1
Fill in the blank. A flow is considered to be compressible if its Mach number is greater than _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0.03 |
||
|
b. 0.3 |
||
|
c. 5 |
||
|
d. 1 |
Question 2
Fill in the blank. Transition from a laminar pipe flow to a turbulent flow typically occurs with a Reynolds number in the range of _______________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 2,300-4,000 |
||
|
b. 500-1,000 |
||
|
c. 105 -106 |
||
|
d. 50,000-100,000 |
Question 3
For a laminar pipe flow, how does the friction factor change when the Reynolds number increases?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The friction factor decreases. |
||
|
b. The friction factor is kept constant. |
||
|
c. The friction factor increases. |
||
|
d. None of the above |
Question 4
What are the dimensions of surface tension?
Choose one answer.
|
a. M L-1 |
||
|
b. M L-1T-2 |
||
|
c. M2L-1T |
||
|
d. M-1T-2 |
Question 5
What does a barometer measure?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Thermal conductivity |
||
|
b. Wind velocity |
||
|
c. Atmospheric pressure |
||
|
d. Relative humidity |
Question 6
What does the Froude number measure?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces. |
||
|
b. The ratio of surface tension to inertial forces. |
||
|
c. The ratio of inertial forces to gravitational forces. |
||
|
d. The ratio of momentum diffusivity to thermal diffusivity. |
Question 7
What does the Reynolds number measure?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The ratio of inertial forces ρV2/L to viscous forces μV/L2 |
||
|
b. The ratio of surface tension to inertial forces |
||
|
c. The ratio of gravitational force to fluid’s inertia |
||
|
d. The ratio of momentum diffusivity to thermal diffusivity |
Question 8
What is a laminar pipe flow?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Movement of fluid slowly in layers in a pipe, without much mixing among the layers |
||
|
b. A flow whose Reynolds number exceeds 2300 |
||
|
c. Movements of fluid are chaotic with significant mixing |
||
|
d. None of the above |
Question 9
What is the pressure on a given object?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Pressure is the force divided by the area over which the force is applied. |
||
|
b. Pressure is equal to surface tension. |
||
|
c. Pressure is the force times the area over which the force is applied. |
||
|
d. Pressure is equal to the object’s acceleration times its mass. |
Question 10
Which of the following dimensionless numbers is used to compare surface tension against inertial forces?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Reynolds number |
||
|
b. Weber number |
||
|
c. Prandtl number |
||
|
d. Froude number |
Question 11
Which of the following is a streamline?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The locus of points of all the fluid particles that have passed through a given point |
||
|
b. A family of curves, which are normal to the velocity vector of the flow |
||
|
c. A family of curves that track the trajectories of fluid particles |
||
|
d. A family of curves that are instantaneously tangent to the velocity vector of the flow |
Question 12
Which of the following is NOT a dimensionless number?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Pressure coefficient |
||
|
b. Mach number M |
||
|
c. Gas constant R |
||
|
d. Friction factor f |
Question 13
Which of the following is the definition of Froude number?
Choose one answer.
|
a. V2/Lg |
||
|
b. µ VL/ρ |
||
|
c. VL/σ |
||
|
d. None of the above |
Question 14
Which of the following statement about streamlines is false?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Streamlines cannot cross each other. |
||
|
b. Streamlines provide a snapshot of the entire flow field. |
||
|
c. Streamlines track trajectories of fluid particles. |
||
|
d. The tangent at each point on a streamline is the direction of the velocity vector at that point. |
Question 15
Which of the following statements about fully developed pipe flows is false?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The streamwise velocity component satisfies uz = 0. |
||
|
b. “Boundary layers” from opposite sides of the pipe are separated and continue growing. |
||
|
c. The radial component of the velocity is zero. |
||
|
d. The entrance length depends on the Reynolds number. |
Question 16
Which of the following statements about surface tension is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Surface tension is responsible for the weight of liquid droplets. |
||
|
b. Surface tension is measured in forces per unit length or of energy per unit area. |
||
|
c. Surface tension is responsible for buoyancy. |
||
|
d. None of the above |
Question 17
Which of the following statements about the Moody chart is false?
