1
Fill in the blank. The equation of continuity (mass conservation) reduces to 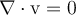 for the special case of ________________.
for the special case of ________________.
Choose one answer.
| A. Steady state | ||
| B. Constant density | ||
| C. Constant temperature | ||
| D. Constant velocity | ||
| E. Constant pressure |
Question
2
Calculate the Reynolds number for water flowing through a 2-inch internal diameter pipe at a flow rate of 500 gallons/hour.
Choose one answer.
| A. 10 | ||
| B. 100 | ||
| C. 1000 | ||
| D. 10,000 | ||
| E. 100,000 |
Question
3
Which group describes the ratio of inertial forces to viscous forces?
Choose one answer.
| A. Re | ||
| B. Pr | ||
| C. Gr | ||
| D. St | ||
| E. Nu |
Question
4
Which group quantifies the ratio of thermal transfer and momentum transfer resistance in a fluid?
Choose one answer.
| A. Re | ||
| B. St | ||
| C. Gr | ||
| D. Pr | ||
| E. Sc |
Question
5
The ratio of convective heat transfer to conductive heat transfer is commonly represented by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| A. Pr | ||
| B. St | ||
| C. Re | ||
| D. Nu | ||
| E. Gr |
Question
6
Fill in the blank. A reversible, adiabatic process may also be called ________________.
Choose one answer.
| A. Isentropic | ||
| B. Isenthalpic | ||
| C. Compressible | ||
| D. Isobaric | ||
| E. Isochoric |
Question
7
The modeling in this course is based upon which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| A. Classical Thermodynamics | ||
| B. Statistical Mechanics | ||
| C. Kinetic Theory | ||
| D. Continuum Mechanics | ||
| E. Both A and D |
Question
8
Which of the following best represents the spark-ignition automobile engine?
Choose one answer.
| A. Brayton cycle | ||
| B. Diesel cycle | ||
| C. Rankine cycle | ||
| D. Carnot cycle | ||
| E. Otto cycle |
Question
9
Which of the following is NOT a state variable?
Choose one answer.
| A. Pressure | ||
| B. Temperature | ||
| C. Specific volume | ||
| D. Internal energy | ||
| E. Flow rate |
Question
10
Which of the following is a state variable?
Choose one answer.
| A. Flow rate | ||
| B. Diffusivity | ||
| C. Reynolds number | ||
| D. Gibbs free energy | ||
| E. Location |
Question
11
Which of the following statements about a thermodynamic cycle is true?
Choose one answer.
| A. A thermodynamic cycle describes a process in which exhange of mass is used to perform work. | ||
| B. A thermodynamic cycle describes a process in which pressure remains constant. | ||
| C. A thermodynamic cycle describes a process in which pressure and temperature do not return to their initial values. | ||
| D. A thermodynamic cycle describes a process in which net variation in state properties is non-zero. | ||
| E. A thermodynamic cycle describes a process in which heat and/or work are exchanged with no net change in state variables. |
Question
12
For a thermodynamic cycle, the first law of thermodynamics implies which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| A. Net heat exchange is zero. | ||
| B. Net heat input equals net work output. | ||
| C. Net work input equals net heat output. | ||
| D. Net work input equals net heat input. | ||
| E. Both B and C |
Question
13
What is the most efficient thermodynamic cycle for interconverting work and heat commonly called?
Choose one answer.
| A. Diesel cycle | ||
| B. Carnot cycle | ||
| C. Rankine cycle | ||
| D. Reversible cycle | ||
| E. Heat engine cycle |
Question
14
Which of the following is a form of anemometry?
Choose one answer.
| A. Wind sock observations | ||
| B. Laser doppler | ||
| C. Particle imaging velocimetry | ||
| D. Hot wire | ||
| E. All of the above |
Question
15
Water flowing at 2 gallons per minute passes through a contraction from 1/2 inch internal diameter pipe to a 1/4 inch internal diameter pipe. Use
Bernoulli's equation to calculate the pressure difference from immediately before the contraction to in the contraction. This pressure difference is
defined as the pressure before the contraction minus the pressure in the contraction.
