1
Suppose G is a group of order 21, and H is a proper subgroup of order 3. How many distinct left cosets of H are there?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 18 |
||
|
b. 24 |
||
|
c. 7 |
||
|
d. 3 |
Question 2
Suppose G is a finite group of order 56, and H and K are proper subgroups of G, such that K is also a proper subgroup of H. If [G:K] = 14 and [H:K] = 2, what would [G:H] have to be equal to?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 7 |
||
|
b. 12 |
||
|
c. 24 |
||
|
d. 1 |
Question 3
Let G be a group of order p4, where p is prime. Which of the following statements must be true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. G is cyclic. |
||
|
b. G has a nontrivial center. |
||
|
c. G is isomorphic to S4 |
||
|
d. G has no proper subgroups. |
Question 4
Let G be a group of order 125. What is true of G’s center?
Choose one answer.
|
a. G’s center must be order 5 or 25. |
||
|
b. G has no trivial center. |
||
|
c. G is cyclic. |
||
|
d. G has no proper subgroups. |
Question 5
Suppose G is a finite abelian group. Suppose the center of G has order 11. Then, which if the following must be true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. G cannot be its own center. |
||
|
b. G cannot be cyclic. |
||
|
c. G must have order 11 or order 121. |
||
|
d. None of the above |
Question 6
Let G be a finite group with proper subgroups H, J and K. Further, let K ⊂ J ⊂ H. If [G:H] = 5, [H:J] = 3 and [J:K] = 7, what is [G:K]?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 15 |
||
|
b. 7 |
||
|
c. 1024 |
||
|
d. 371 |
Question 7
Suppose G is a group of order 98. Which of the following statements must be true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. G must contain a proper subgroup H of order 49. |
||
|
b. G must be abelian. |
||
|
c. G cannot contain a nontrivial center. |
||
|
d. G must be cyclic. |
Question 8
Suppose G is a group with proper subgroups H and K. Further, suppose K ⊂ H and that K has 12 left cosets in G and K has 3 left cosets in H. How many left cosets in G does H have?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 36 |
||
|
b. 9 |
||
|
c. 15 |
||
|
d. 4 |
Question 9
Suppose that G is an abelian group of order 270. To which of the following is G isomorphic?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Z18XZ15 |
||
|
b. Z10XZ9XZ3 |
||
|
c. Z2XZ27XZ5 |
||
|
d. Z6XZ9XZ5 |
Question 10
Suppose G is a finite subgroup of order 39. If H is a proper, nontrivial subgroup, what is the smallest order H might have?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 3 |
||
|
b. 13 |
||
|
c. 39 |
||
|
d. G cannot have a proper, nontrivial subgroup. |
Question 11
Suppose G is a finite subgroup of order 39. If H is a proper, nontrivial subgroup, what is the largest order H might have?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 3 |
||
|
b. 13 |
||
|
c. 39 |
||
|
d. G cannot have a proper, nontrivial subgroup. |
Question 12
Suppose we know that G is a group and that it has no trivial subgroups. Then, which of the following statements is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. G has a prime order. |
||
|
b. G can only be {e}. |
||
|
c. G can only be an infinite group. |
||
|
d. G cannot have cosets. |
Question 13
G is a finite group with proper, nontrivial subgroups H and J. Which of the following statements must be true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The order of H ∩ J must divide the order of G. |
||
|
b. H ∪ J = G. |
||
|
c. H has no nontrivial subgroups. |
||
|
d. J only has a trivial subgroup if H has one. |
Question 14
Let G be a finite group of order 63. If H and J are proper, nontrivial subgroups of G, H ≠ J, what is the largest order H ∩ J may have?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 21 |
||
|
b. 7 |
||
|
c. 3 |
||
|
d. 1 |
Question 15
Suppose G is some cyclic group order n. If we know for some a ∈ G that a5 = e and a11 = e, then what is the smallest order G may take?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1 |
||
|
b. 5 |
||
|
c. 11 |
||
|
d. 55 |
Question 16
Suppose G is an abelian group of order 270. Which of the following statements is false?
