torn Europe with American aid and business connections. | ||
| b. The Marshall Plan was implemented from 1948 to 1952 (after World War II) and was designed to help rebuild war-torn Europe with American aid and business connections. | ||
| c. The Marshall Plan was implemented from 1914 to 1917 (after the Balkan Wars) and was designed to enhance the existing and flourishing business connections between Europe and the United States. | ||
| d. The Marshall Plan was implemented from 2002 to 2006 (after the Third Balkan War) and was designed to enhance the existing and flourishing business connections between Europe and the United States. | ||
| e. Both C and D |
Question
31
Which of the following accurately presents the regional relationship between the main religions and the dominant language groups in Europe?
Choose one answer.
| a. In the east, the Eastern Orthodox Church is dominant. Here, the Slavic language group prevails. | ||
| b. In the north, Protestant Christianity is dominant. Here, the Germanic language group prevails. | ||
| c. In southern, Europe Roman Catholicism is dominant. Here, the Romance languages are more commonly spoken. | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
32
Which of the following currents is perhaps the most important contributing factor to Western Europe's climate and is responsible, in part, for the
temperate climate that north-west Europe enjoys?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Canary Current | ||
| b. The Equatorial Counter Current | ||
| c. The North Equatorial Current | ||
| d. The Gulf Stream | ||
| e. The Labrador Current |
Question
33
Which of the following is a by-product of industrialization and has caused extensive damage to forests as well as fish populations in Northern Europe?
Choose one answer.
| a. Cell phone usage | ||
| b. Cable television | ||
| c. Global wealth | ||
| d. Overpopulation | ||
| e. Acid rain |
Question
34
Which of the following is NOT a dominant climate type of Europe?
Choose one answer.
| a. Type A | ||
| b. Type B | ||
| c. Type C | ||
| d. Type D | ||
| e. Type E |
Question
35
Which of the following is NOT a former republic of the Soviet Union?
Choose one answer.
| a. Russia | ||
| b. Ukraine | ||
| c. Tibet | ||
| d. Moldova | ||
| e. Armenia |
Question
36
Why are the sizes of families declining in Europe today?
Choose one answer.
| a. There is a higher cost of living. | ||
| b. Young people are putting off marriage and family until they are older. | ||
| c. More women are choosing professional careers and are having fewer children. | ||
| d. More people are earning an education and putting off having children. | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
37
Which of the following characteristics accurately portrays the cultural dynamics that make each region of Europe unique?
Choose one answer.
| a. Language | ||
| b. Religion | ||
| c. Heritage | ||
| d. Ethnicity | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
38
A During the Soviet Era, the Chechen Republic was administratively part of the Russian Soviet Socialist Republic with no right to future secession.
Choose one answer.
| a. During the Soviet Era, the Chechen Republic was administratively part of the UK with no right to future secession. | ||
| b. During the Soviet Era, the Chechen Republic was administratively part of the United States, and the Soviet Union wanted the Republic. | ||
| c. During the Soviet Era, the Chechen Republic was administratively part of France with no right to future secession. | ||
| d. None of the above |
Question
39
After World War I, a civil war erupted in Russia. Nicholas II (the last Czar) was forced out of office and executed. During this time, which of the
following groups, led by Vladimir Lenin, was the most powerful group battling for control of Russia?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Mensheviks | ||
| b. The Bolsheviks | ||
| c. The Leonids | ||
| d. The Marxists | ||
| e. The Proletariats |
Question
40
Fill in the blank. Russia needs to modernize its ____ if it is going to compete economically against the European Union, North America, and East Asia.
Choose one answer.
| a. housing infrastructure | ||
| b. entertainment industry | ||
| c. transportation corridor | ||
| d. schools | ||
| e. agricultural system |
Question
41
Fill in the blank. The ____ flows through the core region of Russia, and provides transportation, fresh water, and fishing to the inhabitants of the
region.
Choose one answer.
| a. Volga River | ||
| b. Don River | ||
| c. Baikal River | ||
| d. Ural River | ||
| e. Ganges River |
Question
42
Russia's ____ is a region of planned cities and industrial plants.
Choose one answer.
| a. Lake Baikal region | ||
| b. Gold region | ||
| c. Marxist region | ||
| d. Eastern Frontier | ||
| e. Western Frontier |
Question
43
What climate type dominates most of Russia?
Choose one answer.
| a. Type A | ||
| b. Type B | ||
| c. Type C | ||
| d. Type D | ||
| e. Type E |
Question
44
What is the main difference between a socialist economy and a capitalist economy?
Choose one answer.
| a. In a socialist economy, goods and services are produced directly for their use. In a capitalist system, goods and services are produced to generate profit. | ||
| b. In a socialist economy, goods and services are produced to generate profit. In a capitalist system, goods and services are produced directly for their use. | ||
| c. Production in a socialist economy is planned and does not suffer from the business cycle inherent to capitalism. | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
45
Which of the following is a major environmental problem facing the Russian Republic today?
Choose one answer.
| a. Ozone depletion | ||
| b. Over grazing | ||
| c. Noise pollution | ||
| d. Oil spills | ||
| e. Water pollution |
Question
46
Who was the last leader of the Soviet Union?
Choose one answer.
| a. Stalin | ||
| b. Brezhnev | ||
| c. Gorbachev | ||
| d. Yeltsin | ||
| e. Putin |
Question
47
Why did Russia invade Georgia in 2008?
Choose one answer.
| a. In order to gain greater coal resources | ||
| b. In order to fight against the secession of Georgia from Russia | ||
| c. In order to support South Ossetia's move toward independence from Georgia | ||
| d. Both A and C | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
48
Why were the Soviets sending ethnic Russians to live in non-Russian parts of the Soviet Union?
Choose one answer.
| a. Russians were sent around the empire to work in factories. | ||
| b. Russians were sent around the empire to work in power plants. | ||
| c. Russians were sent around the empire to work in a variety of industries. | ||
| d. Russians were sent around the empire to help administer the government. | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
49
Between 2000 and 2006, which of the following groups accounted for approximately half of the population growth of the United States (growing about four
times faster than the country as a whole)?
Choose one answer.
| a. African-Americans | ||
| b. Hispanics | ||
| c. Asians | ||
| d. Caucasians | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
50
Canada and the United States have the world's largest trading relationship with large amounts of goods (and people) flowing across the border each year.
Since the 1987 Canadian-American Free Trade Agreement, what has aided this trade relationship?
Choose one answer.
| a. There have been no tariffs on most goods passed between the two countries. | ||
| b. New transportation corridors have been opened between the two countries. | ||
| c. All border stoppings have been removed. | ||
| d. Americans are able to buy cheaper prescription drugs from Canada through their insurance. | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
51
Of the following economic sectors, which has shown the most dramatic structural change in the United States?
Choose one answer.
| a. Service sector | ||
| b. Energy sector | ||
| c. Manufacturing | ||
| d. Hi-tech sector | ||
| e. Agriculture |
Question
52
What are the two dominant climate patterns in North America?
Choose one answer.
| a. 1) Temperatures get warmer as you travel from north to south and get closer to the equator; 2) there is a decrease in precipitation as you move from east to west across the continent until you reach the Pacific Coast, where rainfall is abundant again. | ||
| b. 1) Temperatures get cooler as you travel from north to south and get closer to the equator; 2) there is an increase in precipitation as you move from east to west across the continent until you reach the Pacific Coast, where rainfall is sparse. | ||
| c. 1) Temperatures get warmer as you travel from south to north and get closer to the pole; 2) there is a decrease in precipitation as you move from west to east across the continent until you reach the Pacific Coast, where rainfall is sparse. | ||
| d. 1) Temperatures get cooler as you travel from south to north and get closer to the equator; 2) there is a decrease in precipitation as you move from east to west across the continent until you reach the Pacific Coast, where rainfall is abundant again. | ||
| e. 1) Tropical storms dominate the Great Plains; 2) drought dominates the North East. |
Question
53
What is the current pattern of religious affiliation across the United States?
Choose one answer.
| a. Jewish people are concentrated in the Midwest; Buddhists are concentrated in the South; Muslims are concentrated in the Northeast; Christians are concentrated in the West. | ||
| b. One can find observers of nearly every major religion (and many minor ones) in virtually every area of the country. | ||
| c. Christians are concentrated in the Midwest; Buddhists are concentrated in the South; Muslims are concentrated in the Northeast; Jewish people are concentrated in the West. | ||
| d. Buddhists are concentrated in the Midwest; Christians are concentrated in the South; Muslims are concentrated in the Northeast; Jewish people are concentrated in the West. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
54
What is the greatest attribute of the "American Dream" that transcends to people across the world?
Choose one answer.
| a. Through hard work, you can achieve upward mobility, no matter what your background is. | ||
| b. Through hard work, you can achieve financial success, no matter what your background is. | ||
| c. Through hard work, you can achieve land ownership, no matter what your background is. | ||
| d. Through hard work, you can achieve citizenship, no matter what your background is. | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
55
What is the major environmental consequence of rapid population growth in the Mountain West region of the United States?
Choose one answer.
| a. Reduction of grazing lands | ||
| b. Land degradation | ||
| c. Ozone depletion | ||
| d. Strain on physical resources, such as water | ||
| e. Rapid climate change |
Question
56
What is the most densely populated province of Canada, and why?
Choose one answer.
| a. Maritime Provinces, because it is located along coastal trade routes | ||
| b. French Canada, because most Canadians speak French | ||
| c. South Canada, because it has suitable climate and physical geography | ||
| d. Prairie Province, because it has good grazing lands | ||
| e. Pacific Canada, because it has a suitable climate |
Question
57
What was "manifest destiny" in the minds of many Americans of the original thirteen colonies?
Choose one answer.
| a. The belief of some Americans that the original thirteen colonies were predestined to expand across the continent | ||
| b. The belief of some Americans that the original thirteen colonies should be an imperialistic power across the world | ||
| c. The belief of some Americans that the original thirteen colonies were destined to remain thirteen and should not expand | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
58
What was the "Great Migration"?
Choose one answer.
| a. Massive migration of Latinos from the South to cities of the North and West | ||
| b. Massive migration of African Americans from the South to cities of the North and West | ||
| c. Massive migration of Native Americans from the South to cities of the North and West | ||
| d. Massive migration of the French from the South to cities of the North and West | ||
| e. Massive migration of the British from the South to cities of the North and West |
Question
59
Which of the following occurrences spurred the westward migration in North America?
Choose one answer.
| a. Gold boom in California (1849) | ||
| b. Completion of the transcontinental railroad (1869) | ||
| c. The invention of the electric streetcar (1888) | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
60
Which of the following physiographic regions of North America extends from the southern states all the way to the great northeast?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Rocky Mountains | ||
| b. The Canadian Shield | ||
| c. The Interior Lowlands | ||
| d. The Appalachian Highlands | ||
| e. The American Shield |
Question
61
Which three European countries significantly influenced the development of North America?
Choose one answer.
| a. Portugal, Russia, and France | ||
| b. Germany, Spain, and France | ||
| c. Spain, France, and Russia | ||
| d. Spain, France, and England | ||
| e. England, Spain, and Russia |
Question
62
Why are there English-speaking and French-speaking regions in Canada?
Choose one answer.
| a. French fishermen and fur traders initially colonized Canada; the British later took it from the French. | ||
| b. British fishermen and fur traders initially colonized Canada; the French later took it from the British. | ||
| c. French aristocrats initially colonized Canada; British fur traders later took it from the French. | ||
| d. British aristocrats initially colonized Canada; French fur traders later took it from the British. | ||
| e. The French migrated to Canada from the eastern United States; the British migrated to Canada from the western United States. |
Question
63
Why is the proportion of French speakers in Canada declining?
Choose one answer.
| a. French speaking families are having fewer children. | ||
| b. French is not part of the curriculum in the Canadian education system. | ||
| c. More immigrants from other parts of the world have a higher fertility rate than the French speakers. | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
64
The thematic map below shows the locations in the United States where Native Americans and Hispanics make up the majority of the population and
non-Hispanic Caucasians make up the minority of the population? Why is this the case?
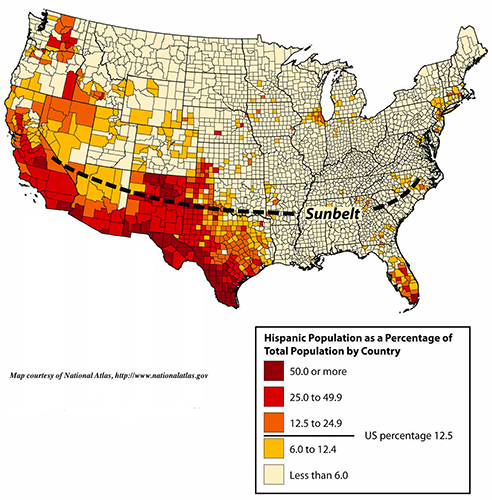
Choose one answer.
| a. Because of proximity to Canada | ||
| b. Because the Midwest offers a strong support infrastructure for immigrants | ||
| c. Because the south provides a lot of the United States' farming needs | ||
| d. Because of proximity to ports | ||
| e. Because of proximity to the Mexican border |
Question
65
How did colonialism alter the ethnic make-up of the Caribbean?
Choose one answer.
| a. Many Africans were brought to the Caribbean via the slave trade. | ||
| b. Colonialism brought many people from Asia to the Caribbean. | ||
| c. The Portuguese took over many parts of the Caribbean during the era of colonialism. | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
66
How has Spanish design influenced the urban centers in Middle and South America?
Choose one answer.
| a. In cities built by the Spanish in Middle and South America, there is a plaza in the center. | ||
| b. In cities built by the Spanish in Middle and South America, there is a church adjacent to a plaza. | ||
| c. In cities built by the Spanish in Middle and South America, residential homes fill in around government offices and stores. | ||
| d. In cities built by the Spanish in Middle and South America, government offices and stores are built adjacent to a plaza. | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
67
How have drug cartels become an integrated part of the fabric of the Mexican economy and society?
Choose one answer.
| a. Drug kingpins have used their economic power to buy off local police forces. | ||
| b. Drug kingpins have provided numerous poor neighborhoods with funding for services that would generally be designated as government obligations. | ||
| c. Drug kingpins have become politicians and high ranking government officials. | ||
| d. Drug kingpins have opened private schools. | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
68
In the tropical areas of Latin America, there are five established temperature-altitude zones. Which of the following elevation zones is typically found at
12,000 to 15,000 feet?
Choose one answer.
| a. Tierra caliente | ||
| b. Tierra templada | ||
| c. Tierra fria | ||
| d. Tierra helada | ||
| e. Tierra nevada |
Question
69
The current social status of Mexican society can be illustrated by three distinct classes: the wealthy elite, the middle class, and the poor majority. Of
what primary descent are the wealthy elite?
Choose one answer.
| a. European descent | ||
| b. Mestizo | ||
| c. Amerindian and African | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
70
What are the two primary climatic zones of Mexico?
Choose one answer.
| a. Polar and tropical | ||
| b. Temperate and tropical | ||
| c. Humid continental and temperate | ||
| d. Polar and humid continental | ||
| e. Marine west coast and polar |
Question
71
What country initially took on the task of building the Panama Canal?
Choose one answer.
| a. The United States | ||
| b. Spain | ||
| c. Germany | ||
| d. Mexico | ||
| e. France |
Question
72
What do most researchers believe to be the cause of the decline of the Mayan Empire?
Choose one answer.
| a. Ecological degradation resulting from slash-and-burn farming techniques | ||
| b. Earthquake activity | ||
| c. Never-ending wars between neighboring Mayan city-states | ||
| d. Congenital disorders | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
73
What is typically the greatest danger associated with hurricanes?
Choose one answer.
| a. Storm surges | ||
| b. Devastating winds | ||
| c. Lightning | ||
| d. Large hail stones | ||
| e. Fires |
Question
74
What leads to the end of a hurricane?
Choose one answer.
| a. Collision with land | ||
| b. Collision with cold water | ||
| c. Lack of wind | ||
| d. Collision with another storm | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
75
Which of Fidel Castro's policy raised major concerns in the United States to the extent that diplomatic relations with Cuba were severed in 1960?
Choose one answer.
| a. Farming practices | ||
| b. Communist activities | ||
| c. The nationalization of businesses and property | ||
| d. Gambling | ||
| e. The prohibition of United States goods |
Question
76
Which of the following statements about the influence on economic and employment situations in Mexico is true?
Choose one answer.
| a. NAFTA (the North American Free Trade Agreement) theoretically allows more corporate investments across borders and increases foreign ownership of business facilities. | ||
| b. A maquiladora theoretically allows more corporate investments across borders and increases foreign ownership of business facilities. | ||
| c. Banking reform theoretically allows more small business investments across borders and increases foreign ownership of business facilities. | ||
| d. A stratified economy theoretically allows more corporate investments across borders and increases foreign ownership of business facilities. | ||
| e. Cheap labor theoretically allows more small business investments across borders and increases foreign ownership of business facilities. |
Question
77
Which of the following statements that compares and contrasts Central American countries is true?
Choose one answer.
| a. Central American countries share similar political dynamics, but they do not share similar climate patterns. | ||
| b. Central American countries share similar climate patterns and similar economic dynamics. | ||
| c. Central American countries share similar climate patterns, but they do not share similar political dynamics. | ||
| d. Central American countries do not share similar climate patterns nor do they share similar political dynamics. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
78
Why did colonialism thrive in the rimland of Middle America?
Choose one answer.
| a. The rimland consists mainly of islands and coastal areas that were accessible to European ships. | ||
| b. The rimland consisted mainly of English speaking people, which made it easier to set up trade agreements. | ||
| c. The rimland is nice and flat, making it easy to explore and conquer. | ||
| d. The rimland had a lot of diamond resources, making it quite appealing to the Europeans. | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
79
Why is the southern region of the Americas commonly referred to as "Latin America"?
Choose one answer.
| a. Because the lingua franca of the region is Latin | ||
| b. Because European colonialism diffused the Christian religion throughout the region, which included Latin Mass (a tradition in the Roman Catholic Church) | ||
| c. Because in Mexico, the largest country in Middle America, speaks primarily Latin (with Spanish being a close second) | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
80
As a result of the Spanish-American War, why did the United States find the need to build the Panama Canal?
Choose one answer.
| a. New colonies had been acquired in Africa. | ||
| b. The United States Navy could then move more quickly between oceans. | ||
| c. Spanish opposition to the canal had ended. | ||
| d. The present transportation infrastructure of the United States could not transport enough manufactured goods. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
81
Although Paraguay's economy is afflicted by poverty and an absence of opportunities, what economic activities have flourished due to Paraguay's
geographical setting and physical geography?
Choose one answer.
| a. Hydroelectricity | ||
| b. Soy bean production | ||
| c. Cattle ranching | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
82
Despite its cultural diversity, residents of Brazil have a strong sense of nationalism and identity. Which of the following overarching cultural forces
have helped hold the country together?
Choose one answer.
| a. Portuguese language | ||
| b. Catholicism | ||
| c. Islam | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
83
Fill in the blank. The continent of South America can be divided into regions by ____, influenced by early colonial development.
Choose one answer.
| a. ethnic majorities | ||
| b. rivers | ||
| c. villages | ||
| d. climate | ||
| e. native minorities |
Question
84
South America was colonized exclusively by which two main Iberian powers?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Netherlands and Great Britain | ||
| b. France and Portugal | ||
| c. Turkey and Spain | ||
| d. Spain and Portugal | ||
| e. Spain and France |
Question
85
The Atacama Desert is the driest place on the planet. Which mountain range creates the rain shadow that contributes to the dry conditions?
Choose one answer.
| a. Andes Mountains | ||
| b. Atlas Mountains | ||
| c. Himalaya Mountains | ||
| d. Cascade Mountains | ||
| e. Sierra Nevada Mountains |
Question
86
The three main export products of Colombia are illegal drugs, oil, and coffee. Which of the following countries is the largest consumer of all three?
Choose one answer.
| a. Mexico | ||
| b. Guatemala | ||
| c. The United States | ||
| d. Cuba | ||
| e. Chile |
Question
87
What are the countries of the Southern Cone, and what has been a major focus of their early development pattern?
Choose one answer.
| a. The countries of the Southern Cone are Uruguay, Argentina, and Chile. The major focus of their early development pattern has been agriculture. | ||
| b. The countries of the Southern Cone are Uruguay, Argentina, and Paraguay. The major focus of their early development pattern has been mining. | ||
| c. The countries of the Southern Cone are Uruguay, Argentina, and Chile. The major focus of their early development pattern has been urbanization. | ||
| d. The countries of the Southern Cone are Uruguay, Argentina, and Brazil. The major focus of their early development pattern has been agriculture. | ||
| e. The countries of the Southern Cone are Uruguay, Paraguay, and Argentina. The major focus of their early development pattern has been urbanization. |
Question
88
What are the main economic activities of the Amazon Basin, and what is the main environmental concern due to those activities?
Choose one answer.
| a. The main economic activities are cattle ranching, logging, and mining. The major environmental concern is water pollution. | ||
| b. The main economic activities are cattle ranching, logging, and mining. The major environmental concern is deforestation. | ||
| c. The main economic activities are cattle ranching, farming, and hydroelectricity. The major environmental concern is water pollution. | ||
| d. The main economic activities are farming, logging, and hydroelectricity. The major environmental concern is desertification. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
89
Which of the following is a benefit of Chile's stable government and growing economy?
Choose one answer.
| a. Inflation has been kept low. | ||
| b. Employment has been high. | ||
| c. Poverty has been reduced. | ||
| d. Foreign investment has increased. | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
90
Which of the following is a cultural sphere of South America?
Choose one answer.
| a. Tropical Plantation Region | ||
| b. Rural Amerindian Region | ||
| c. Amazon Basin | ||
| d. Mixed Mestizo Region | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
91
Which of the following islands has Argentina claimed and battled Great Britain for?
Choose one answer.
| a. Falkland Islands | ||
| b. Galapagos Islands | ||
| c. Easter Island | ||
| d. Robinson Crusoe Island | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
92
Which region of Brazil is one of the most affluent regions, and what activities have led to its wealth?
Choose one answer.
| a. Southwest; agricultural activities | ||
| b. West central; mining activities | ||
| c. Northeast; tourism | ||
| d. South; agricultural activities | ||
| e. Amazon basin; mining activities |
Question
93
Although Argentina is politically unstable, how does the country have great potential for economic growth?
Choose one answer.
| a. The country has abundant natural resources. | ||
| b. The country has adequate infrastructure. | ||
| c. The country has an educated work force. | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. B and C only |
Question
94
Alcoholic beverages are more common south of the African Transition Zone. Why?
Choose one answer.
| a. Yeast and hops, major ingredients in beer making, are more plentiful in the south. | ||
| b. The climate in the south is good for grape growing. | ||
| c. There is a greater Christian population in the south, and the Christian religion allows for drinking of alcoholic beverages whereas the Muslim religion does not. | ||
| d. Both A and C | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
95
Despite a lack of effective national governance, the informal economy in Somalia continues to thrive. How is this possible?
Choose one answer.
| a. Trading through personal transactions | ||
| b. Trading through the private marketplace | ||
| c. Donations from charitable organizations | ||
| d. Donations from wealthy countries | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
96
Early kingdoms in Subsaharan Africa flourished prior to the Colonial Era. What was an important early trading commodity especially for the kingdoms of West
Africa?
Choose one answer.
| a. Gold | ||
| b. Salt | ||
| c. Copper | ||
| d. Ivory | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
97
How many distinct languages are spoken in all of Africa?
Choose one answer.
| a. 500 | ||
| b. 1000 | ||
| c. 1500 | ||
| d. 2000 | ||
| e. 2500 |
Question
98
In which way has the end of apartheid had a positive economic effect on South Africa?
Choose one answer.
| a. Black South African managers have increased industrial productivity throughout the nation. | ||
| b. The introduction of communism has led to a more equal distribution of income. | ||
| c. Many foreign companies have resumed trading and investing in South Africa. | ||
| d. All profits of South Africa's industries are now reinvested out of the country. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
99
Niger has the highest birth rate in the world. Why?
Choose one answer.
| a. Religious beliefs | ||
| b. Polygamy | ||
| c. Marriage and child-bearing at a young age | ||
| d. Poverty | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
100
What economic resource makes Southern Africa one of the wealthiest regions of Africa with the greatest potential for economic growth?
Choose one answer.
| a. Forests | ||
| b. Tourism | ||
| c. Mineral resources | ||
| d. Manufacturing | ||
| e. Technology |
Question
101
What is a major difference between Madagascar and Southern Africa?
Choose one answer.
| a. Cultural geography | ||
| b. Biodiversity | ||
| c. Religion | ||
| d. Climate | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
102
What is one reason why there is diminished support for public services in Subsaharan Africa?
Choose one answer.
| a. The lack of government regulation and control prevents taxes from being assessed or collected. | ||
| b. There is too much government regulation. | ||
| c. The formal section is too big in Subsaharan Africa. | ||
| d. Too many taxes are simply a burden to residents of Subsaharan Africa. | ||
| e. The unemployment rate is too high. |
Question
103
What is the African Transition Zone, and what is it based on?
Choose one answer.
| a. The zone that divides North Africa from the rest of Africa, which is based on climatic and cultural dynamics | ||
| b. The zone that divides South Africa from the rest of Africa, which is based on climatic and cultural dynamics | ||
| c. The zone that divides North Africa from the rest of Africa, which is based solely on climatic dynamics | ||
| d. The zone that divides North Africa from the rest of Africa, which is based solely on cultural dynamics | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
104
What is the reason behind many of the civil wars in Central Africa?
Choose one answer.
| a. Control over resources | ||
| b. Political control | ||
| c. Ethnic conflict | ||
| d. Civil unrest | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
105
What was the purpose of the Berlin Conference in 1884?
Choose one answer.
| a. To divide Africa and agree on colonial boundary lines | ||
| b. To divide Germany | ||
| c. To define the location of the African Transition Zone | ||
| d. To set up trade routes into and out of Africa | ||
| e. To set up a United African government |
Question
106
Which of the following has led to some of the political divisions that we see among different African countries today?
Choose one answer.
| a. Language barriers | ||
| b. Religious differences | ||
| c. Cold War divisions between the United States and the old Soviet Union | ||
| d. Both A and C | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
107
Which of the following rivers in the south is famous for the Victoria Falls on the Zambia and Zimbabwe border?
Choose one answer.
| a. Congo River | ||
| b. Niger River | ||
| c. Nile River | ||
| d. Orange River | ||
| e. Zambezi River |
Question
108
Which of the following statements accurately characterizes the impact of HIV/AIDS on Subsaharan Africa?
Choose one answer.
| a. 67% of the 40 million people infected with HIV/AIDS were in Subsaharan Africa. | ||
| b. Life expectancies have dropped rapidly in the past decade. | ||
| c. Countries in the southern part of the region may see population decline over the next two decades. | ||
| d. Women account for 58% of the reported cases in the region. | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
109
Why is it that women in Central Africa do not always have the opportunity to earn an education or obtain the training required for employment
opportunities?
Choose one answer.
| a. Because of cultural circumstances | ||
| b. Because of tradition | ||
| c. Because women must care for large families | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
110
Language is one aspect of culture that indicates a colonial relationship. Due to colonialism, what is the official language of most of West Africa?
Choose one answer.
| a. French | ||
| b. German | ||
| c. English | ||
| d. Arabic | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
111
Fill in the blanks. Women's rights and opportunities in Arab countries are generally related to family size. When family size ____, women's rights and
opportunities usually ____.
Choose one answer.
| a. increases, decrease | ||
| b. decreases, increase | ||
| c. stays the same, increase | ||
| d. decreases, stay the same | ||
| e. stays the same, stay the same |
Question
112
Historically, the ethnicity of North Africa was predominately ____ with the nomadic ____ and other local groups interspersed.
Choose one answer.
| a. Berber, Tuareg | ||
| b. Tuareg, Berber | ||
| c. Hindu, Tuareg | ||
| d. Christian, Berber | ||
| e. Tuareg, Christian |
Question
113
Lebanon has a unique parliamentary democratic system devised to relieve some of the tension between the various cultural-political factions. In fact, a
number of positions in government are reserved for specific religious parties. What religious party is reserved for the prime minister position?
Choose one answer.
| a. Orthodox Christian | ||
| b. Sunni Muslim | ||
| c. Shia Muslim | ||
| d. Maronite Catholic Christian | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
114
The African Transition Zone creates the southern boundary for North Africa. This zone serves as the transition between what two climate zones?
Choose one answer.
| a. Arid Type B and Tropical Type A | ||
| b. Mediterranean Type C and Tropical Type A | ||
| c. Arid Type B and Mediterranean Type C | ||
| d. Tropical Type A and Microthermal Type D | ||
| e. Mediterranean Type C and Microthermal Type D |
Question
115
The government of Syria is difficult to define. Technically, it was established in 1946 as a Parliamentary Republic. In contrast, what is the type of
government in Jordan?
Choose one answer.
| a. Constitutional monarchy | ||
| b. Dictatorship | ||
| c. Democracy | ||
| d. Absolute monarchy | ||
| e. Elective monarchy |
Question
116
The main rivers of Uzbekistan have been diverted for irrigation and are often depleted before reaching which body of water?
Choose one answer.
| a. Caspian Sea | ||
| b. Aydat Lake | ||
| c. Aral Sea | ||
| d. Black Sea | ||
| e. Caspian Sea |
Question
117
What are the two main subtypes of expansion diffusion?
Choose one answer.
| a. Spatial diffusion and relocation diffusion | ||
| b. Relocation diffusion and contagious diffusion | ||
| c. Contagious diffusion and spatial diffusion | ||
| d. Hierarchical diffusion and contagious diffusion | ||
| e. Spatial diffusion and hierarchical diffusion |
Question
118
What climate type dominates the Arabian Peninsula?
Choose one answer.
| a. Type A climate (tropical) | ||
| b. Type B climate (dry/desert) | ||
| c. Type C climate (moderate/temperate) | ||
| d. Type D climate (cold winters) | ||
| e. Type E climate (tundra/polar) |
Question
119
What is a common trait that each of the countries in North Africa have in common?
Choose one answer.
| a. Climate | ||
| b. Religion | ||
| c. Natural resources | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
120
What territory did Israel take control over as a result of the 1967 war between Arab armies and Israel?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Gaza Strip | ||
| b. The Sinai Peninsula | ||
| c. The West Bank | ||
| d. The Golan Heights | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
121
What were the general reasons for the massive wave of protests and demonstrations by citizens of the North Africa and Southwest Asia realm beginning in
2011 (known as the Arab Spring of 2011)?
Choose one answer.
| a. Poor living conditions and high unemployment | ||
| b. Government corruption and the lack of democratic reforms | ||
| c. Lack of shared oil revenue and too many regulations on small businesses | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
122
Which of the following accurately identifies one of the five pillars of Islam?
Choose one answer.
| a. Express the basic creed | ||
| b. Perform the prayers | ||
| c. Pay alms or give to charity | ||
| d. Fast | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
123
Which of the following ethnic groups follows the Sunni division and dominates northern Iraq?
Choose one answer.
| a. Kurdish | ||
| b. Turkish | ||
| c. Arab | ||
| d. Persian | ||
| e. Muslim |
Question
124
Which of the following is a region extending from Morocco to Libya that is distinguished by the main ranges of the Atlas Mountains?
Choose one answer.
| a. Sahara Desert | ||
| b. The Middle East | ||
| c. The Levant | ||
| d. The Maghreb | ||
| e. The African Transition Zone |
Question
125
Which of the following is the cultural hearth located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers, and why did it develop where it did?
Choose one answer.
| a. The cultural hearth located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers is Mesopotamia; it developed there because of the climate, soils, and availability of fresh water provided the ingredients for the growth of a human civilization. | ||
| b. The cultural hearth located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers is the Ganges River Valley; it developed there because the cities in the region formed around long established tribal communities, therefore becoming the center-point of human civilization. | ||
| c. The cultural hearth located between the Tigris and Euphrates Rivers is the Wei-Huang River Valley; it developed there, because this was the strongest trade port in the world. | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
126
Which of the following rivers provides fresh water to Syria?
Choose one answer.
| a. Tigris River | ||
| b. Euphrates River | ||
| c. Nile River | ||
| d. Ganges River | ||
| e. Indus River |
Question
127
Which of the following statements about Iran's physical geography and natural resources is true?
Choose one answer.
| a. Iran's landscape can be described as mountainous. | ||
| b. Iran's physical geography is characterized by deserts. | ||
| c. Iran has an abundant oil supply. | ||
| d. Iran has an abundant natural gas supply. | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
128
Which of the following statements that identifies what organization designated a Jewish state from the lands of Palestine as well as when this occurred is
true?
Choose one answer.
| a. In 1950, the United Nations accepted a proposal to create a Jewish state out of land in Palestine. | ||
| b. In 1945, Palestine accepted a proposal to create a Jewish state out of the land in Palestine. | ||
| c. In 1945, the United Nations accepted a proposal to create a Jewish state out of land in Palestine. | ||
| d. In 1940, Israel accepted a proposal to create a Jewish state out of the land in Palestine. | ||
| e. In 1950, both Palestine and Israel accepted a proposal to create a Jewish state out of the land in Palestine. |
Question
129
Which of the following was an excuse that Saddam Hussein used to invade Kuwait in 2003?
Choose one answer.
| a. Kuwait was the nineteenth province of Iraq. | ||
| b. Kuwait used slant oil wells along the Iraqi border. | ||
| c. Kuwait had stolen the crown jewels of Iraq. | ||
| d. Saddam Hussein felt threatened by the Kuwaiti army. | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
130
Who does Christianity, Judaism, and Islam all acknowledge as a founding patriarch of their religions?
Choose one answer.
| a. Adam Smith | ||
| b. Christ | ||
| c. Moses | ||
| d. Abraham | ||
| e. Muhammad |
Question
131
Why does Afghanistan's national, central government (based in the capital city of Kabul) have minimal influence in the country's rural regions?
Choose one answer.
| a. Pashtun interference | ||
| b. Taliban interference | ||
| c. Pakistani interference | ||
| d. Ethnic factions | ||
| e. Tajik interference |
Question
132
Why has Turkey not been accepted as a member of the European Union (EU)?
Choose one answer.
| a. Controversial human rights record | ||
| b. Conflicts with the Kurds | ||
| c. Disagreements with Greece over Cyprus | ||
| d. Low economic indicators | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
133
What are the main economic sources for countries of the Arabian Peninsula?
Choose one answer.
| a. Manufacturing | ||
| b. Tourism | ||
| c. Natural resources | ||
| d. Agricultural | ||
| e. Renewable energy (such as solar) |
Question
134
Fill in the blank. Rapid population growth in the countries of South Asia is a major concern. For example, in Nepal the combination of the fast growing
population with the loss of ____ means a major crisis will be forthcoming.
Choose one answer.
| a. food-growing capacity | ||
| b. housing | ||
| c. water resources | ||
| d. housing and water resources | ||
| e. medicine |
Question
135
How has the Indian government responded to the threat of reduced biodiversity?
Choose one answer.
| a. With the creation of sanctuaries | ||
| b. With the creation of national parks | ||
| c. With the creation of protected wildlife areas | ||
| d. With the creation of biosphere reserves | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
136
How was the landmass of South Asia formed?
Choose one answer.
| a. By the Indian Plate colliding with the North American Plate | ||
| b. By the Indian Plate colliding with the Eurasian Plate | ||
| c. By the Indian Plate colliding with the South American Plate | ||
| d. By the Indian Plate colliding with the African Plate | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
137
The Kingdom of Kashmir, located between Pakistan, India, Afghanistan, and China, is independent but divided with Pakistan controlling the northern region,
India controlling the southern region, and China controlling a portion of the eastern region. The future of Kashmir is unclear, as none of the countries
involved want to start a large-scale war. What is preventing this type of escalation from happening?
Choose one answer.
| a. Political similarity; that is, all of the countries share the same politics and therefore realize no one country is a threat to the other | ||
| b. Economic factors; that is, the cost of war is too high, and none of the nations involved have the economic resources to support those costs | ||
| c. Realism; that is, each country realizes that it cannot defeat the other countries | ||
| d. Nuclear deterrent; that is, each country (Pakistan, India, and China) all have nuclear weapons, and the use of those weapons would ensure mutual destruction | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
138
What is a common environmental concern for both Pakistan and Bangladesh?
Choose one answer.
| a. Desertification | ||
| b. Water pollution | ||
| c. Earthquakes | ||
| d. Deforestation | ||
| e. Both B and D |
Question
139
What prompted the Indo-Pakistan War in 1970, which led to the eventual creation of the independent Bangladesh in 1972?
Choose one answer.
| a. Weak reaction from the central government in West Pakistan to a massive cyclone that hit the coast of East Pakistan | ||
| b. Weak reaction from the central government in East Pakistan to a massive cyclone that hit the coast of West Pakistan | ||
| c. Land conflict over mineral rights between East and West Pakistan | ||
| d. Both B and C | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
140
What specifically were early European colonizers of South Asia seeking?
Choose one answer.
| a. Raw materials | ||
| b. Cheap labor | ||
| c. Trade partners (for expanding markets) | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
141
Where is the city of Karachi, Pakistan's largest city and major port?
Choose one answer.
| a. Punjab | ||
| b. Baluchistan | ||
| c. Sindh | ||
| d. Khyber Pakhtunkhwa | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
142
Which of the five main levels of the Hindu castes system are "untouchables"?
Choose one answer.
| a. Brahmin | ||
| b. Kshatriya | ||
| c. Vaishya | ||
| d. Shudra | ||
| e. Dalits |
Question
143
Which of the following best characterizes the summer winds of the Indian Monsoon?
Choose one answer.
| a. They move across India toward the Indian Ocean. | ||
| b. They move from the Indian Ocean across India. | ||
| c. They are hot and dry as they blow across India. | ||
| d. They are cool and wet as they blow across India. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
144
Which of the following countries in South Asia is becoming a major manufacturing country for vehicles and high-tech industries?
Choose one answer.
| a. India | ||
| b. Pakistan | ||
| c. Nepal | ||
| d. Sri Lanka | ||
| e. Bangladesh |
Question
145
Which of the following was the earliest civilization on the subcontinent of India in existence from about 3300 BCE to 1500 BCE?
Choose one answer.
| a. Brahmaputra civilization | ||
| b. Mesopotamian civilization | ||
| c. Mauryan civilization | ||
| d. Bronze Age civilization | ||
| e. Indus Valley civilization |
Question
146
Which of the world's seven continents is the largest?
Choose one answer.
| a. North America | ||
| b. South America | ||
| c. Australia | ||
| d. Antarctica | ||
| e. Asia |
Question
147
Why are there continued conflicts over the land expanses around Pakistan's northern areas?
Choose one answer.
| a. Religious differences in the region, especially between Islam and Hinduism | ||
| b. Politics | ||
| c. Oil Resources | ||
| d. Both A and B | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
148
Why did the British move their colonial capital from Kolkata (on the coast) to inland New Delhi?
Choose one answer.
| a. In order to link to the interior of India | ||
| b. In order to provide for the interior of India | ||
| c. In order to develop the interior of India | ||
| d. In order to exploit the interior of India | ||
| e. In order to modernize the interior of India |
Question
149
As a result of the one-child-only policy in China, there is a disproportionate number of males versus females across the country with an average difference
being 10% more males. Why is this?
Choose one answer.
| a. Naturally, more male babies are born than female babies. | ||
| b. Female babies are aborted more often than male babies in order to have a male baby instead. | ||
| c. This is actually an urban myth; there are not more males in China than females. | ||
| d. Female infanticide is higher in China than male infanticide for some unknown, medical reason. | ||
| e. Both A and C |
Question
150
In 2000, which of the following nations renewed its efforts to be internationally recognized as a sovereign nation (and introduced plans to formally secede
from China)?
Choose one answer.
| a. Tibet | ||
| b. Hong Kong | ||
| c. Japan | ||
| d. Taiwan | ||
| e. Mongolia |
Question
151
South Korea has used what type of method to develop its economy?
Choose one answer.
| a. State capitalism | ||
| b. Free-enterprise capitalism | ||
| c. Communism | ||
| d. Agricultural exports | ||
| e. Laissez-faire capitalism |
Question
152
The three-way split in China was a three-way war over the control of China by the Nationalists, Communists, and Japanese. Eventually, which group took
control and what happened to the other two?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Communists took control, the Japanese were pushed out after World War II, and the Nationalists fled to Formosa (Taiwan). | ||
| b. The Nationalists took control, the Japanese were pushed out after World War II, and the Communists fled to Formosa. | ||
| c. The Japanese took control, the Communists were pushed out after World War II, and the Nationalists fled to Formosa. | ||
| d. The Japanese took control, the Nationalists were pushed out after World War II, and the Communists fled to Formosa. | ||
| e. The Communists took control, the Nationalists were pushed out after World War II, and the Japanese fled to Formosa. |
Question
153
What is a major concern in Japan today for the continuation of its economic growth in the future?
Choose one answer.
| a. Dwindling resources | ||
| b. Overpopulation | ||
| c. The eruption of Mount Fuji | ||
| d. The country's small family size and declining population, which leads to a labor shortage | ||
| e. Both C and D |
Question
154
What is the primary purpose of the Three Gorges Dam?
Choose one answer.
| a. Control flooding along the Yangtze River | ||
| b. Produce hydroelectric power | ||
| c. Increase shipping capacity along the river | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
155
What is the primary reason that Chinese culture has endured for thousands of years?
Choose one answer.
| a. A strong sense of nationalism; that is, a sense of unity due to cultural background | ||
| b. A strong sense of patriotism; that is, a love for one's nation | ||
| c. Isolationism from European colonialism and Central Asian imperialism due to the Himalayas and other high mountain ranges that encircle China | ||
| d. The demands of Communism | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
156
When did European colonialism arrive in China?
Choose one answer.
| a. During the Shang Dynasty | ||
| b. During the Han Dynasty | ||
| c. During the Tang Dynasty | ||
| d. During the Ming Dynasty | ||
| e. During the Qing Dynasty |
Question
157
Which of the following countries is NOT in the realm of East Asia?
Choose one answer.
| a. China | ||
| b. Japan | ||
| c. Taiwan | ||
| d. Sri Lanka | ||
| e. Mongolia |
Question
158
Which of the following nations has isolated itself behind an authoritarian dictatorship since World War II?
Choose one answer.
| a. South Korea | ||
| b. North Korea | ||
| c. Singapore | ||
| d. Taiwan | ||
| e. Japan |
Question
159
Which of the following reasons best describes how Hong Kong created a doorway for British expansion into China?
Choose one answer.
| a. By establishing a free port for imports and exports, Hong Kong was able to enhance China's economy, eventually resulting in Hong Kong's transformation from a British colony to an autonomous region of China. | ||
| b. By building up a strong military, Hong Kong was able to provide a stronghold for the British in China. | ||
| c. By disseminating information about religious conversion, Hong Kong was able to bridge the religious and cultural gaps between Britain and China, allowing for British expansion. | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
160
Which of the following statements accurately describes an impact of physical geography on the history of the Korean Peninsula?
Choose one answer.
| a. Lack of natural resources has prevented development of manufacturing. | ||
| b. Lack of rivers has limited food production. | ||
| c. Large deserts have led to isolation. | ||
| d. Location has led to invasion and occupation by other nations. | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
161
Why does most of China's population live in its eastern region?
Choose one answer.
| a. Fresh water, good soil, and A-type climates | ||
| b. Fresh water, good soil, and B-type climates | ||
| c. Fresh water, good soil, and C-type climates | ||
| d. Fresh water, good soil, and D-type climates | ||
| e. Fresh water, good soil, and E-type climates |
Question
162
Why has China transitioned from strict Communism to a capitalist-influenced economy?
Choose one answer.
| a. In a series of statements in the 1990s, China's political leaders suggested that in order for China to enjoy a more mature form of socialism, greater national wealth was needed. | ||
| b. In a series of statements in the 1990s, China's political leaders suggested that in order for China to enjoy a more mature form of socialism, greater cultural control was needed. | ||
| c. In a series of statements in the 1990s, China's political leaders suggested that in order for China to enjoy a more mature form of socialism, greater military power was needed. | ||
| d. In a series of statements in the 1990s, China's political leaders suggested that in order for China to enjoy a more mature form of socialism, greater industrialization was needed. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
163
In China, what was the purpose of the Great Leap Forward?
Choose one answer.
| a. To promote democratic reform | ||
| b. To end the private ownership of land | ||
| c. To strengthen economic ties with Europe | ||
| d. To increase agricultural and industrial production | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
164
Before the Philippines gained independence from the United States, what country colonized it?
Choose one answer.
| a. Great Britain | ||
| b. France | ||
| c. Portugal | ||
| d. The United States | ||
| e. Spain |
Question
165
Fill in the blank. Despite the harsh discrimination directed at the Chinese minority overseas in Southeast Asia, the Chinese have been instrumental in
promoting global ____ arrangements that have established the Pacific Rim as a major player in the international economy.
Choose one answer.
| a. trade | ||
| b. treaty | ||
| c. peace | ||
| d. business | ||
| e. shipping |
Question
166
Indonesia is home to over 150 active volcanoes, including which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. Mt. Pinatubo | ||
| b. Krakatoa | ||
| c. Tambora | ||
| d. Mt. Kilimanjaro | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
167
Singapore is considered an economic tiger due to its economic growth and relative wealth, yet Singapore does not have any natural resources. How has it
developed such a strong economy?
Choose one answer.
| a. Singapore received a lot of financial assistance from neighboring countries and then invested well. | ||
| b. Singapore has made good strategic utilization of its geographic location by serving as a distribution center for goods and materials processed in the region. | ||
| c. Singapore has a desalination plant and sells fresh water to Middle Eastern countries. | ||
| d. Singapore offers cheap labor and is subsequently hired by large corporations to do manufacturing work. | ||
| e. Both A and D |
Question
168
Thailand is a newly industrialized country. What will its future economy primarily be based on?
Choose one answer.
| a. Agriculture | ||
| b. Mining | ||
| c. Manufacturing | ||
| d. Tourism | ||
| e. Retail |
Question
169
What has been responsible for the creation of many of the islands of Southeast Asia?
Choose one answer.
| a. Sea level change | ||
| b. Tectonic plate activity | ||
| c. Erosion due to the movement of rivers | ||
| d. Tsunami activity | ||
| e. Wind erosion and deposition |
Question
170
What was a factor that led to the civil war in Vietnam?
Choose one answer.
| a. After 1954, during the quest to establish a government for an independent Vietnam, the northern portion of Vietnam rallied around Hanoi and aligned itself with a Communist ideology. | ||
| b. After 1954, during the quest to establish a government for an independent Vietnam, the northern portion of Vietnam rallied around Hanoi and aligned itself with a Democratic ideology. | ||
| c. After 1954, during the quest to establish a government for an independent Vietnam, the northern portion of Vietnam rallied around Hanoi and aligned itself with a Socialist ideology. | ||
| d. After 1954, during the quest to establish a government for an independent Vietnam, the northern portion of Vietnam rallied around Hanoi and aligned itself with a Marxist ideology. | ||
| e. After 1954, during the quest to establish a government for an independent Vietnam, the northern portion of Vietnam rallied around Hanoi and aligned itself with a Buddhist ideology. |
Question
171
Which of the following is the home to the largest Muslim population in the world?
Choose one answer.
| a. China | ||
| b. Saudi Arabia | ||
| c. Egypt | ||
| d. Indonesia | ||
| e. The United States |
Question
172
Which of the following is the only region of Southeast Asia that was not colonized by the Europeans?