Choose one answer.
| A. 11 mm Hg | ||
| B. 55 mm Hg | ||
| C. 1120 mm Hg | ||
| D. -1120 mm Hg | ||
| E. -112 mm Hg |
Question
16
Water flowing at 10 gallons per minute passes through a contraction from 1 inch internal diameter pipe to a 1/2 inch internal diameter pipe. Use
Bernoulli's equation to calculate the pressure difference from immediately before the contraction to immediately after the contraction. This pressure
difference is defined as the pressure before the contraction minus the pressure after the contraction.
Choose one answer.
| A. 87 mm Hg | ||
| B. 17.5 mm Hg | ||
| C. 1750 mm Hg | ||
| D. -17.5 mm Hg | ||
| E. -175 mm Hg |
Question
17
Water flowing at 200 gallons per minute passes through an expansion from 2 inch internal diameter pipe to a 2.25 inch internal diameter pipe. Use
Bernoulli's equation to calculate the pressure difference from immediately before the expansion to immediately after the expansion. This pressure
difference is defined as the pressure before the contraction minus the pressure after the contraction.
Choose one answer.
| A. 110 mm Hg | ||
| B. -56 mm Hg | ||
| C. -1110 mm Hg | ||
| D. 1110 mm Hg | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
18
In studying Bernoulii's equation and the forms for the relationship between pressure drop and flow rate for an orifice plate and venturi meter, the results
can be summarized by which of the following statements?
Choose one answer.
| A. Q is proportional to pressure drop. | ||
| B. Q is inversely proportional to pressure drop. | ||
| C. Q is inversely proportional to the square root of pressure drop. | ||
| D. Q is proportional to the square root of pressure drop. | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
19
What is the lowest absolute pressure that can exist?
Choose one answer.
| A. 14.7 psi | ||
| B. -14.7 psi | ||
| C. -29.4 psi | ||
| D. 0 psi | ||
| E. -1 atm |
Question
20
Air is flowing through a pipe with an internal diameter of 15 cm. It passes through an orifice of diameter 8 cm. The air density at the operating
conditions is about 1.3 kg/m3. The observed pressure difference across the orifice is approximately 100 mm Hg, and the flow coefficient for the
orifice is approximately 0.7. What is the mass flow rate of air?
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.506 kg/s | ||
| B. 0.503 kg/s | ||
| C. 6.5 kg/s | ||
| D. 0.05 kg/s | ||
| E. 0.65 kg/s |
Question
21
Water is flowing through a pipe with an internal diameter of 15 cm. It passes through an orifice of diameter 8 cm. The fluid density at the operating
conditions is about 1000 kg/m3. The observed pressure difference across the orifice is approximately 100 mm Hg, and the flow coefficient for the
orifice is approximately 0.7. What is the mass flow rate of water?
Choose one answer.
| A. 2 kg/s | ||
| B. 8.1 kg/s | ||
| C. 18 kg/s | ||
| D. 180 kg/s | ||
| E. 81 kg/s |
Question
22
A liquid with 5.3 times the density of water is used in a manometer. A pressure difference of 4 psi corresponds to how many mm head of this liquid?
Choose one answer.
| A. 53 | ||
| B. 530 | ||
| C. 5.3 | ||
| D. 5300 | ||
| E. 22 |
Question
23
A liquid with a density 8 times that of water is used in a manometer. A pressure difference of 0.25 atm corresponds to how many mm head of that liquid?
Choose one answer.
| A. 32 | ||
| B. 3200 | ||
| C. 320 | ||
| D. -32 | ||
| E. 3.2 |
Question
24
Which of the following best characterizes the inner channel of a rotameter?
Choose one answer.
| A. It is typically close to perfectly cylindrical. | ||
| B. It is typically tapered from top to bottom. | ||
| C. It is typically roughened to promote turbulence. | ||
| D. It is typically notched for each flow rate increment. | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
25
A sharp crested, contracted, rectangular weir of length 12 ft and height 1 ft exhibits a head (h0) of 2 inches of water. Calculate the water
flow in ft3/s. Assume the head of velocity approach is small.
