1
Suppose that matrix 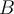 is obtained by performing a sequence of row operations on
is obtained by performing a sequence of row operations on  . Can
. Can  be obtained by performing row operations on
be obtained by performing row operations on 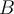 ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. No |
||
|
B. In special cases |
||
|
C. Yes |
||
|
D. There is not enough information provided to determine this. |
Question 2
If 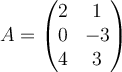 and
and 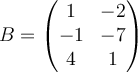 , then which of the following cannot exist?
, then which of the following cannot exist?
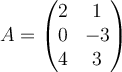 and
and 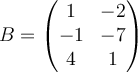 , then which of the following cannot exist?
, then which of the following cannot exist?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 3
If  and
and 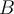 are symmetric matrices, then the product
are symmetric matrices, then the product 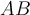 is also symmetric only when
is also symmetric only when  and
and 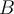 are
are
Choose one answer.
|
A. matrices that commute. |
||
|
B. square matrices. |
||
|
C. Hermitian matrices. |
||
|
D. invertible matrices. |
Question 4
Which of the following expresses the complex number  in polar coordinates?
in polar coordinates?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 5
Let 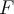 be a field. Then,
be a field. Then, 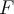 is an ordered field if there exists an order
is an ordered field if there exists an order 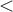 that satisfies which of the following properties?
that satisfies which of the following properties?
Choose one answer.
|
A. For any |
||
|
B. If |
||
|
C. If |
||
|
D. All of these. |
Question 6
Choose one answer.
|
A. Boundedness |
||
|
B. Finiteness |
||
|
C. Archimedean |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 7
For 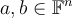 , which of the following inequalities is true?
, which of the following inequalities is true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 8
Two matrices are row equivalent if and only if
Choose one answer.
|
A. one can be obtained from the other by a finite number of elementary row operations. |
||
|
B. one is the negative of the other. |
||
|
C. the product of the two matrices is zero. |
||
|
D. none of these. |
Question 9
Which matrix below would you row reduce to solve the following system of equations?

Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
C. 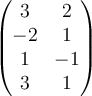 |
||
D. 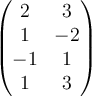 |
Question 10
The complex numbers 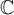 are a field in part because
are a field in part because
Choose one answer.
|
A. for every non-zero |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 11
Which of the following fields has the Archimedean property?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. Every finite field |
||
|
C. The field of rational functions with real coefficients |
||
|
D. None of these |
Question 12
Determine the angle between the vectors 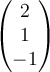 and
and 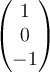 in
in  .
.
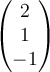 and
and 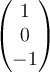 in
in
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 13
Which of the following computes the length of the vector 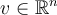 ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 14
According to the fundamental theorem of algebra, how many complex solutions does the equation 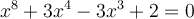 have, counted with multiplicity?
have, counted with multiplicity?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Eight |
||
|
B. At least one |
||
|
C. Exactly two |
||
|
D. Infinitely many |
Question 15
Fill in the blanks. Consider the polynomial 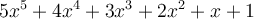 . Counted with multiplicity, this polynomial has ________ roots in
. Counted with multiplicity, this polynomial has ________ roots in 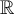 and ________ roots in
and ________ roots in 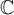 .
.
Choose one answer.
|
A. at least one; exactly five |
||
|
B. zero; exactly five |
||
|
C. exactly five; exactly five |
||
|
D. zero; exactly five |
Question 16
Calculate the determinant of 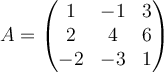 .
.
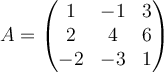 .
.
Choose one answer.
|
A. 24 |
||
|
B. 10 |
||
|
C. 12 |
||
|
D. 42 |
Question 17
Find the eigenvalues of 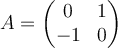 .
.
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 18
What are the eigenvalues of  ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Negative |
||
|
B. Real |
||
|
C. Complex |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 19
Calculate the eigenvalues of 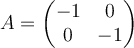 .
.