Choose one answer.
|
a. In the laminar zone, friction factor decreases as the Reynolds number increases. |
||
|
b. In the turbulent zone, friction factor increases as the relative roughness (D/ε) increases. |
||
|
c. Within the zone of complete turbulence, friction factor is independent of Reynolds number. |
||
|
d. As relative roughness increases, the boundary of the complete turbulence zone shifts to the right. |
Question 18
Which of the following statements about viscosity is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Viscosity of a fluid depends strongly on its temperature. |
||
|
b. Viscosity measures the friction between the fluid and the wall. |
||
|
c. Shear stress is independent of viscosity. |
||
|
d. For a given rate of angular deformation of a fluid, shear stress is inversely proportional to viscosity. |
Question 19
A liquid with a specific gravity of 0.8 forms a layer of 2 m deep in a tank. There is nothing on top of the liquid except for air. What is the gage pressure at the bottom of the tank?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 15.7 kPa |
||
|
b. 25.3 kPa |
||
|
c. 3.21 kPa |
||
|
d. 1.24 kPa |
Question 20
Calculate the entrance length of a flow of water in a pipe with diameter of 10 cm. The Reynolds number of the flow is 1000.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1 m |
||
|
b. 60 cm |
||
|
c. 6 m |
||
|
d. 20 cm |
Question 21
Calculate the speed of sound in an ideal gas (γ = 1.4) at temperature 273°K.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 331.3 m/s |
||
|
b. 13.2 m/s |
||
|
c. 1520.2 m/s |
||
|
d. 212.5 m/s |
Question 22
Calculate the total hydrostatic force acting on the roof of a semicircular tunnel built under a lake. The tunnel is 1600 feet long and has a diameter of 30 feet. The distance from the top of the tunnel to the water surface is 120 feet.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1.14 108 lbf |
||
|
b. 4.14 108 lbf |
||
|
c. 6.14 108 lbf |
||
|
d. 9.14 108 lbf |
Question 23
Consider a flow of water (ρ = 998 kg/m3, µ = 10-3 N∙s/m2) through a straight smooth pipe with a diameter of 1 cm. Approximately, what is the velocity of the flow at which transition to turbulence occurs?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0.06 m3/s |
||
|
b. 1.2 m3/s |
||
|
c. 0.01 m3/s |
||
|
d. 0.12 cm3/s |
Question 24
Consider a steady incompressible flow with velocity field: u(x, y, z) = 3x + y + z, v(x, y, z) = -y + 5x + 3z, w(x, y, z) = Cz + x + y, where C is a constant. Calculate the value of C so the given flow is physically possible.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 3 |
||
|
b. 5 |
||
|
c. 12 |
||
|
d. -2 |
Question 25
Consider a steady, incompressible flow with a velocity distribution given as V = axi + byj + 0k, where a and b are constants. What is the relationship between a and b required to satisfy the principle of mass conservation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. a = b |
||
|
b. a = 2b |
||
|
c. a = -b |
||
|
d. a = -2b |
Question 26
Consider a steady, incompressible flow with a velocity distribution given as V = 5xi + 3yj + Czk, where C is a constant. What is the value of C so that the principle of mass conservation is satisfied?
Choose one answer.
|
a. -3 |
||
|
b. 2 |
||
|
c. 32 |
||
|
d. -8 |
Question 27
Glycerin (ρ = 1258 kg/m3, µ = 0.96 Pa∙s) flows in a pipe with a diameter of 15 cm. What is the characteristic of the flow if its velocity is 4 m/s?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Supersonic |
||
|
b. Both turbulent and laminar |
||
|
c. Turbulent |
||
|
d. Laminar |
Question 28
The absolute viscosity of oil is 0.1 kg/m∙s. Its specific gravity is 0.8. Calculate kinematic viscosity of the oil.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1.55 10-4 m2/s |
||
|
b. 1.25 10-4 m2/s |
||
|
c. 0.5 10-4 m2/s |
||
|
d. 1.55 10-6 m2/s |
Question 29
The specific gravity of oil is 0. Calculate the pressure represented by a 5 cm column of oil.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 367 N/m2 |
||
|
b. 65 N/m2 |
||
|
c. 550 N/m2 |
||
|
d. 107 N/m2 |
Question 30
The speed of sound in an ideal gas at temperature 200°K is 100 m/s. What is the speed of sound of the same gas at temperature 800°K?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 100 m/s |
||
|
b. 400 m/s |
||
|
c. 200 m/s |
||
|
d. 50 m/s |
Question 31
Water is supplied to a 1.5 hP pump at a flow rate of 250 gal/min. What is the maximum height this water jet can achieve?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 15 m |
||
|
b. 50 m |
||
|
c. 12 m |
||
|
d. 8 m |
Question 32
What is the shear stress τxy at point (x, y, z) of an incompressible fluid flow with the following velocity distribution V = 5xi + 6yj + 0k? The viscosity of the fluid is µ.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 11 µ |
||
|
b. 0 |
||
|
c. µ |
||
|
d. 2 µ |
Question 33
What is the shear stress τxy at point (x, y, z) of an incompressible fluid flow with the following velocity distribution V = 50yi + 12xj + 0k? The viscosity of the fluid is µ.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 62 µ |
||
|
b. 0 |
||
|
c. 22µ |
||
|
d. 38 µ |
Question 34
The velocity distribution in a boundary layer near a wall is given by u = 2 sin(5πy). The viscosity of the fluid is µ. What is the shear stress on the wall at y = 0?