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.2 ft3/s | ||
| B. 0.4 ft3/s | ||
| C. 20 ft3/s | ||
| D. 2.6 ft3/s | ||
| E. 1 ft3/s |
Question
26
Which of the following statements about pump affinity laws is true?
Choose one answer.
| A. Pump affinity laws describe similarity to other pumps. | ||
| B. Pump affinity laws describe cost versus performance. | ||
| C. Pump affinity laws describe relationship of geometric variables and dynamic performance. | ||
| D. Pump affinity laws describe dynamic head versus fluid viscosity. | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
27
When does cavitation occur?
Choose one answer.
| A. When vapor appears in the suction line | ||
| B. When the net postive suction head at the pump input is less than the vapor pressure of the liquid | ||
| C. When the liquid to be pumped begins to boil in the suction line | ||
| D. All of the above | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
28
In considering the exits of two pumps or blowers configured in parallel, which of the following statements is true?
Choose one answer.
| A. The flow rates from the two pieces of equipment are equal. | ||
| B. The total mass flow rate is the sum of the mass flow rates from each piece of equipment. | ||
| C. The temperatures of the streams from each piece of equipment are equal. | ||
| D. The pressures in the output streams from each piece of equipment are nearly equal. | ||
| E. Both A and C | ||
| F. Both B and D |
Question
29
In considering two pumps (1 and 2) connected in series, which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
| A. The flow rates are the same in 1 and 2. | ||
| B. The inlet pressures are the same for 1 and 2. | ||
| C. The outlet pressures are the same for 1 and 2. | ||
| D. The inlet pressure of one of the pumps is equivalent to the outlet pressure of the other pump. | ||
| E. Both A and D |
Question
30
Fill in the blank. For both pumps and fans, the system resistance varies as the __________________.
Choose one answer.
| A. Square root of flow rate | ||
| B. Cube root of flow rate | ||
| C. Flow rate | ||
| D. Flow rate squared | ||
| E. Cube of flow rate |
Question
31
Air is moved through a conduit at a volumetric rate of 100 m3/min. The conditions are P=18 psi, T = 27°C. What is the mass flow rate of air in
the conduit?
Choose one answer.
| A. 2.4 lb/min | ||
| B. 2.4 g/s | ||
| C. 2.4 kg/min | ||
| D. 2.4 kg/s | ||
| E. 2.4 kg/hr |
Question
32
Positive displacement pumps do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| A. Produce a flow rate independent of operating speed | ||
| B. Produce a flow rate independent of discharge pressure | ||
| C. Produce a flow rate independent of suction head | ||
| D. Usually require a relief or safety valve | ||
| E. Both B and D |
Question
33
A centrifugal pump is used to lift water at five gallons per minute against a head of 50 feet of water. The efficiency of the pump is 70%. Approximately,
what is the power required by the pump?
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.7 kW | ||
| B. 0.07 kW | ||
| C. 7 kW | ||
| D. 70 kW | ||
| E. 750 kW |
Question
34
A centrifugal pump is used to lift water at fifty gallons per minute against a head of 75 feet of water. The efficiency of the pump is 65%. Approximately,
what is the power required by the pump?
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.1 kW | ||
| B. 0.01 kW | ||
| C. 1 kW | ||
| D. 10 kW | ||
| E. 100 kW |
Question
35
A centrifugal pump is used to lift water at 75 gallons per minute against a head of 175 feet of water. The efficiency of the pump is 75%. Approximately,
what is the power required by the pump?
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.33 kW | ||
| B. 3.3 W | ||
| C. 3.3 hp | ||
| D. 3.3 tons | ||
| E. 3.3 kw |
Question
36
You have a pump that is using 8.5 kW of power to pump water at about 450 gallons per minute against a head of 32 psi. What is the operating efficiency of
the pump?
Choose one answer.
| A. 93% | ||
| B. 85% | ||
| C. 79% | ||
| D. 74% | ||
| E. 65% |
Question
37
What is the primary difference between a pump and a blower or fan?