Choose one answer.
|
A. -1, degenerate |
||
|
B. 1, -1 |
||
|
C. 1 degenerate |
||
|
D. 0, -1 |
Question 20
17. If  , then compute
, then compute  and determine whether or not
and determine whether or not  is a normal matrix.
is a normal matrix.
 , then compute
, then compute
Choose one answer.
A. 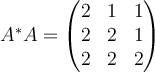 , , |
||
B. 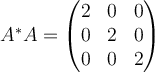 , , |
||
C. 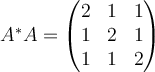 , , |
||
D. 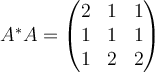 , , |
Question 21
The eigenvalues of a real skew-symmetric matrix must be
Choose one answer.
|
A. zero. |
||
|
B. non-negative. |
||
|
C. purely real. |
||
|
D. purely imaginary. |
Question 22
Determine the Jordan form for the  matrix
matrix 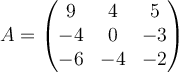 .
.
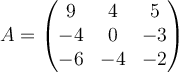 .
.
Choose one answer.
A. 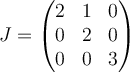 |
||
B. 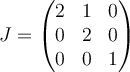 |
||
C. 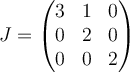 |
||
|
D. None of these |
Question 23
Compute the Jordan canonical form for the matrix 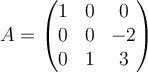 .
.
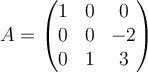 .
.
Choose one answer.
A. 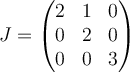 |
||
B. 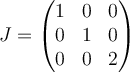 |
||
C. 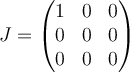 |
||
D. 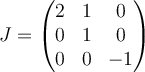 |
Question 24
The determinant rank of the matrix is 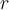 , where
, where 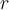 is the
is the
Choose one answer.
|
A. smallest number such that some |
||
|
B. largest number such that some |
||
|
C. largest number such that some |
||
|
D. none of these. |
Question 25
Suppose 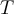 is the zero map defined by
is the zero map defined by 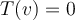 for all
for all 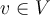 . Then what is an eigenvector of
. Then what is an eigenvector of 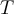 ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. Every nonzero vector |
||
|
D. All of these. |
Question 26
What does Schur’s Theorem say?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Every square matrix |
||
|
B. Every matrix |
||
|
C. Every matrix |
||
|
D. Every upper triangular matrix |
Question 27
For the set 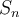 , which of the following properties is not true?
, which of the following properties is not true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Composition of permutations is associative. |
||
|
B. Composition of permutations is commutative. |
||
|
C. There is an identity element for composition. |
||
|
D. There is an inverse element for composition. |
Question 28
Fill in the blanks. Let  be an
be an 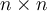 matrix. Then
matrix. Then 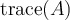 equals __________ and
equals __________ and 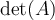 equals _________.
equals _________.
Choose one answer.
|
A. sum of the eigenvalues of |
||
|
B. product of the eigenvalues of |
||
|
C. sum of the eigenvalues of |
||
|
D. |
Question 29
What does the second derivative test tell us?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Whether or not critical points of a function exist |
||
|
B. Where the derivative is zero for certain types of functions |
||
|
C. Whether a critical point of a function is a local minimum or a maximum |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 30
Suppose 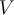 is a finite dimensional vector space and
is a finite dimensional vector space and 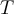 is a linear operator on
is a linear operator on 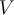 . Then which of the following conditions must be true for a subspace
. Then which of the following conditions must be true for a subspace 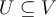 to be an invariant subspace under
to be an invariant subspace under 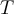 ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 31
Suppose 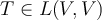 is a linear operator. Then
is a linear operator. Then 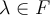 is an eigenvalue of
is an eigenvalue of 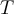 if and only if
if and only if
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 32
Let 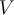 be a finite dimensional vector space and let
be a finite dimensional vector space and let 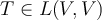 be invertible. Then
be invertible. Then 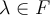 is an eigenvalue for
is an eigenvalue for 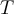 if and only if
if and only if
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. all of these. |
Question 33
If  is a real
is a real 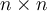 matrix and one of its eigenvalues is
matrix and one of its eigenvalues is 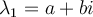 with eigenvector
with eigenvector 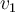 , then what can be said about another one of its eigenvalues and eigenvectors?