Choose one answer.
|
a. µ |
||
|
b. 10µ |
||
|
c. 20πµ |
||
|
d. 10πµ |
Question 35
A ping-pong ball with a diameter of 3.8 cm is suspended in an upward airflow. The density of the air is 1.184 kg/m3. The air velocity is 33.5 km/h. The drag coefficient is 0. What is the weight of the ping-pong ball?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0.5 g |
||
|
b. 2.6 g |
||
|
c. 5.2 g |
||
|
d. 7.9 g |
Question 36
A tank of water with uniform area of cross section A has a hole at its bottom with an area of a. There was a water column of 4 m height in the tank initially. It took 5 second for the water level in the tank to reduce to 1 m. How long did it take totally to empty the whole tank?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 10 s |
||
|
b. 12 s |
||
|
c. 7 s |
||
|
d. 20 s |
Question 37
A water jet strikes normal to a fixed vertical plate. The diameter of the jet is 2 cm. The velocity is 1 m/s. What is the force of the jet acting on the plate? (Hint: Neglect friction and gravitation forces.)
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1.26 N |
||
|
b. 5.23 N |
||
|
c. 2.12 N |
||
|
d. 0.12 N |
Question 38
A water jet strikes normal to a fixed vertical plate. A force of 31.4 N is needed to keep the plate in place. The diameter of the jet is 5 cm. What is the velocity of the jet?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 5 m/s |
||
|
b. 1 m/s |
||
|
c. 2 m/s |
||
|
d. 0.5 m/s |
Question 39
A water vessel has a 2-m-high and 1-m-wide gate in its vertical wall. The top of the gate is at the level of the water surface. Calculate the hydrostatic force acting on the gate.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 31.1 kN |
||
|
b. 27.2 kN |
||
|
c. 19.6 kN |
||
|
d. 59.5 kN |
Question 40
Air flows over a sharp flat plate with a velocity of 2.5 m/s. Calculate the thickness of the boundary layer about 50 cm away from the edge. Density and kinematic viscosity of air are 1.2 kg/m3 and 1.5 10-5 m2/s, respectively.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 7.6 mm |
||
|
b. 5.3 mm |
||
|
c. 1.2 mm |
||
|
d. 8.7 mm |
Question 41
Calculate the total or stagnation pressure at the nose of an aircraft, which is in steady level flight at sea level. The standard temperature and pressure at sea level is 581.69°R and 2116.2 lb/ft2. The specific heat ratio γ and the gas constant for air are 1.4 and 1716 ft-lb/slug-R, respectively. The airspeed of the aircraft is 300 mph.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0.15 psi |
||
|
b. 1.24 psi |
||
|
c. 16.3 psi |
||
|
d. 350 psi |
Question 42
Pressure drop in a fully developed flow of oil in a smooth and straight pipe is 2500 kPa per meter. The specific gravity of oil is 0.9 and its viscosity is 0.1 kg/m.s. The diameter of the pipe is 5 cm. What is the flow rate?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1.2 l/s |
||
|
b. 3.9 l/s |
||
|
c. 45.1 l/s |
||
|
d. 0.2 l/s |
Question 43
Water flows in a pipe with a roughness ε of 8 10-4 ft. The diameter D of the pipe is 1 inch. The flow velocity is 30 ft/s. The kinematic viscosity of water is 4.38 x 10-6 ft2/s. Determine the friction factor.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0.0004 |
||
|
b. 0.004 |
||
|
c. 0.04 |
||
|
d. 0.4 |
Question 44
Oil flows in a pipe of diameter of 15 cm. The mass flow rate is 14.17 l/s. The viscosity and density of oil are 0.1041 Pa∙s and 917 kg/m3. What is the approximate pressure drop in the pipe per meter?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 119 Pa/m |
||
|
b. 1049 Pa/m |
||
|
c. 22 Pa/m |
||
|
d. 11 Pa/m |
Question 45
Capillary viscometer.
You have already measured the density of an unknown fluid and found it to be 1.35 g/ml. You wish to determine the fluid viscosity from measurement of the pressure drop through a 1 mm ID by 1 m long capillary as a function of the flow rate. For a flow rate of 45 ml/min, you find the pressure drop to be.
Which of the following is the best estimate of the fluid viscosity?
You have already measured the density of an unknown fluid and found it to be 1.35 g/ml. You wish to determine the fluid viscosity from measurement of the pressure drop through a 1 mm ID by 1 m long capillary as a function of the flow rate. For a flow rate of 45 ml/min, you find the pressure drop to be.
Which of the following is the best estimate of the fluid viscosity?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 5.3 mPa s |
||
|
b. 0.005 cP |
||
|
c. 5.3 Pa s |
||
|
d. 5.3 P |
Question 46
Consider water flowing through a 10 m section of 4 inch ID smooth pipe followed by an abrupt contraction to a 1 m section of 0.25 inch ID smooth pipe. If the water is flowing at 2 gal/min, calculate the total pressure drop over the two sections (remember to include the effect of the contraction).
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0.3 atm |
||
|
b. 0.03 atm |
||
|
c. 3 Pa |
||
|
d. 30 Pa |
Question 47
Dimensional Analysis. Which of the following groups is proportional to a Reynolds number for flow in a pipe? (Mf = mass flow rate, D = pipe diameter, ρ = fluid density, v = fluid velocity, μ = dynamic viscosity).
Choose one answer.
|
a. Mf D v/μ |
||
|
b. Mf/(D μ) |
||
|
c. Mf v ρ/μ |
||
|
d. Mf ρ D/μ |
Question 48
For fully turbulent flow of a Newtonian fluid in a circular pipe and moderate Re, the velocity profile can well—approximated by v/vmax = (1-r/R)(1/n) , with n=7. Calculate the ratio of the largest or peak fluid velocity to the cross-sectional average velocity. Which of the following numbers best represents that ratio?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1.22 |
||
|
b. 2.0 |
||
|
c. 0.52 |
||
|
d. 7 |
Question 49
For laminar flow of a Newtonian fluid in a circular pipe, calculate the ratio of the maximum or peak fluid velocity to the cross-sectional average velocity. Which of the following numbers best represents that ratio?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 1 |
||
|
b. 2 |
||
|
c. 1.5 |
||
|
d. 5 |
Question 50
Fully developed, laminar flow of a Newtonian fluid in a round pipe is well—described by 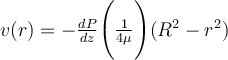 Use this expression to calculate the product τrz 2 π R (where τrz = μ dv/dr) for a Newtonian fluid evaluated at the pipe wall. Which of the following expressions matches your result?
Use this expression to calculate the product τrz 2 π R (where τrz = μ dv/dr) for a Newtonian fluid evaluated at the pipe wall. Which of the following expressions matches your result?
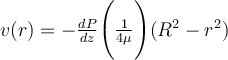 Use this expression to calculate the product τrz 2 π R (where τrz = μ dv/dr) for a Newtonian fluid evaluated at the pipe wall. Which of the following expressions matches your result?
Use this expression to calculate the product τrz 2 π R (where τrz = μ dv/dr) for a Newtonian fluid evaluated at the pipe wall. Which of the following expressions matches your result?
Choose one answer.
|
a. dP/dz |
||
|
b. 2 π R dP/dz |
||
|
c. μ dP/dz |
||
|
d. R2π dP/dz |
Question 51
Pipe Bend
Consider a 90 degree pipe bend through which water is flowing at 20 gal/min. The internal diameter of the pipe is 4 inches. The radius of curvature of the bend is about 20 inches. We wish to calculate the pressure drop associated with the bend. Which of the following best matches your calculation?
Consider a 90 degree pipe bend through which water is flowing at 20 gal/min. The internal diameter of the pipe is 4 inches. The radius of curvature of the bend is about 20 inches. We wish to calculate the pressure drop associated with the bend. Which of the following best matches your calculation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 225 atm |
||
|
b. 0.225 atm |
||
|
c. 2250 Pa |
||
|
d. 225 Pa |
Question 52
Stokes flow past a sphere – falling ball viscometer.
You have already measured the density of an unknown fluid to be 0.78 g/ml. You with to estimate the viscosity of the fluid by measuring the time it takes for a brass ball bearing (D= 2 mm) to fall 25 cm through the fluid. Several experiments indicate that this time is about 2.8 s. Which of the following is the best estimate of the fluid viscosity?
You have already measured the density of an unknown fluid to be 0.78 g/ml. You with to estimate the viscosity of the fluid by measuring the time it takes for a brass ball bearing (D= 2 mm) to fall 25 cm through the fluid. Several experiments indicate that this time is about 2.8 s. Which of the following is the best estimate of the fluid viscosity?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 0.2 Pa s |
||
|
b. 1 cP |
||
|
c. 0.2 cP |
||
|
d. 1 Pa s |
Question 53
Terminal velocity of a flat plate falling aligned in air.
Consider the fortuitous situation that a flat, steel plate 5 mm in thickness, 1 m in length and 0.5 m in width is falling through the atmosphere with its long side (1m) aligned with the direction of gravity. The density of the steel is 7800 kg/m3. The properties of the atmosphere are ρ=1.2 kg/m3; k=0.026 W/m K; υ=15 x 10-6 m2/s. Which of the following best represents the terminal velocity of the plate in mph?
Consider the fortuitous situation that a flat, steel plate 5 mm in thickness, 1 m in length and 0.5 m in width is falling through the atmosphere with its long side (1m) aligned with the direction of gravity. The density of the steel is 7800 kg/m3. The properties of the atmosphere are ρ=1.2 kg/m3; k=0.026 W/m K; υ=15 x 10-6 m2/s. Which of the following best represents the terminal velocity of the plate in mph?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 112 |
||
|
b. 225 |
||
|
c. 325 |
||
|
d. 176 |
Question 54
Viscosity vs. Temperature (Gases)
We have data for the viscosity of a dilute, inert gas at two temperatures ( μ (100 K) = 20 μPa s ; μ(500 K) = 45 μPa s ). Estimate the viscosity at T= 300 K in μPa s.
We have data for the viscosity of a dilute, inert gas at two temperatures ( μ (100 K) = 20 μPa s ; μ(500 K) = 45 μPa s ). Estimate the viscosity at T= 300 K in μPa s.
Choose one answer.
|
a. 40 |
||
|
b. 33 |
||
|
c. 32 |
||
|
d. 35 |
Question 55
Terminal velocities of spheres.
Calculate the approximate terminal velocities of a bowling (US) ball and a table-tennis (ping-pong) ball falling through air under the acceleration of gravity. The properties of the balls and air are summarized below. You may assume that gravity has an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2, that the air is stagnant, and that the drag over a sphere is well represented by the curves in this link from NASA.
Properties of air at 20 C: ρ=1.2 kg/m3; k=0.026 W/m K; υ=15 x 10-6 m2/s.
Bowling Ball: d=8.5 inches; m= 14 lb. The ball is smooth.
Table Tennis Ball: m=2.7g; d = 40 mm. The ball is smooth.
Which of the following pairs of numbers best represent the terminal velocities of the bowling ball and the tennis ball, respectively, in miles per hour?
Calculate the approximate terminal velocities of a bowling (US) ball and a table-tennis (ping-pong) ball falling through air under the acceleration of gravity. The properties of the balls and air are summarized below. You may assume that gravity has an acceleration of 9.8 m/s2, that the air is stagnant, and that the drag over a sphere is well represented by the curves in this link from NASA.
Properties of air at 20 C: ρ=1.2 kg/m3; k=0.026 W/m K; υ=15 x 10-6 m2/s.
Bowling Ball: d=8.5 inches; m= 14 lb. The ball is smooth.
Table Tennis Ball: m=2.7g; d = 40 mm. The ball is smooth.
Which of the following pairs of numbers best represent the terminal velocities of the bowling ball and the tennis ball, respectively, in miles per hour?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 280, 10 |
||
|
b. 210, 10 |
||
|
c. 280, 20 |
||
|
d. 210, 20 |