Choose one answer.
| A. Blowers have an unconstrained exit stream, and pumps do not. | ||
| B. Blowers move gases, and pumps move liquids and gases. | ||
| C. Pumps pressurize liquids, and blowers move gases. | ||
| D. Pumps operate at lower pressures than blowers. | ||
| E. Pumps operate on incompressible fluids, and blowers operate on compressible fluids. |
Question
38
One atmosphere of pressure corresponds to a water head of how many feet?
Choose one answer.
| A. 33.9 ft | ||
| B. 3.39 ft | ||
| C. 340 ft | ||
| D. 3340 ft | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
39
Water flows through a 1 inch ID 90-degree elbow at 100 L/min. What is the pressure drop associated with the fitting?
Choose one answer.
| A. 3.3 Pa | ||
| B. 2.2 Pa | ||
| C. 2.2 kPa | ||
| D. 3.7 kPa | ||
| E. 440 kPa |
Question
40
Water flows through a 2 inch ID 90-degree elbow at 300 L/min. What is the pressure drop associated with the fitting?
Choose one answer.
| A. 1 psi | ||
| B. 2.5 psi | ||
| C. 0.25 psi | ||
| D. 43 psi | ||
| E. 10 psi |
Question
41
A fluid with density 0.78 g/cm3 and viscosity 2.3 cP flows at 1 gallon per minute through a 2 inch internal diameter pipe. The flow should be
considered as which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| A. Turbulent | ||
| B. Laminar | ||
| C. Transitional | ||
| D. None of the above | ||
| E. All of the above |
Question
42
For gas flow in a pipe, as the pressure decreases downstream the gas velocity does which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| A. Remains constant | ||
| B. Decreases | ||
| C. Increases | ||
| D. Doubles | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
43
A centrifugal pump can provide a flow of 20 L/min at a pressure of 20 psi above atmospheric pressure. What is the minimum pipe diameter (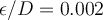 ) that can be used to carry water for 50 m?
) that can be used to carry water for 50 m?
Choose one answer.
| A. 5 cm | ||
| B. 0.6 cm | ||
| C. 2.0 cm | ||
| D. 15 cm | ||
| E. 7 cm |
Question
44
A centrifugal pump can provide flow of 100 L/min at 1.7 atm gauge. What is the minimum pipe diameter (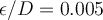 ) that can be used to carry water under these conditions for 100 m?
) that can be used to carry water under these conditions for 100 m?
Choose one answer.
| A. 1.4 cm | ||
| B. 2.5 cm | ||
| C. 3.9 cm | ||
| D. 5.0 cm | ||
| E. 1.1 cm |
Question
45
Important factors for choosing a pipe material include which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| A. Presence/absence of organic chemicals in the pipe environment | ||
| B. Installation cost and lifetime | ||
| C. Brittleness | ||
| D. Ease of corrosion | ||
| E. All of the above |
Question
46
Choose the best answer to the following question. How are pipe diameters most commonly specified and tabulated?
Choose one answer.
| A. Internal diameter | ||
| B. Internal and external diameter | ||
| C. External diameter (OD) and wall thickness | ||
| D. External Diameter | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
47
A piece of analytical equipment employs very narrow diameter tubing to supply solvent (density = 0.9 g/cm3, viscosity = 0.78 cP) to a
workstation at a flow rate of 5 ml/min. The internal diameter of the tubing is 1000 m and the length of the tubing is 75 cm. What is the pressure drop in the
tubing?
m and the length of the tubing is 75 cm. What is the pressure drop in the
tubing?
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.5 atm | ||
| B. 1 atm | ||
| C. 0.2 atm | ||
| D. 0.02 | ||
| E. 5 atm |
Question
48
Water flows through a 3 inch internal diameter 75 ft long pipe at 0.1 gallon per minute. The surface roughness of the pipe is 0.02 cm. What is the pressure
drop over the entire length of the pipe?
Choose one answer.
| A. 1.8 kPa | ||
| B. 1800 Pa | ||
| C. 17.6 Pa | ||
| D. 1.16 Pa | ||
| E. 0.18 Pa |
Question
49
Water flows through a 5 inch internal diameter pipe 50 m long at 5000 liters /min. The roughness of the pipe is characterized by 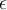 /D = 0.002. What is the pressure drop over the entire length of pipe?
/D = 0.002. What is the pressure drop over the entire length of pipe?
Choose one answer.
| A. 24 kPa | ||
| B. 90 Pa | ||
| C. 900 Pa | ||
| D. 9 kPa | ||
| E. 45 kPa |
Question
50
A fluid of density 0.83 g/cm3 and viscosity 1.8 cP flows through a 1 inch internal diameter pipe 50 m long at 80 kg/min. The roughness of the
pipe is characterized by 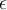 /D = 0.005. What is the
pressure drop over the entire length of pipe?
/D = 0.005. What is the
pressure drop over the entire length of pipe?
Choose one answer.
| A. 112 kPa | ||
| B. 269 Pa | ||
| C. 2.69 Pa | ||
| D. 524 kPa | ||
| E. 262 kPa |
Question
51
Fill in the blank. Pressure drops for elements in series are _________________.
Choose one answer.
| a. Additive | ||
| b. Multiplicative | ||
| c. Equal | ||
| d. Related reciprocally |
Question
52
A fluid with Cp = 4 kJ/kg K enters at point 1 at 3 kg/s and 10°C. It exits at point 3 at 15°C. Another fluid with Cp = 2 kJ/kg K enters at point 4 at 90°C
and leaves at point 2 at 30°C. If the overall heat-transfer coefficient is estimated to be 1500 W/m2 K, what is the area for heat transfer in
m2?![s&t s&t]()
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.96 m2 | ||
| B. 11.9 m2 | ||
| C. 0.85 m2 | ||
| D. 1.4 m2 | ||
| E. 0.75 m2 |
Question
53
A fluid with Cp = 4 kJ/kg K enters at point 1 at 3 kg/s and 10°C. It exits at point 3 at 15°C. Another fluid with Cp = 2 kJ/kg K enters at point 4 at 90°C
and leaves at point 2 at 30°C. If the inlet temperature of the cooling fluid increases to 20°C for a few days, what do you expect the exit temperature of
cooled fluid to be during that time?![s&t s&t]()
Choose one answer.
| A. 35°C | ||
| B. 31°C | ||
| C. 38°C | ||
| D. 45°C | ||
| E. 50°C |
Question
54
A fluid with Cp = 4 kJ/kg K enters at point 1 at 3 kg/s and 10°C. It exits at point 3 at 15°C. Another fluid with Cp = 2 kJ/kg K enters at point 4 at 90°C
and leaves at point 2 at 30°C. If the inlet temperature of the cooling fluid increases to 30°C for a few days, what do you expect the exit temperature of
cooled fluid to be during that time?![s&t s&t]()
Choose one answer.
| A. 40°C | ||
| B. 45°C | ||
| C. 50°C | ||
| D. 35°C | ||
| E. 55°C |
Question
55
A fluid with Cp = 4 kJ/kg K enters at point 1 at 3 kg/s and 10°C. It exits at point 3 at 15°C. Another fluid with Cp = 2 kJ/kg K enters at point 4 at 90°C