, then what can be said about another one of its eigenvalues and eigenvectors?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. None of these. |
Question 34
Suppose one eigenvalue of a real matrix  is
is 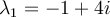 and the corresponding eigenvector is
and the corresponding eigenvector is 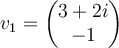 . Then which of the following must also be an eigenpair of
. Then which of the following must also be an eigenpair of  ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 35
Suppose that 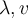 is an eigenpair of the invertible matrix
is an eigenpair of the invertible matrix  . Then
. Then 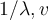 is an eigenpair of which of the following matrices?
is an eigenpair of which of the following matrices?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 36
A quadratic form in three dimensions can be written as  , where
, where  satisfies which of the following properties?
satisfies which of the following properties?
 , where
, where
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 37
Suppose at a critical point of a function 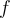 , the Hessian matrix is given by
, the Hessian matrix is given by 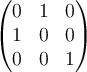 . Then what does the second derivative test tell us about this critical point?
. Then what does the second derivative test tell us about this critical point?
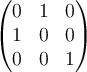 . Then what does the second derivative test tell us about this critical point?
. Then what does the second derivative test tell us about this critical point?
Choose one answer.
|
A. It is a local maximum. |
||
|
B. It is a local minimum. |
||
|
C. It is a saddle point. |
||
|
D. It is zero. |
Question 38
Let 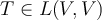 where
where 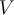 is an
is an 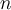 -dimensional
-dimensional 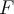 -vector space. Then
-vector space. Then 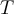 is guaranteed to have an eigenvalue when
is guaranteed to have an eigenvalue when
Choose one answer.
|
A. the minimal polynomial for |
||
|
B. the minimal polynomial for |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. the only |
Question 39
Let 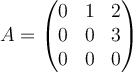 . Determine the Jordan normal form for
. Determine the Jordan normal form for  .
.
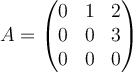 . Determine the Jordan normal form for
. Determine the Jordan normal form for
Choose one answer.
A. 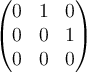 |
||
B. 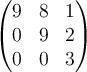 |
||
C. 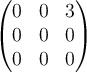 |
||
D. 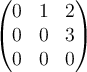 |
Question 40
What are the proper subspaces of 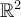 ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Trivial subspaces |
||
|
B. Lines through the origin |
||
|
C. Both A and B |
||
|
D. None of these |
Question 41
Let 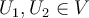 be subspaces, then
be subspaces, then 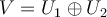 , if and only if two conditions hold. One is that
, if and only if two conditions hold. One is that  . What is the other condition?
. What is the other condition?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 42
Which of the following subsets of 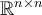 is NOT a subspace of
is NOT a subspace of 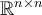 ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Symmetric matrices |
||
|
B. Diagonal matrices |
||
|
C. Nonsingular matrices |
||
|
D. Upper triangular matrices |
Question 43
Fill in the blank. The ___________ of 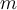 orthogonal vectors is
orthogonal vectors is 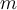 -dimensional.
-dimensional.
Choose one answer.
|
A. collection |
||
|
B. span |
||
|
C. kernel |
||
|
D. transformation |
Question 44
Which of the following is NOT a vector space associated with the 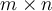 matrix
matrix  ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 45
Suppose  is a nonsingular
is a nonsingular 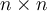 matrix. Then which of the following best describes its four fundamental subspaces?
matrix. Then which of the following best describes its four fundamental subspaces?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 46
If 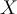 and
and 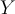 are subspaces of a vector space
are subspaces of a vector space 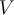 , then
, then 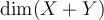 equals which of the following?
equals which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 47
Consider the following linear transformation 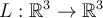 where
where 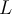 rotates each vector 90 degrees about the
rotates each vector 90 degrees about the 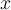 -axis. Find the matrix representation of
-axis. Find the matrix representation of 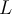 in the standard basis.
in the standard basis.