Choose one answer.
|
a. G will not have a subgroup of order 15. |
||
|
b. G cannot have a subgroup of order 3. |
||
|
c. G may not have a subgroup of order 30. |
||
|
d. G may have a normal subgroup of order 27. |
Question 17
Suppose G is some cyclic group of order 91. Let a ∈ G, such that an = e. What is the largest value n may take?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1 |
||
|
b. 7 |
||
|
c. 13 |
||
|
d. 91 |
Question 18
Let G be a group and H be one of G’s subgroups. If H has order 19 and has 5 left cosets in G, what is the order of G?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 5 |
||
|
b. 19 |
||
|
c. 95 |
||
|
d. 190 |
Question 19
Suppose K is the result of several intersections of proper subgroups of some finite abelian group G, with G having order 1024. What is true of K?
Choose one answer.
|
a. K has to be {e}. |
||
|
b. K has to have an order of 2. |
||
|
c. K has to have an order of 2n, where n ≤ 10. |
||
|
d. K has to be G. |
Question 20
Fill in the blank. Let G be a group G, and let H be a proper subgroup in G. If for all x, y ∈ G, and h ∈ H we know that xh = hy ∈ H implies that x = y, then ________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. G must be abelian |
||
|
b. H must be {e} |
||
|
c. H must be G |
||
|
d. H must be normal |
Question 21
Suppose that we know some group G contains the elements {a, b, c, d, e}, where e is the identity. What is the largest subgroup of G?
Choose one answer.
|
a. {e} |
||
|
b. {a, e} |
||
|
c. {a, c, e} |
||
|
d. G |
Question 22
Suppose some subgroup H of G has order 5 and suppose H ≠ G. If G is abelian, what is the smallest order G may have?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 5 |
||
|
b. 25 |
||
|
c. 125 |
||
|
d. 625 |
Question 23
Suppose G is a finite group and for every a ∈ G, n ∈ Z, an = e. What has to be true about G?
Choose one answer.
|
a. G has to have a prime order. |
||
|
b. G cannot be abelian. |
||
|
c. G has to have order of 1. |
||
|
d. G has to be empty. |
Question 24
Let G have a center of order 7 and let the center have 12 left cosets in G. What must be true about G?
Choose one answer.
|
a. G is not abelian. |
||
|
b. G has order 84. |
||
|
c. G may have subgroups of order 3 and 4. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
Question 25
Suppose G = {a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j} is a group. What are the only possible orders of subgroups of G?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1 |
||
|
b. 1,2 |
||
|
c. 1,2,5 |
||
|
d. 1,2,5,10 |
Question 26
Compute (5x2 + 3x - 4) + (4x2 - x + 9) in Z12.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 20x4 + 7x3 + 42x2 + 23x – 36 |
||
|
b. 9x2 + 2x + 5 |
||
|
c. 8x4 + 7x3 + 6x2 + 9x |
||
|
d. x2 – 4x – 13 |
Question 27
Fill in the blank. If a commutative ring R has no zero divisors (that is, if ab = 0, then either a = 0 or b = 0), then R is also called a(n) ________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Unique factorization ring |
||
|
b. Ideal |
||
|
c. Integral domain |
||
|
d. Module |
Question 28
Let R be an integral domain and let 3, b be elements in R. If 3b = 0, then what might b equal?
Choose one answer.
|
a. b might be equal to any multiple of 3. |
||
|
b. b must equal 0. |
||
|
c. b cannot be a multiple of 3. |
||
|
d. b must be the multiplicative inverse of 3. |
Question 29
If f(x) is an irreducible polynomial, with f(x) | p(x)q(x), then which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. f(x) is a zero divisor. |
||
|
b. f(x) = either p(x) or q(x). |
||
|
c. f(x) | p(x) or f(x) | q(x) |
||
|
d. f(x) = p(x)q(x). |
Question 30
Let F be a field and let a(x) = p(x)q(x) + r(x) have coefficients in F. Then, which of the following statements is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. r(x) must be the zero polynomial. |
||
|
b. deg r(x) must be less than deg q(x). |
||
|
c. r(x) must be irreducible. |
||
|
d. deg r(x) must be zero. |
Question 31
Suppose f(x) is a polynomial with rational coefficients. If f(x) can be expressed as the product of two non-constant polynomials p and q, then what must be true of p and q?
Choose one answer.
|
a. p and q cannot have the same degrees. |
||
|
b. p and q MUST have the same degrees. |
||
|
c. The degrees of p and q must be smaller than the degree of f. |
||
|
d. f must be a monic polynomial. |
Question 32
If F is an integral domain, and f(x) is a polynomial with coefficients in F, then which of the following is true of f(x)?
Choose one answer.
|
a. f(x) is irreducible. |
||
|
b. f(x) must have a unique factorization. |
||
|
c. f(x) is either irreducible or factorable. |
||
|
d. f(x) is a constant polynomial. |
Question 33
If F is an integral domain and every polynomial with coefficients in F can be factored in distinct ways, then what is true of F?
Choose one answer.
|
a. F is a unique factorization domain. |
||
|
b. F must be a field. |
||
|
c. F must be a module. |
||
|
d. F must be a commutative ring. |
Question 34
If a ring R of square matrices under matrix addition and cross multiplication is isomorphic to a commutative ring, then what must be true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. R must be a UFD. |
||
|
b. R must be of finite order. |
||
|
c. R must be a commutative ring. |
||
|
d. The image of R must be the set of rational numbers. |
Question 35
Which of the following statements is true of a subring of a commutative ring?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A subring of a commutative ring must itself be commutative. |
||
|
b. A subring of a commutative ring may not be commutative. |
||
|
c. A subring of a commutative ring may not be associative under multiplication. |
||
|
d. A subring of a commutative ring is always a prime ideal. |
Question 36
Fill in the blank. Suppose R is a commutative ring such that for a, b, and c in R, ab = ac implies b = c. At the very least, R has to be a(n) _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. UFD |
||
|
b. Field |
||
|
c. Prime ideal |
||
|
d. Integral domain |
Question 37
Which of the following is true of a ring with a zero divisor?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It can never be an integral domain. |
||
|
b. It may be an integral domain if it is commutative. |
||
|
c. It is a UFD. |
||
|
d. It is a prime ideal. |
Question 38
B A field is a commutative division ring.
Choose one answer.
|
a. A field has no zero divisors. |
||
|
b. A division ring has no unity. |
||
|
c. A division ring may have non-zero elements that have no inverses under multiplication. |
Question 39
Fill in the blank. Let R be a Boolean ring. Then, for every a in R, a2 = a. Then, R must be ________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Finite |
||
|
b. A non-trivial ideal |
||
|
c. Commutative |
||
|
d. A field |
Question 40
Suppose L is a lattice. Then, which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Each element is divisible by all the elements less than itself. |
||
|
b. Each element is equal to all other elements in L. |
||
|
c. L has a partial order defined on it. |
||
|
d. L has to be a Boolean algebra. |
Question 41
Which of the following best describes Boolean algebras?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Boolean algebras are ring-like structures that form incomplete lattices. |
||
|
b. Boolean algebras are ring-like structures that have no zero elements. |
||
|
c. Boolean algebras are ring-like structures that use both set and logic operations. |
||
|
d. Boolean algebras are ring-like structures that have no unique upper and lower bounds. |
Question 42
What does the following lattice best represent?
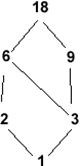
Choose one answer.
|
a. A partial ordering of the unique divisors of 18 |
||
|
b. A random walk between points 1 and 18 |
||
|
c. A process map of steps in a program, where numbers represent called subroutines |
||
|
d. All of the above |
Question 43
Boolean algebras are useful for their ability to do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Represent complex circuitry |
||
|
b. Assist in finding exploits in a computer network |
||
|
c. Represent physical security layouts |
||
|
d. Locate trends in a social network |
Question 44
Which of the following terms is defined as a complemented, distributed lattice?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A module |
||
|
b. A partially ordered set |
||
|
c. An invertible matrix |
||
|
d. A Boolean algebra |
Question 45
If a polynomial of degree n is factorable, then what must be true of any factor?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The degree of the factor must be less than n. |
||
|
b. The degree of the factor must be 0. |
||
|
c. The degree of the factor must be 1. |
||
|
d. The degree of the factor must divide n evenly. |
Question 46
Let f be a polynomial with rational coefficients and let it be factorable into two polynomials p and q. If deg p(x) = j and deg q(x) = k, then what must the degree of f be?
Choose one answer.
|
a. deg f(x) = 1. |
||
|
b. deg f(x) = 0. |
||
|
c. deg f(x) = jk. |
||
|
d. There is not enough information given to determine the answer. |
Question 47
Fill in the blank. The property that says that if a, b are in some set R and (a,b), (b,a) are both in some relation, P implies that a = b is called the _______________ property.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Transitive |
||
|
b. Reflexive |
||
|
c. Antisymetric |
||
|
d. Symmetric |
Question 48
Let X = {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12, 24} be the set of divisors of 24, and let M = {2,3,4,6} be a proper subset of X. What is the least upper bound of M?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 6 |
||
|
b. 12 |
||
|
c. 24 |
||
|
d. There is no least upper bound. |
Question 49
Fill in the blank. Suppose a lattice L has a largest element I and a smallest element O, and there exists binary operations ⋀ and ⋁ on the elements of L. If for every a in L, there exists an a' in L such that a ⋀ a' = O and a ⋁ a' = I, we say that L is _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Invertible |
||
|
b. Commutative |
||
|
c. Complemented |
||
|
d. Associative |
Question 50
Which of the following is an example of Boolean algebra?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Power set of some random set X |
||
|
b. Any finite group |
||
|
c. A group with a prime order |
||
|
d. Any commutative ring |
Question 51
Fill in the blank. The _______________ of real numbers, denoted by Rn, form a vector space over R.
Choose one answer.
|
a. n-tuples |
||
|
b. n-dimensional arrays |
||
|
c. Power set of any n elements |
||
|
d. Set of all permutations of any n elements |
Question 52
What is a vector space?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A vector space is a non-abelian ring made up of n-tuples. |
||
|
b. A vector spaces is an abelian ring made up of n-tuples. |
||
|
c. A vector space is a non-abelian group extended by scalar multiplication. |
||
|
d. A vector spaces is an abelian group extended by scalar multiplication. |
Question 53
Choose the best answer to fill in the blanks. A subset of a vector space is itself a vector space (called a subspace), if it is closed under _______________ multiplication and ______________ addition.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Scalar, scalar |
||
|
b. Vector, vector |
||
|
c. Scalar, vector |
||
|
d. Vector, scalar |
Question 54
A set of all linear combinations of some vector set V is called which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. V’s combination class |
||
|
b. V’s spanning set |
||
|
c. V’s linear representation |
||
|
d. V’s rank |
Question 55
Fill in the blank. Let S be a set of vectors of some n-dimensional vector space V. If there exist scalars a1 through an, such that a1v1 + … + anvn = 0, but not all a’s = 0, then S is said to be linearly _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Independent |
||
|
b. Combined |
||
|
c. Dependent |
||
|
d. Represented |
Question 56
If S, a set of vectors of V, spans V, then S is said to be a _______________ of V.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Representation |
||
|
b. Projection |
||
|
c. Basis |
||
|
d. Linear combination |
Question 57
Fill in the blank. A mapping of a set V onto itself that changes the spanning set of V is called a change of _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Status |
||
|
b. Basis |
||
|
c. Identification |
||
|
d. Projection |
Question 58
An nxn matrix M can only change a basis for an n-dimensional vector space if which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. M is nonsingular. |
||
|
b. M has a 0 determinant. |
||
|
c. M has rank less than n. |
||
|
d. M cannot be reduced to I by row operations. |
Question 59
What is the product of a 5 X 3 matrix and a 3 X 4 matrix?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A 3 X 3 matrix |
||
|
b. A 4 X 5 matrix |
||
|
c. A 15 X 12 matrix |
||
|
d. A 5 X 4 matrix |
Question 60
A homomorphism between two vector spaces can always be represented by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A power set |
||
|
b. An abelian group |
||
|
c. A projection |
||
|
d. A matrix |
Question 61
Fill in the blank. The rank of a matrix must be _______________ the rank of a map it represents.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Less than |
||
|
b. Greater than |
||
|
c. Equal to |
||
|
d. At least one less than |
Question 62
Which of the following can serve as a change of basis map for a n-dimensional space?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A lattice of n partially ordered elements |
||
|
b. An invertible nxn matrix |
||
|
c. Any nxn matrix |
||
|
d. A pair of n-tuples |
Question 63
Fill in the blank. The composition of linear maps is a ________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Scalar |
||
|
b. Single vector |
||
|
c. Linear map |
||
|
d. Non-reversible projection |
Question 64
Fill in the blank. The rank of a linear map is also the dimension of the map’s _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Range space |
||
|
b. Null space |
||
|
c. Domain |
||
|
d. Projection space |
Question 65
The dimension of a map’s domain is equal to which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The dimension of its rank |
||
|
b. The dimension of its nullity |
||
|
c. The sum of its rank and nullity |
||
|
d. None of the above |
Question 66
Fill in the blank. The kernel of a linear map from vector space V to vector space W is the inverse image of W’s ______________ vector.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Unity |
||
|
b. Zero |
||
|
c. Largest |
||
|
d. Smallest |
Question 67
Fill in the blank. The rank of a linear map is only equal to the dimension of the map’s domain if the nullity of the map is _________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Exactly zero |
||
|
b. Exactly one |
||
|
c. The multiplicative identity vector |
||
|
d. The rank of the map’s codomain |
Question 68
A linear map that is one-to-one must have which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An invertible matrix |
||
|
b. A singular matrix |
||
|
c. A non-trivial nullity |
||
|
d. rank less than the domain |
Question 69
Which of the following statements is true of a vector homomorphism?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It is always onto and one-to-one. |
||
|
b. It is always onto but not necessarily one-to-one. |
||
|
c. It is always one-to-one but not necessarily onto. |
||
|
d. It is not always one-to-one nor onto. |
Question 70
What is a vector homomorphism that is one-to-one and onto called?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A linear map |
||
|
b. An isomorphism |
||
|
c. A projective map |
||
|
d. A change of representation |
Question 71
An isomorphism maps a zero vector in one space to which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A non-trivial kernel in another |
||
|
b. The zero vector of another |
||
|
c. The multiplicative identity of another |
||
|
d. The entire span of another |
Question 72
An isomorphism preserves which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Rank |
||
|
b. Identity |
||
|
c. Structure |
||
|
d. All of the above |
Question 73
What is an isomorphism?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An isomorphism is a type of equivalence relation. |
||
|
b. An isomorphism is a type of lattice. |
||
|
c. An isomorphism is a type of Boolean algebra. |
||
|
d. An isomorphism is a type of non-invertible function. |
Question 74
What is an isomorphism from V onto itself called?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A self-projection |
||
|
b. A reversible map |
||
|
c. A power map |
||
|
d. An automorphism |
Question 75
Fill in the blank. Vector spaces are isomorphic if, and only if, the vector spaces have _________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. A linear map between them |
||
|
b. The same identity |
||
|
c. The same dimension |
||
|
d. The same kernel |
Question 76
Fill in the blank. The set of all field automorphisms is a group under _________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Set addition |
||
|
b. Composition of functions |
||
|
c. Translations of axes |
||
|
d. Matrix multiplication |
Question 77
What is the set of all automorphisms of some field extension E of a field F that fix F elementwise called?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The power set of E over F |
||
|
b. The Galois group of E over F |
||
|
c. The super group of E over F |
||
|
d. The kernel of E over F |
Question 78
Fill in the blank. Complex conjugation (f: a + bi ⇒ a – bi) is a(n) ______________ of the complex numbers.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Automorphism |
||
|
b. Bifurcation |
||
|
c. Splitting field |
||
|
d. Radial transformation |
Question 79
If E is a field extension of F and f(x) is a polynomial in F|x|, then any automorphism in G(E/F) defines which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A permutation of the roots of f(x) that lie in E |
||
|
b. A projection of the kernel of F in E |
||
|
c. A bijection from all elements in E to all elements in F |
||
|
d. None of the above |
Question 80
Fill in the blank. Let E be an algebraic extension of a field F. If every irreducible polynomial in F|x| with a root in E has ALL its roots in E, then E is called a _________________ extension of F.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Galois |
||
|
b. Projective |
||
|
c. Normal |
||
|
d. Power |
Question 81
E being a finite, normal, separable extension of F is the same as saying which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. F is a splitting field over E of a separable polynomial. |
||
|
b. E is a Galois group of F. |
||
|
c. F is a Galois group of E. |
||
|
d. F = EG for some finite group of aut(E). |
Question 82
Which of the following statements about the Galois group of E over F is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Galois group of E over F is infinite. |
||
|
b. Galois group of E over F is abelian. |
||
|
c. Galois group of E over F has order equal to F. |
||
|
d. Galois group of E over F has a non-trivial center. |
Question 83
What is a root of multiplicity of 1 called?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Simple root |
||
|
b. Solitary root |
||
|
c. Unitary root |
||
|
d. Sole root |
Question 84
Suppose E is a field extension of F and further suppose there existed an element a in E such that F(a) = E. What is such an element called?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A simple element |
||
|
b. A solitary element |
||
|
c. A primitive element |
||
|
d. A unitary element |
Question 85
Fill in the blank. If every element in E, which is an extension of F, is a root of a separable polynomial in F|x|, then E is called a ________________ extension of F.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Separable |
||
|
b. Galois |
||
|
c. Simple |
||
|
d. Primitive |
Question 86
Fill in the blank. A Galois group of E over F is a group of automorphisms of E that _______________ F elementwise (that is, f: Aut(E), such that f(a) = a for all a in F).
Choose one answer.
|
a. Fixes |
||
|
b. Transposes |
||
|
c. Translates |
||
|
d. Rotates |
Question 87
What is the set of all automorphisms of an extension field that fix elements of the extended field called?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Commutative ring |
||
|
b. Abelian group |
||
|
c. Extended group |
||
|
d. Vector field |
Question 88
Fill in the blank. Suppose E is a finite separable extension of a field F, then there must exist an element m in E, such that _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. E = F(m) |
||
|
b. F = E(m) |
||
|
c. F = E |
||
|
d. m = e(m) |
Question 89
Fill in the blank. If F is a field and G is a subgroup of Aut(F), then the set {a in F, such that f(a) = a for all f in G} is a ________________ of F.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Galois group |
||
|
b. Communtator ring |
||
|
c. Subfield |
||
|
d. Noncommutative subring |
Question 90
Fill in the blank. If f(x) in F|x| of degree n has n distinct roots in F’s splitting field E, then f is ________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Fixed |
||
|
b. Separable |
||
|
c. Simple |
||
|
d. Complex |
Question 91
Suppose f(x) is irreducible over F. If F has characteristic 0, then which is true of f(x)?
Choose one answer.
|
a. f(x) is separable. |
||
|
b. f(x) is a linear transformation. |
||
|
c. f(x) is the kernel of F. |
||
|
d. f(x) is an element of the automorphism of an extension field of F. |
Question 92
Fill in the blank. A function f(x) is separable if it has n distinct roots in F’s ________________ field E.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Extension |
||
|
b. Splitting |
||
|
c. Fixed |
||
|
d. Embedded |
Question 93
Which of the following of the automorphisms of F is a subfield of F?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A general extension field |
||
|
b. A fixed field |
||
|
c. A power set |
||
|
d. A symmetric group |
Question 94
Fill in the blank. A ______________ of a field F is a field E containing an element x, such that E = F(x).
Choose one answer.
|
a. Separable extension |
||
|
b. Prime ideal |
||
|
c. Quotient ring |
||
|
d. Galois group |
Question 95
Fill in the blank. The Galois group of some field E over F has a(n) _______________ center.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Trivial |
||
|
b. Non-trivial |
||
|
c. Normal |
||
|
d. Extended |
Question 96
Fill in the blank. A simple root of some polynomial has multiplicity of _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0 |
||
|
b. 1 |
||
|
c. 2 |
||
|
d. 3 |
Question 97
Fill in the blank. If a polynomial of degree n in F that has fewer than n roots in an extension field E, then E cannot be _________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Simple |
||
|
b. Complex |
||
|
c. Separable |
||
|
d. F’s extension field |
Question 98
Fill in the blank. If an irreducible polynomial f has characteristic 0, then f is _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Monic |
||
|
b. Separable |
||
|
c. Simple |
||
|
d. Algebraic |
Question 99
Fill in the blank. If some extension field E over F does not contain all the roots of F, then E cannot be ________________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. Separable |
||
|
b. Primitive |
||
|
c. Solvable |
||
|
d. Monic |
Question 100
A Galois group is a subgroup of which group of automorphisms?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Permutation |
||
|
b. Power |
||
|
c. Partially ordered |
||
|
d. Separable |