and leaves at point 2 at 30°C. What is the flow rate of the second fluid?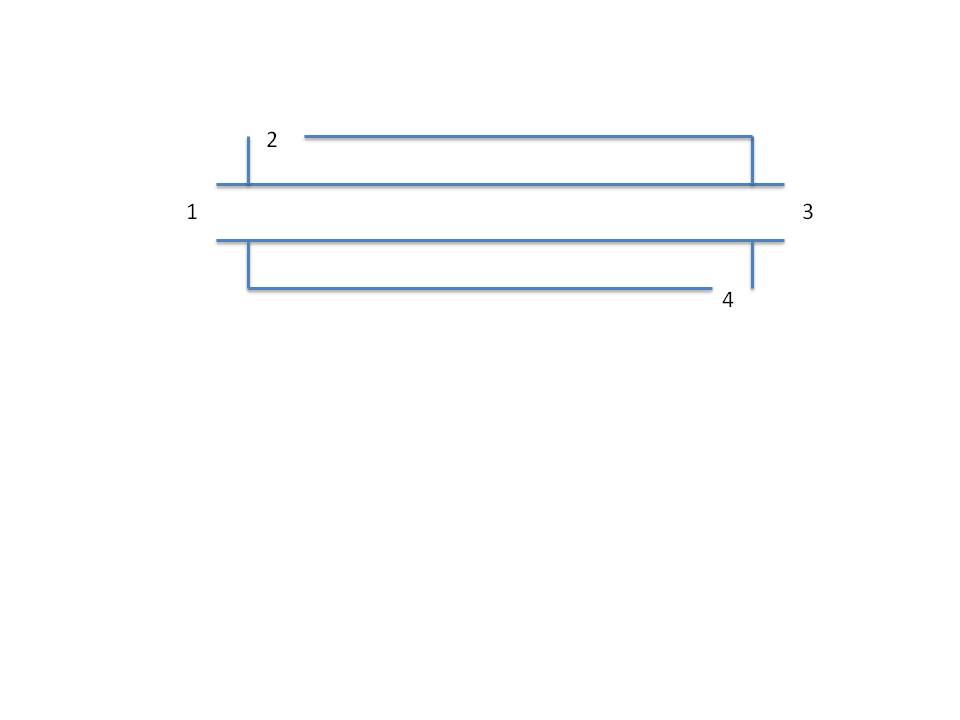

Choose one answer.
| A. 0.5 kg/s | ||
| B. 2 kg/s | ||
| C. 5 kg/s | ||
| D. 1 kg/s | ||
| E. 50 kg/s |
Question
56
A fluid with Cp = 4 kJ/kg K enters at point 1 at 3 kg/s and 10°C. It exits at point 3 at 15°C. Another fluid with Cp = 2 kJ/kg K enters at point 4 at 90°C
and leaves at point 2 at 30°C. It is known that the area for heat transfer is 2 square meters. What is the overall heat transfer coefficient in W/m
2K?![s&t s&t]()
Choose one answer.
| A. 715 W/m2K | ||
| B. 800 W/m2K | ||
| C. 615 W/m2K | ||
| D. 0.715 W/m2K | ||
| E. 1.43 W/m2K |
Question
57
A fluid with Cp = 4 kJ/kg K enters at point 1 at 3 kg/s and 10°C. It exits at point 3 at 15°C. Another fluid with Cp = 2 kJ/kg K enters at point 4 at 90°C
and leaves at point 2 at 30°C. What is the total Q for the system?![s&t s&t]()
Choose one answer.
| A. 60 kW | ||
| B. 60 kJ/s | ||
| C. 6 kW | ||
| D. 6000 W | ||
| E. Both A and B |
Question
58
The schematic depicts a shell-and-tube heat exchanger. If fluids enter at 1 and 2, then the flow configuration is said to be which of the
following?

Choose one answer.
| A. Parallel | ||
| B. Cocurrent | ||
| C. Countercurrent | ||
| D. Cross flow | ||
| E. Both A and B |
Question
59
A fluid with Cp = 4 kJ/kg K enters at point 1 at 3 kg/s and 10°C. It exits at point 3 at 15°C. Another fluid with Cp = 2 kJ/kg K enters at point 4 at 90°C
and leaves at point 2 at 30°C. What is the logarithmic-mean temperature difference in degrees C?![s&t s&t]()
Choose one answer.
| A. 47.5°C | ||
| B. 41.6°C | ||
| C. 45.3°C | ||
| D. 27.5°C | ||
| E. 17.5°C |
Question
60
Calculate the Carnot coefficient of performance for a refrigeration system operating with a condenser temperature of 300°K and an evaporator temperature of
260°K.
Choose one answer.
| A. 6.5 | ||
| B. 0.15 | ||
| C. 6.0 | ||
| D. 0.2 | ||
| E. 10 |
Question
61
A Carnot refrigerator operates between 30°C and -5°C. What is its COP?
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.1 | ||
| B. 0.027 | ||
| C. 7.7 | ||
| D. 7.3 | ||
| E. 0.03 |
Question
62
A refrigerator with a COP of 3 is used to produce 1000 lbs/day of ice from water at 0°C. What is the minimum power required using this refrigerator?
Choose one answer.
| A. 60 W | ||
| B. 6 W | ||
| C. 600 W | ||
| D. 6000 W | ||
| E. 600 kW |
Question
63
Solvent pairs used for refrigeration-absorption include all of the following, EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| A. Ammonia-water. | ||
| B. Lithium bromide-water. | ||
| C. Lithium chloride-water. | ||
| D. Water-sulfuric acid. | ||
| E. Water-octane. |
Question
64
The power input for vapor absorption refrigeration systems is best described by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
| A. Electricity | ||
| B. Motion | ||
| C. Kinetic Energy | ||
| D. Heat | ||
| E. Fuel oil |
Question
65
Vapor compression refrigeration systems are most closely associated with which cycle?
Choose one answer.
| A. Rankine cycle | ||
| B. Diesel cycle | ||
| C. Carnot cycle | ||
| D. Reverse Rankine cycle | ||
| E. All of the above |
Question
66
For a vapor compression refrigeration operation, the enthalpies at the compressor input and output are 200 kJ/kg and 254 kJ/kg. The entropies are
identical. The enthalpy at the evaporator input is 90 kJ/kg. What is the coefficient of performance?
Choose one answer.
| A. 2.04 | ||
| B. 0.49 | ||
| C. 2.49 | ||
| D. 0.51 | ||
| E. -1.1 |
Question
67
For a vapor compression refrigeration operation, the enthalpies at the compressor input and output are 200 kJ/kg and 254 kJ/kg. The entropies are
identical. The enthalpy at the evaporator input is 90 kJ/kg. What is the compressor work?
Choose one answer.
| A. 54 kJ/kg | ||
| B. 108 kJ/kg | ||
| C. 110 kJ/kg | ||
| D. 164 kJ/kg | ||
| E. 208 kJ/kg |
Question
68
For a vapor compression refrigeration operation, the enthalpies at the compressor input and output are 200 kJ/kg and 254 kJ/kg. The entropies are
identical. The enthalpy at the evaporator input is 90 kJ/kg. What is the refrigeration effect (heat removed)?
Choose one answer.
| A. 110 kJ/kg | ||
| B. 54 kJ/kg | ||
| C. 108 kJ/kg | ||
| D. 220 kJ/kg | ||
| E. 400 kJ/kg |
Question
69
Calculate the maximum COP for a vapor absorption refrigeration system operating with a heat source (generator) at 90°C, a chiller temperature (absorber) of
5°C, and a condenser temperature of 30°C.
Choose one answer.
| A. 0.54 | ||
| B. 2.0 | ||
| C. 1.8 | ||
| D. 0.6 | ||
| E. 0.25 |
Question
70
When are water-LiBr absorption systems for cooling useful?
Choose one answer.
| A. Only for providing cooling for temperatures above 0°C | ||
| B. Only for providing cooling for temperatures above 200°K | ||
| C. Only for very small-scale operations | ||
| D. Only for very large-scale operations | ||
| E. All of the above |
Question
71
Combustion of a fuel at 900°K at a rate of 2 kW produces steam at 500°K. The steam then produces 1 kW of work and rejects some heat to 300°K. What is the
thermal (or first-law) efficiency of the process?
Choose one answer.
| A. 200% | ||
| B. 100% | ||
| C. 50% | ||
| D. 5% | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
72
Combustion of a fuel at 900°K at a rate of 2 kW produces steam at 500°K . The steam then produces 500kW of work and rejects some heat to 300°K. What is the
second-law efficiency (or efficiency compared to a Carnot engine) of the process?
Choose one answer.
| A. 38% | ||
| B. 58% | ||
| C. 25% | ||
| D. 50% | ||
| E. 100% |
Question
73
The first practical steam engine was produced about how many years ago?
Choose one answer.
| A. 100 years ago | ||
| B. 300 years ago | ||
| C. 700 years ago | ||
| D. 900 years ago | ||
| E. 1200 years ago |
Question
74
For an isentropic expansion of an ideal gas from state 1 to state 2, the relationship between temperatures and pressures can be written as which of the
following?
Choose one answer.
|
A. |
||
|
B. |
||
|
C. |
||
|
D. |
||
|
E. |
Question
75
For the same compression ratios, how do the efficiencies of the spark-ignition cycle (SI) and compression ignition cycle (CI) compare?
Choose one answer.
| A. SI > CI | ||
| B. SI = CI | ||
| C. SI >> CI | ||
| D. CI >> SI | ||
| E. CI > SI |
Question
76
Four states of an ideal Rankine cycle for an unknown fluid are shown in the table below. Calculate the turbine power for a fluid rate of 10 kg/s.
|
State |
T(C) |
P (kPa) |
H(kJ/kg) |
S (kJ/kg K) |
|
1 |
300 |
1000 |
750 |
10 |
|
2 |
50 |
10 |
512 |
10 |
|
3 |
50 |
10 |
75 |
2 |
|
4 |
50 |
1000 |
75 |
2 |
Choose one answer.
| A. 2.4 MW | ||
| B. 2.4 kW | ||
| C. 24MW | ||
| D. 24 kW | ||
| E. 240 MW |
Question
77
Four states of an ideal Rankine cycle for an unknown fluid are shown in the table below. Which state corresponds to the turbine inlet conditions?
|
State |
T(C) |
P (kPa) |
H(kJ/kg) |
S (kJ/kg K) |
|
1 |
300 |
1000 |
750 |
10 |
|
2 |
50 |
10 |
512 |
10 |
|
3 |
50 |
10 |
75 |
2 |
|
4 |
50 |
1000 |
75 |
2 |
Choose one answer.
| A. 1 | ||
| B. 2 | ||
| C. 3 | ||
| D. 4 | ||
| E. None of the above |
Question
78
A reciprocating, spark ignition, engine takes in an air-fuel mixture at 20°C. It has a compression ratio of 10. The air-to-fuel ratio is 12, and the
heating value of the fuel is 60,000 kJ/kg. For an air standard cycle analysis, what is the highest temperature reached? You may assume Cv is
approximately 0.7 kJ/kg K and Cp/Cv is approximately 1.4.
Choose one answer.
| A. 571° K | ||
| B. 7879 °K | ||
| C. 57,360°K | ||
| D. 5000°K | ||
| E. 7143° K |
Question
79
A reciprocating, spark ignition, engine takes in an air-fuel mixture at 20°C. It has a compression ratio of 10. The air-to-fuel ratio is 12, and the
heating value of the fuel is 60,000 kJ/kg. For an air standard cycle analysis, what is the largest pressure reached? You may assume Cv is
approximately 0.7 kJ/kg K and Cp/Cv approximately 1.4.
Choose one answer.
| A. 267 atm | ||
| B. 25 atm | ||
| C. 7.7 atm | ||
| D. 136 atm | ||
| E. 5000 atm |
Question
80
A reciprocating, spark ignition, engine takes in an air-fuel mixture at 20°C. It has a compression ratio of 10. The air-to-fuel ratio is 12, and the
heating value of the fuel is 60,000 kJ/kg. For an air standard cycle analysis, what is the thermal efficiency? You may assume Cv is
approximately 0.7 kJ/kg K and Cp/Cv is approximately 1.4.
Choose one answer.
| A. 82% | ||
| B. 77% | ||
| C. 66% | ||
| D. 44% | ||
| E. 60% |
Question
81
A reciprocating, spark ignition, engine takes in an air-fuel mixture at 20°C. It has a compression ratio of 10. The air-to-fuel ratio is 12, and the
heating value of the fuel is 60,000 kJ/kg. For an air standard cycle analysis, what is the heat rejected to the surroundings? You may assume Cv
is approximately 0.7 kJ/kg K and Cp/Cv is approximately 1.4.
Choose one answer.
| A. 1100 kJ/kg | ||
| B. 3000 kJ/kg | ||
| C. 1991 kJ/kg | ||
| D. 912 kJ/kg | ||
| E. 500 kJ/kg |