Choose one answer.
A.  |
||
B. 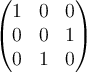 |
||
C. 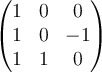 |
||
D.  |
Question 48
Which of the following is a basis of  ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 49
Let 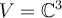 be a complex vector space. Let
be a complex vector space. Let 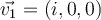 ,
, 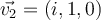 and
and 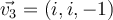 . Then, which of the following is true?
. Then, which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. None of these |
Question 50
Fill in the blank. A linear map 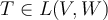 is _____________, if and only if
is _____________, if and only if 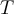 is injective and surjective.
is injective and surjective.
Choose one answer.
|
A. singular |
||
|
B. invertible |
||
|
C. continuous |
||
|
D. one-to-one |
Question 51
Let 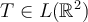 be such that
be such that 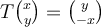 for all
for all 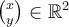 written in the standard basis. Then,
written in the standard basis. Then, 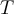 is a
is a
Choose one answer.
|
A. zero map. |
||
|
B. identity map. |
||
|
C. vector space. |
||
|
D. surjective linear map. |
Question 52
Consider the following linear transformation 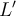 :
: 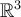 →
→ 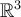 where
where 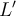 rotates each vector 90 degrees counterclockwise about the
rotates each vector 90 degrees counterclockwise about the 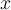 -axis and then rotates 45 degrees counterclockwise about the
-axis and then rotates 45 degrees counterclockwise about the  -axis. Find the matrix representation of
-axis. Find the matrix representation of 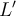 in the standard basis.
in the standard basis.
Choose one answer.
A. 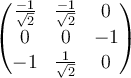 |
||
B. 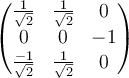 |
||
C. 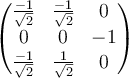 |
||
D. 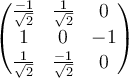 |
Question 53
Consider the following linear transformation 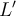 :
: 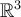 →
→ 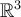 , where
, where 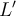 rotates each vector 90 degrees counterclockwise about the
rotates each vector 90 degrees counterclockwise about the 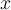 -axis and then rotates 45 degrees counterclockwise about the
-axis and then rotates 45 degrees counterclockwise about the  -axis. Find
-axis. Find 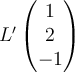 in the standard basis.
in the standard basis.
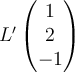 in the standard basis.
in the standard basis.
Choose one answer.
A. 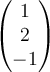 |
||
B. 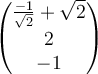 |
||
C. 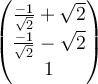 |
||
D.  |
Question 54
What is the characteristic polynomial of the matrix 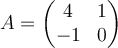 ?
?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 55
Let 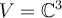 and let
and let 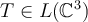 be defined by
be defined by 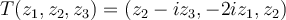 . Then what is the matrix,
. Then what is the matrix, 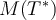 , for
, for 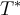 using the standard basis?
using the standard basis?
Choose one answer.
A. 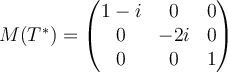 |
||
B. 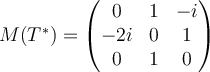 |
||
C. 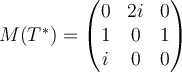 |
||
|
D. None of these |
Question 56
All  have a singular value decomposition, meaning there exists an orthonormal basis
have a singular value decomposition, meaning there exists an orthonormal basis  and
and 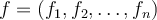 such that
such that 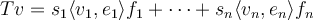 , where the
, where the 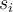 's are
's are
Choose one answer.
|
A. any positive numbers. |
||
|
B. singular values of |
||
|
C. complex values. |
||
|
D. obtained from the dot product of |
Question 57
An 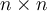 matrix
matrix 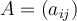 is called a Markov matrix if the following is satisfied:
is called a Markov matrix if the following is satisfied:
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 58
What can be said about eigenvalues of a Markov matrix?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Every eigenvalue |
||
|
B. Every eigenvalue |
||
|
C. Every eigenvalue |
||
|
D. All of these. |
Question 59
What does it mean for a matrix 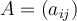 to be stochastic?