Choose one answer.
| a. Burma | ||
| b. Thailand | ||
| c. Laos | ||
| d. Vietnam | ||
| e. Indonesia |
Question
173
What led to the creation of Democratic Kampuchea?
Choose one answer.
| a. Pol Pot's desire to create a rural agrarian utopian society | ||
| b. Pol Pot's desire to set up a base for the Khmer Rouge | ||
| c. Pol Pot's desire to establish a refugee camp for Cambodians | ||
| d. Both A and C | ||
| e. Both B and C |
Question
174
Fill in the blank. A "____" in the 1950s in New Zealand yielded tremendous profits for New Zealand.
Choose one answer.
| a. kiwi boom | ||
| b. tourism boom | ||
| c. lamb boom | ||
| d. wool boom | ||
| e. marsupial boom |
Question
175
What are the Wallace Line and the Weber Line?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Wallace and Weber Lines are demarcation lines of clear environmental differences in species development between two sides. They are located just north of Australia to indicate the division between the Asian realm and the Austral realm. | ||
| b. The Wallace and Weber Lines are demarcation lines of clear environmental similarities in species development between two sides. They are located just north of Australia to indicate the division between the Asian realm and the Austral realm. | ||
| c. The Wallace and Weber Lines are demarcation lines of clear environmental differences in species development between two sides. They are located just south of Australia to indicate the division between the Asian realm and the Austral realm. | ||
| d. The Wallace and Weber Lines demarcation lines of clear environmental similarities in species development between two sides. The Wallace and Weber Lines are located just south of Australia to indicate the division between the Asian realm and the Austral realm. | ||
| e. The Wallace and Weber Lines are trade routes developed by Wallace and Weber. |
Question
176
Which country first colonized Australia and used it as a prison colony?
Choose one answer.
| a. Spain | ||
| b. The United States | ||
| c. France | ||
| d. China | ||
| e. Great Britain |
Question
177
Which of the following statements best explains why the geographic isolation of Australia and New Zealand led to such high levels of biodiversity (i.e.,
speciation) in the realm?
Choose one answer.
| a. Physical separation of population reduces biological competition. | ||
| b. Physical separation of populations prevents interbreeding and the mixing of gene pools. | ||
| c. Physical separation of populations provides more physical space for each group to grow in size and distribution. | ||
| d. Physical separation of populations stresses the organisms, thus causing genetic mutations. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
178
In 1840, British colonizers and the Maori signed the Treaty of Waitangi. What did the treaty provide to both the British and the Maori?
Choose one answer.
| a. The treaty granted British sovereignty over the islands but allowed the Maori certain rights over tribal lands. | ||
| b. The treaty granted Maori sovereignty over the islands but allowed the British certain rights over tribal lands. | ||
| c. The treaty was essentially a purchase; the British purchased much of New Zealand from the Maori. | ||
| d. The treaty established a free trade agreement between the British and the Maori. | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
179
Although natural causes of climate change occur, humans also play a role. The burning of fossil fuels and the chopping down of the rainforests are
increasing the volume of which of the following chemicals in the atmosphere and therefore accelerating climate change?
Choose one answer.
| a. Glucose | ||
| b. Carbon dioxide | ||
| c. Methane | ||
| d. Both B and C | ||
| e. None of the above |
Question
180
Approximately how many total feet would sea level rise if the polar ice caps were to completely melt?
Choose one answer.
| a. 20 feet | ||
| b. 30 feet | ||
| c. 1000 feet | ||
| d. 2000 feet | ||
| e. 200 feet |
Question
181
If an island does not extend too far above sea level, what is it called?
Choose one answer.
| a. A high island | ||
| b. A low island | ||
| c. A marsh island | ||
| d. A coral island | ||
| e. An everglade island |
Question
182
In which season are ozone levels over Antarctica reduced, and why?
Choose one answer.
| a. Summer, because of the development of more polar stratospheric clouds | ||
| b. Winter, because of the development of more polar stratospheric clouds | ||
| c. Spring, because of the development of more polar stratospheric clouds | ||
| d. Autumn, because of the development of more polar stratospheric clouds | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
183
The Pacific Islands are divided into three main groups based on which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. Physical geography | ||
| b. Local inhabitants | ||
| c. Location | ||
| d. All of the above | ||
| e. A and B only |
Question
184
What does the ozone layer protect us from?
Choose one answer.
| a. Nothing, really | ||
| b. Infrared radiation | ||
| c. Ultraviolet radiation | ||
| d. Gamma radiation | ||
| e. Meteorites |
Question
185
What is the primary economic activity of the islands in the Pacific?
Choose one answer.
| a. Tourism | ||
| b. Mining | ||
| c. Fishing | ||
| d. Offshore banking | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
186
Which country has jurisdiction over Antarctica?
Choose one answer.
| a. The United States | ||
| b. Australia | ||
| c. England | ||
| d. Russia | ||
| e. None of the above; Antarctica is not under the jurisdiction of any one government. |
Question
187
Which of the following absorbs large quantities of carbon dioxide?
Choose one answer.
| a. The oceans | ||
| b. The continents | ||
| c. Fossil fuels | ||
| d. Zooplankton | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
188
Which of the following is a cause of climate change?
Choose one answer.
| a. Variation in solar radiation due to changes in the Earth-Sun geometry | ||
| b. Variation in incoming solar radiation due to changes in Earth's atmosphere | ||
| c. Changes in the positions of continents and ocean basins | ||
| d. Overuse of fossil fuels and the addition of greenhouse gases to the atmosphere | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
189
Which of the following is the greatest environmental concern for both Antarctica and the islands of the South Pacific?
Choose one answer.
| a. Global warming leading to sea level rise | ||
| b. Ozone depletion | ||
| c. Changes in weather | ||
| d. Nuclear testing | ||
| e. None of the above; there are no environmental concerns. |
Question
190
Which of the following island groups of Melanesia is under the rule of the French government?
Choose one answer.
| a. Vanuatu | ||
| b. New Caledonia | ||
| c. The Solomon Islands | ||
| d. Fiji | ||
| e. Papua New Guinea |
Question
191
The most recent wave of globalization, which began in the 1980s, has emphasized the outsourcing of which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| a. Services and white-collar jobs | ||
| b. Manufacturing and blue-collar jobs | ||
| c. Mining jobs | ||
| d. Agriculture and farming | ||
| e. All of the above |
Question
192
What is one of the more commonly expressed views on how globalization affects culture?
Choose one answer.
| a. Culture is becoming more commercialized (that is, people are pretending to be of a certain culture or background simply to make money). | ||
| b. World culture is becoming homogenized, especially through the domination of Western influences. | ||
| c. Globalization is leading to greater diversity in cultural traditions and norms. | ||
| d. Globalization does not affect culture. | ||
| e. Both A and B |
Question
193
What is one of the major driving forces of globalization today?
Choose one answer.
| a. Economic downturn across nations of the world | ||
| b. The rising power of individual, multinational corporations | ||
| c. Technological advancements, including the Internet and social media | ||
| d. The United Nations and the Arab League | ||
| e. Both C and D |