to be stochastic?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 60
If 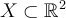 is the union of the coordinate axes, then
is the union of the coordinate axes, then 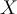 is NOT a real vector space because
is NOT a real vector space because
Choose one answer.
|
A. it is not closed under addition. |
||
|
B. it is infinite. |
||
|
C. it is not closed under multiplication. |
||
|
D. it does not contain a zero vector. |
Question 61
Suppose  ,
, 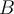 , and
, and 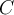 are invertible
are invertible 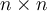 matrices. Which of the following is false?
matrices. Which of the following is false?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 62
Fill in the blank. Columns of an 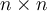 matrix
matrix  are an orthonormal basis for
are an orthonormal basis for  , if and only if
, if and only if  is a _____________ matrix.
is a _____________ matrix.
Choose one answer.
|
A. normal |
||
|
B. unitary |
||
|
C. symmetric |
||
|
D. square |
Question 63
Using the standard inner product, which of the following pairs are orthogonal vectors in 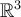 ?
?
Choose one answer.
A. 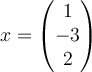 , , 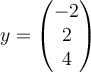 |
||
B. 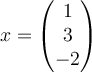 , ,  |
||
C. 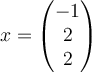 , , 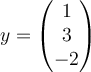 |
||
|
D. None of these |
Question 64
The spectral theorem states which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Normal operators are diagonal with respect to an orthonormal basis. |
||
|
B. Normal operators are diagonal with respect to a singular set of vectors. |
||
|
C. Nilpotent operators are diagonal with respect to an orthonormal basis. |
||
|
D. Semi-symmetric operators are diagonal with respect to any basis. |
Question 65
Given 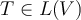 , the adjoint of
, the adjoint of 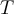 is defined to be the operator
is defined to be the operator 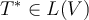 , such that which is true?
, such that which is true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. None of these |
Question 66
Which of the following best describes every eigenvalue of a self-adjoint operator?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Real |
||
|
B. Complex |
||
|
C. Degenerate |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 67
According to the spectral theorem, if 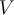 is a finite dimensional inner product space over
is a finite dimensional inner product space over 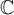 and
and 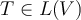 , then which of the following must be true?
, then which of the following must be true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. None of these. |
Question 68
What are operators that preserve the inner product called?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Orthogonal |
||
|
B. Isometries |
||
|
C. Normal |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 69
Which of the following is an example of a normal operator?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Symmetric matrices |
||
|
B. Hermitian matrices |
||
|
C. Orthogonal matrices |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 70
In order to unitarily diagonalize an 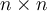 matrix
matrix  , what do you need to do?
, what do you need to do?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Find a unitary matrix |
||
|
B. Find a unitary matrix |
||
|
C. Find a unitary matrix |
||
|
D. Find a diagonal matrix |
Question 71
It is possible for an operator 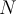 to be normal but not satisfy which of the following conditions?
to be normal but not satisfy which of the following conditions?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 72
For all 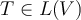 ,
, 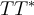 is
is
Choose one answer.
|
A. self-adjoint. |
||
|
B. nilpotent. |
||
|
C. orthogonal. |
||
|
D. diagonal. |
Question 73
Let 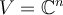 and let
and let 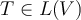 be a normal operator such that
be a normal operator such that 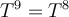 . Then, which of the following is true?
. Then, which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 74
If 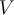 is a complex vector space and
is a complex vector space and 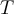 is a normal operator with only one distinct eigenvalue
is a normal operator with only one distinct eigenvalue 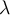 , then which of the following is true?
, then which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 75
Suppose 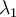 and
and 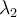 are two distinct eigenvalues of a real symmetric matrix
are two distinct eigenvalues of a real symmetric matrix  . Then what are their corresponding eigenvectors?
. Then what are their corresponding eigenvectors?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Similar |
||
|
B. Equal |
||
|
C. Orthogonal |
||
|
D. None of these |
Question 76
Which of the following properties should a norm on a normed linear space satisfy?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 77
According to the Cauchy-Schwarz inequality, on any inner product space which of the following must be true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 78
Fill in the blanks. Suppose 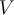 and
and 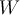 are inner product spaces,
are inner product spaces, 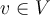 , and
, and 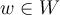 . Then the tensor product
. Then the tensor product 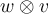 is an element of ______ defined by _______.
is an element of ______ defined by _______.
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 79
What is the Riesz representation theorem?
Choose one answer.
|
A. Let |
||
|
B. Let |
||
|
C. Let |
||
|
D. None of these. |
Question 80
A Hilbert space is
Choose one answer.
|
A. a complete inner product space. |
||
|
B. an inner product space. |
||
|
C. a normed space. |
||
|
D. none of these. |
Question 81
In an abstract vector space, what does the norm measure?
Choose one answer.
|
A. The angle between two vectors |
||
|
B. The length of a vector |
||
|
C. The direction of a vector |
||
|
D. All of these |
Question 82
Consider the vector space 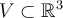 with basis vectors
with basis vectors 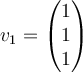 and
and 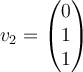 . Applying the Gram-Schmidt process to
. Applying the Gram-Schmidt process to 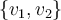 produces which orthonormal basis for
produces which orthonormal basis for 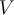 ?
?
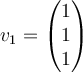 and
and 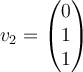 . Applying the Gram-Schmidt process to
. Applying the Gram-Schmidt process to
Choose one answer.
A. 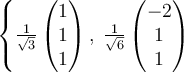 |
||
B.  |
||
C.  |
||
D. 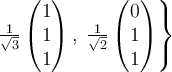 |
Question 83
If 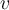 ,
, 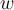 , and
, and 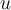 are three linearly independent vectors in
are three linearly independent vectors in 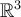 , then the volume of the parallelepiped determined by
, then the volume of the parallelepiped determined by 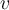 ,
, 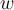 , and
, and 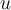 is
is
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 84
Let  be an
be an 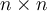 matrix with characteristic polynomial
matrix with characteristic polynomial 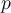 . Which of the following is true?
. Which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 85
Let 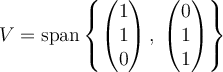 ,
, 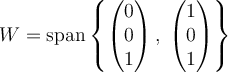 , and
, and 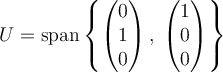 . Which of the following is true?
. Which of the following is true?
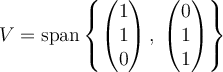 ,
, 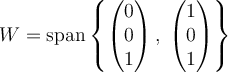 , and
, and 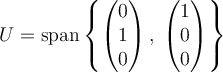 . Which of the following is true?
. Which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 86
Let 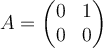 . Determine the range-nullspace decomposition of
. Determine the range-nullspace decomposition of 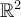 relative to
relative to  .
.
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 87
Let 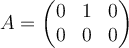 . If
. If 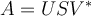 is the singular-value decomposition of
is the singular-value decomposition of  , then
, then
Choose one answer.
A. 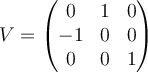 |
||
B. 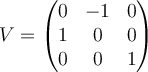 |
||
C. 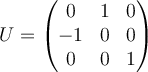 |
||
D. 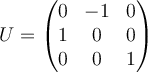 |
Question 88
Let 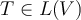 be a linear transformation. Suppose the matrix for
be a linear transformation. Suppose the matrix for  relative to a basis
relative to a basis  for
for 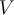 is
is 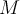 . Suppose
. Suppose  is the transition matrix from another basis
is the transition matrix from another basis 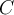 to
to 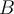 . Then the matrix for
. Then the matrix for 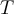 with respect to
with respect to 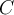 is
is
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
Question 89
Let 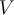 be an inner product space with inner product
be an inner product space with inner product 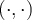 . Then the length of a vector
. Then the length of a vector 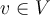 is
is
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |