1
Consider the following scenario and choose the correct answer from the options below.
Barney worked 46.75 hours last week. His rate of pay is $16.00 per hour. Barney's job is regulated by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and on his tax forms, Barney claims married status with two (2) children as dependents.
What is Barney's gross pay for the week?
Barney worked 46.75 hours last week. His rate of pay is $16.00 per hour. Barney's job is regulated by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and on his tax forms, Barney claims married status with two (2) children as dependents.
What is Barney's gross pay for the week?
Choose one answer.
| a. $640.00 | ||
| b. $748.00 | ||
| c. $784.00 | ||
| d. $802.00 |
Question
2
Consider the following scenario and choose the correct answer from the options below.
Roxanne worked 37.5 hours last week. Her rate of pay is $18.80 per hour. Roxanne's job is regulated by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and on her tax forms, Roxanne claims single status with five (5) children as dependents. In addition, Roxanne has $5.00 a week taken out of her paycheck to go toward her union dues.
What were Roxanne's gross earnings for last week?
Roxanne worked 37.5 hours last week. Her rate of pay is $18.80 per hour. Roxanne's job is regulated by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and on her tax forms, Roxanne claims single status with five (5) children as dependents. In addition, Roxanne has $5.00 a week taken out of her paycheck to go toward her union dues.
What were Roxanne's gross earnings for last week?
Choose one answer.
| a. $635.40 | ||
| b. $700.00 | ||
| c. $705.00 | ||
| d. $750.00 |
Question
3
Consider the following scenario and choose the correct answer from the options below.
Sandra worked 48 hours last week. Her rate of pay is $13.75 per hour. Sandra's job is regulated by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and on her tax forms, Sandra claims single status with one (1) child as a dependent. Sandra also donates $7.00 per week to the United Way.
What are Sandra's gross earnings for the week?
Sandra worked 48 hours last week. Her rate of pay is $13.75 per hour. Sandra's job is regulated by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), and on her tax forms, Sandra claims single status with one (1) child as a dependent. Sandra also donates $7.00 per week to the United Way.
What are Sandra's gross earnings for the week?
Choose one answer.
| a. $550.00 | ||
| b. $660.00 | ||
| c. $670.00 | ||
| d. $715.00 |
Question
4
Tips received by employees:
Choose one answer.
| a. are not taxable. | ||
| b. are taxable to the employer but not the employee. | ||
| c. are taxable to the employee but not the employer. | ||
| d. are taxable to both the employee and the employer. |
Question
5
What is a tip credit?
Choose one answer.
| a. A tip left on a customer's credit card | ||
| b. A tip made up by an employer when a customer does not leave one | ||
| c. A policy that allows employers to pay less than minimum wage | ||
| d. A policy that allows employees to apply tips toward fringe benefits |
Question
6
What is one of the functions of the Voluntary Classification Settlement Program (VCSP)?
Choose one answer.
| a. It allows an employer to reclassify workers as employees for future periods. | ||
| b. It relieves an employer from the employee-vs.-contractor decision. | ||
| c. It eliminates future Social Security and Medicare obligations for an employer. | ||
| d. It allows an employer more freedom to decide whether a worker is an employee or an independent contractor. |
Question
7
When a business is regulated under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA), under what conditions is the business required to pay overtime compensation to an
employee?
Choose one answer.
| a. After the employee has worked 8 hours in a day | ||
| b. After the employee has worked 40 hours in a week | ||
| c. After the employee has worked on a legal holiday | ||
| d. After the employee has worked 120 hours in a month |
Question
8
When deciding whether a worker is an employee or an independent contractor, all of the following factors should be considered EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| a. The worker's physical location | ||
| b. The worker's financial relationship with the employer | ||
| c. The worker's job-duties relationship with the employer | ||
| d. The worker's behavior on the job |
Question
9
Which of the following examples of an employee would most likely be considered an independent contractor?
Choose one answer.
| a. An evening assembly-line maintenance worker | ||
| b. A plumber who specializes in installing new sinks | ||
| c. The US president's personal assistant | ||
| d. A part-time fork-lift driver |
Question
10
Which of the following types of employees are NOT protected by the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)?
Choose one answer.
| a. Community college employees | ||
| b. Full-time housekeepers | ||
| c. Firework-stand attendants | ||
| d. State driving-license examiners |
Question
11
For the purposes of Earned Income Credit (EIC), which of the following is considered earned income?
Choose one answer.
| a. Retirement income | ||
| b. Social Security income | ||
| c. Union strike benefits | ||
| d. Unemployment benefits |
Question
12
What governing body enforces the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)?
Choose one answer.
| a. The Wage and Hour Division of the US Department of Labor | ||
| b. The US National Economic Council | ||
| c. The Under Secretary of Political Affairs for the US State Department | ||
| d. The US Small Business Administration |
Question
13
What is a consequence of withholding allowances?
Choose one answer.
| a. Withholding allowances increases the amount of taxes payable. | ||
| b. Withholding allowances legally reduces the amount of taxes payable. | ||
| c. Withholding allowances decreases the net amount of your paycheck. | ||
| d. The withholding amount must be equal to the number of your dependents. |
Question
14
What is the main function of the 1947 Portal-to-Portal Act?
Choose one answer.
| a. It provides compensation for business travel expenses. | ||
| b. It excludes compensation for business travel expenses. | ||
| c. It provides compensation for travel home after work. | ||
| d. It excludes compensation for travel to and from work. |
Question
15
What is the main function of the Family and Medical Leave Act of 1993?
Choose one answer.
| a. It enables employees to keep their jobs while taking leave for medical emergencies. | ||
| b. It requires paid leave in cases of family medical emergencies. | ||
| c. It pays for medical care in case of injury on the job. | ||
| d. It prevents termination whenever workers are absent from work. |
Question
16
When completing a form W-4:
Choose one answer.
| a. the number of withholding allowances must equal the number of dependents on your tax return. | ||
| b. the withholding allowances are related to, but not the same as, the number of dependents on your tax return. | ||
| c. claiming greater than nine (9) allowances is prohibited. | ||
| d. you should claim fewer withholding allowances than you do on your tax return. |
Question
17
For what amount of time must employers keep employee pay records, according to the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)?
Choose one answer.
| a. A minimum of 3 months | ||
| b. A minimum of 3 years | ||
| c. A minimum of 6 months | ||
| d. A minimum of 6 years |
Question
18
Transparency surrounding compensation is essential because:
Choose one answer.
| a. many employees develop their own perceptions of how pay is determined. | ||
| b. employees are likely to quit when pay rates are not known. | ||
| c. employees typically feel shortchanged when they see their pay stub. | ||
| d. many employees are likely to sue if they aren't paid what they want. |
Question
19
What are internal controls?
Choose one answer.
| a. Procedures intended to track the work of management | ||
| b. Procedures designed to be punitive in nature | ||
| c. Procedures intended to withhold and remit employee taxes and benefits | ||
| d. Procedures designed to increase the efficiency of an organization |
Question
20
What is the major advantage of processing payroll by hand?
Choose one answer.
| a. It is an error-free method that enables a business to maintain control. | ||
| b. It is a low-cost solution that enables small businesses to save money. | ||
| c. It is a fast method that frees time for handling other aspects of the business. | ||
| d. It allows for more creativity than does using employee payroll software. |
Question
21
What negative result/s can occur when a business fails to meet deadlines for depositing withheld income taxes, Social Security, Medicare contributions, and
employer-matching amounts?
Choose one answer.
| a. Fines for the business manager, but not the business owners | ||
| b. The organization being classified as "exempt" | ||
| c. The business declaring bankruptcy | ||
| d. Penalties and interest charges held against the business |
Question
22
When determining how much to pay your employees, the first step you should take is to:
Choose one answer.
| a. take a local survey to determine what competitors are paying. | ||
| b. make sure that you're in compliance with wage and hour laws. | ||
| c. ask a potential employee how much he or she is making at his or her current job. | ||
| d. conduct an Internet search to determine industry wage standards. |
Question
23
All of the following are subject to withholding EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| a. Bonuses | ||
| b. Commissions | ||
| c. Vacations | ||
| d. Scholarships |
Question
24
All of the following must be withheld from an employee's paycheck EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| a. Federal Income Tax | ||
| b. Federal Unemployment Tax | ||
| c. Old Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance | ||
| d. Medicare Insurance |
Question
25
If an employee refuses to fill out a form W-4 when hired:
Choose one answer.
| a. the employee can be fined 25% of his or her salary. | ||
| b. the employer cannot hire the person. | ||
| c. the employer must withhold the employee's income taxes at the highest rate. | ||
| d. the employee can be jailed. |
Question
26
The amount of withholding for Federal Income Tax (FIT) that is reported on a W-4 is calculated using all of the following information EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| a. The employee's birth date | ||
| b. The number of allowances | ||
| c. Additional amounts to voluntarily withhold | ||
| d. Marital status |
Question
27
The Old-Age, Survivors, and Disability Insurance (OASDI) component of Social Security is:
Choose one answer.
| a. financed by Medicare. | ||
| b. financed by the Social Security tax. | ||
| c. withheld from employees only. | ||
| d. paid by the employer only. |
Question
28
When an employer withholds income taxes from your pay:
Choose one answer.
| a. the amount withheld is paid to the IRS in your name. | ||
| b. the amount is paid back to you in the form of Social Security payments. | ||
| c. the tax liability of the employer is reduced. | ||
| d. the employer keeps the money until the end of the year. |
Question
29
Consider the following scenario and choose the correct answer from the options below.
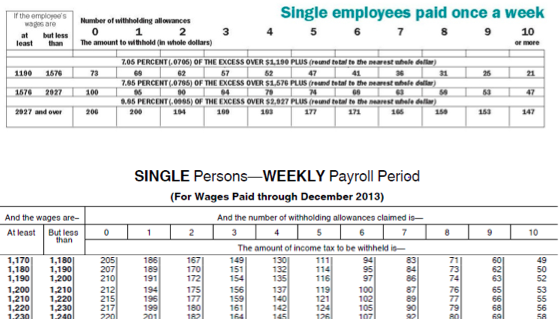
Sandra earned $1,200 last week. Sandra works and lives in Minnesota. She is single, claims one (1) allowance, and is paid weekly.
Below is a partial table from the 2013 Minnesota Withholding Tax Tables and a partial table from the 2013 federal withholding tables. Use these tables and the wage-bracket method to determine Sandra's net pay for the week. What is Sandra's net pay for the week?
Sandra earned $1,200 last week. Sandra works and lives in Minnesota. She is single, claims one (1) allowance, and is paid weekly.
Below is a partial table from the 2013 Minnesota Withholding Tax Tables and a partial table from the 2013 federal withholding tables. Use these tables and the wage-bracket method to determine Sandra's net pay for the week. What is Sandra's net pay for the week?
Choose one answer.
| a. $120.07 | ||
| b. $191.95 | ||
| c. $765.25 | ||
| d. $845.29 |
Question
30
Consider the following scenario and choose the correct answer from the options below.
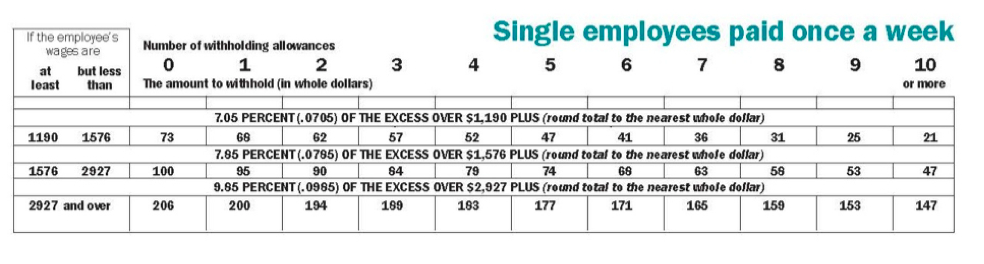
Sandra earned $1,200 last week. Sandra works and lives in Minnesota. She is single, claims one (1) allowance, and is paid weekly.
Below is a partial table from the 2013 Minnesota Withholding Tax Tables. Use this table to determine the amount of Sandra's state withholding for the week. Sandra's state withholding for the week is:
Sandra earned $1,200 last week. Sandra works and lives in Minnesota. She is single, claims one (1) allowance, and is paid weekly.
Below is a partial table from the 2013 Minnesota Withholding Tax Tables. Use this table to determine the amount of Sandra's state withholding for the week. Sandra's state withholding for the week is:
Choose one answer.
| a. $68.00 | ||
| b. $69.00 | ||
| c. $196.45 | ||
| d. $198.70 |
Question
31
Consider the following scenario and choose the correct answer from the options below.
Sandra earned $1,200 last week. Sandra works and lives in Minnesota. She is single, claims one (1) allowance, and is paid weekly.
The amounts Sandra's employer will deduct from her paycheck for Social Security and Medicare, respectively, are:
Sandra earned $1,200 last week. Sandra works and lives in Minnesota. She is single, claims one (1) allowance, and is paid weekly.
The amounts Sandra's employer will deduct from her paycheck for Social Security and Medicare, respectively, are:
Choose one answer.
| a. $7.44 and $1.74 | ||
| b. $74.40 and $17.40 | ||
| c. $9.18 and $2.15 | ||
| d. $91.80 and $21.46 |
Question
32
Consider the following scenario and choose the correct answer from the options below.
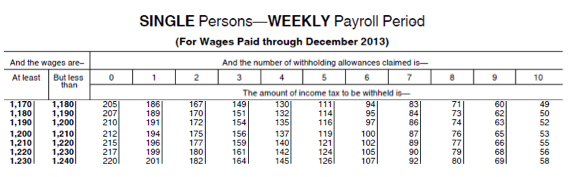
Sandra earned $1,200 last week. Sandra works and lives in Minnesota. She is single, claims one (1) allowance, and is paid weekly.
Use the wage-bracket method and the section of the 2013 federal wage tables shown below to determine Sandra's federal withholding for the week. Sandra's federal withholding for the week is:
Sandra earned $1,200 last week. Sandra works and lives in Minnesota. She is single, claims one (1) allowance, and is paid weekly.
Use the wage-bracket method and the section of the 2013 federal wage tables shown below to determine Sandra's federal withholding for the week. Sandra's federal withholding for the week is:
Choose one answer.
| a. $186.00 | ||
| b. $191.00 | ||
| c. $194.00 | ||
| d. $212.00 |
Question
33
Which of the following is NOT a legal category for an employer to deduct from an employee's paycheck?
Choose one answer.
| a. State tax withholdings | ||
| b. Payment to a credit union | ||
| c. The price of shares in a mutual fund | ||
| d. Cash drawer shortages |
Question
34
Which of the following is NOT one of the three categories of withholding deductions?
Choose one answer.
| a. Federal, state, and local taxes | ||
| b. Employee FICA withholdings | ||
| c. Employee Federal Unemployment Taxes | ||
| d. Voluntary deductions |
Question
35
Educational assistance includes all of the following EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| a. The cost of textbooks | ||
| b. The cost of supplies | ||
| c. The cost of tools | ||
| d. The cost of tuition |
Question
36
Excluded fringe benefits:
Choose one answer.
| a. are not subject to Federal Income Tax withholding. | ||
| b. may not be offered by employers. | ||
| c. usually only apply to highly paid employees. | ||
| d. include year-end bonuses. |
Question
37
What is the main purpose of the Consolidated Omnibus Reconciliation Act (COBRA)?
Choose one answer.
| a. It permits all employees to buy health insurance. | ||
| b. It permits all employees to insure their spouses. | ||
| c. It permits all employees to have health coverage for their entire family. | ||
| d. It permits former employees to continue their health coverage for a limited period of time. |
Question
38
What type of benefits may a cafeteria plan NOT include?
Choose one answer.
| a. Accident and health benefits | ||
| b. Health savings accounts | ||
| c. Group-term life insurance | ||
| d. Educational assistance |
Question
39
Which of the following employee benefits is considered to be de minimis?
Choose one answer.
| a. Employee housing | ||
| b. A company picnic | ||
| c. Education reimbursement | ||
| d. Personal use of a company car |
Question
40
Which of the following employee benefits is required by federal law?
Choose one answer.
| a. Unpaid time off to vote | ||
| b. Paid holidays | ||
| c. Retirement plans | ||
| d. Dental insurance |
Question
41
Deferred-compensation plans:
Choose one answer.
| a. are safe, tax-free retirement plans. | ||
| b. protect employees from bankruptcy. | ||
| c. must be made available to all employees. | ||
| d. are only available to highly paid employees. |
Question
42
Flexible benefit plans:
Choose one answer.
| a. are a required employee benefit. | ||
| b. can let employees buy healthcare-related items, such as eyeglasses, tax free. | ||
| c. can let employees save flexible amounts for retirement. | ||
| d. are reported as income on an employee's W-4. |
Question
43
Generally, contributions made by an employer to a plan providing accident or health insurance to its employees and their spouses and dependents are:
Choose one answer.
| a. considered earned compensation and are subject to withholding. | ||
| b. not subject to Federal Income Tax withholding. | ||
| c. taxable for Federal Unemployment Tax (FUTA) purposes. | ||
| d. considered income, and subject to State Unemployment Taxes (SUTA). |
Question
44
Social Security is:
Choose one answer.
| a. a tax paid by an employee only. | ||
| b. a tax paid by an employer only. | ||
| c. was originally a retirement program. | ||
| d. was originally a health insurance program. |
Question
45
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA):
Choose one answer.
| a. directly insures workers who change jobs. | ||
| b. allows health insurance participation for workers who lose their jobs. | ||
| c. requires employers to offer health plans. | ||
| d. allows workers to continue health coverage at an employer's expense. |
Question
46
Which of the following employee benefits is NOT required by law?
Choose one answer.
| a. Health insurance | ||
| b. Workers' compensation | ||
| c. Unemployment insurance | ||
| d. Social Security matching |
Question
47
An accrual:
Choose one answer.
| a. means that liabilities are increased as cash is paid out. | ||
| b. means that cash increases as liabilities increase. | ||
| c. means that an expense is recorded before cash is paid out. | ||
| d. means that an expense is recorded only when cash is paid out. |
Question
48
Bonuses and commissions that are paid to employees:
Choose one answer.
| a. are usually calculated separately from the "regular" payroll. | ||
| b. are usually considered part of a "regular" salary. | ||
| c. must be kept, and calculated, separately from a "regular" salary because they are taxed differently. | ||
| d. must be taxed for Federal Income Tax (FIT) withholding, but not FICA withholding. |
Question
49
Consider the following scenario and choose the correct answer from the options below.
Harry is covered by the Fair Labor Standards Act. Last week, he worked 47.5 hours at his regular rate of pay, $16.50 per hour.
Harry's overtime pay and gross pay for the week, respectively, are:
Harry is covered by the Fair Labor Standards Act. Last week, he worked 47.5 hours at his regular rate of pay, $16.50 per hour.
Harry's overtime pay and gross pay for the week, respectively, are:
Choose one answer.
| a. $182.62 and $783.75 | ||
| b. $182.62 and $842.62 | ||
| c. $118.60 and $1,175.62 | ||
| d. $118.60 and $1,350.31 |
Question
50
The journal entry below:

Choose one answer.
| a. records the payment of net payroll to an employee. | ||
| b. records the payment of gross payroll to an employee. | ||
| c. decreases a liability and increases an asset. | ||
| d. increases a liability and decreases an asset. |
Question
51
The journal entry below:
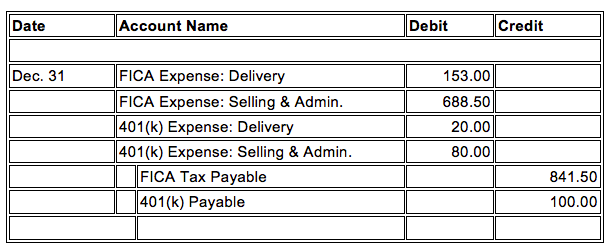
Choose one answer.
| a. records the payment of employee taxes. | ||
| b. records the payment of employer taxes. | ||
| c. records the accrual of employee taxes. | ||
| d. records the accrual of employer taxes. |
Question
52
What does the matching principle state?
Choose one answer.
| a. Assets should be matched with liabilities. | ||
| b. Expenses should be matched with revenues. | ||
| c. Assets equal liabilities plus owner equity. | ||
| d. Assets should equal owner equity. |
Question
53
A Form W-2:
Choose one answer.
| a. must be filled out by an employee upon hire. | ||
| b. must be filled out by an employer upon hire. | ||
| c. reports miscellaneous earnings by employees. | ||
| d. reports employee earnings at the end of the year. |
Question
54
An accountable plan is a reimbursement or allowance arrangement that meets all of the following conditions EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| a. An employee pays for deductible expenses while performing as an employee | ||
| b. An employee accounts for expenses within a reasonable time | ||
| c. An employee returns any excess amounts above expenses to the employer | ||
| d. An employee pays for employer expenses using cash or check |
Question
55
FTD deposit rules are:
Choose one answer.
| a. based on when salaries are paid, not earned. | ||
| b. based on when salaries are earned, not paid. | ||
| c. based on a business's fiscal year. | ||
| d. based on regular monthly payments. |
Question
56
FTD deposits:
Choose one answer.
| a. are made at the end of the calendar year. | ||
| b. may be remitted with Form 941. | ||
| c. must be filed electronically. | ||
| d. may be remitted by cash (check) or electronic transfer. |
Question
57
In order to avoid penalties related to Electronic Federal Tax Payment System (EFTPS) payments, an employer must do all of the following EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| a. Submit a tax payment to EFTPS by 8 p.m. EST at least one calendar day before the tax due date | ||
| b. Mail the organization's check immediately after making the EFT deposit | ||
| c. Record the EFT acknowledgement number | ||
| d. Make sure there are enough funds to cover the tax payment |
Question
58
Who among the following types of employees must make Federal Tax Deposits (FTD)?
Choose one answer.
| a. Employees making over $2,500 per year | ||
| b. Employers who pay more than $2,500 per year in wages | ||
| c. Employees who owe more than $2,500 in taxes per quarter | ||
| d. Employers who owe more than $2,500 in taxes per quarter |
Question
59
Betsy earned $57,000 last year. For Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA) purposes, Betsy's employer will pay a net FUTA amount of:
Choose one answer.
| a. $42.00 | ||
| b. $56.00 | ||
| c. $420.00 | ||
| d. $560.00 |
Question
60
Forms that most employers must file for payroll tax purposes include all of the following EXCEPT:
Choose one answer.
| a. Form 940: Employer's Annual Federal Unemployment (FUTA) Tax Return | ||
| b. Form 941: Employer's Quarterly Federal Tax Return | ||
| c. Form 945: Annual Return of Withheld Federal Income Tax | ||
| d. Form 987: Wire Transfer Authorization |
Question
61
In Kentucky, a new employer pays a 2.7% State Unemployment Tax (SUTA) up to $9,300. Karen earned $28,900 this year. For SUTA tax purposes, Karen's employer
will pay a total of:
Choose one answer.
| a. $25.11 | ||
| b. $251.10 | ||
| c. $78.03 | ||
| d. $780.30 |
Question
62
The Federal Unemployment Tax Act (FUTA):
Choose one answer.
| a. pays unemployment benefits directly to unemployed persons. | ||
| b. pays for state job service programs. | ||
| c. is used solely for the payment of benefits to eligible unemployed workers. | ||
| d. is used solely for federal workers who become unemployed. |
Question
63
What does the 98% Safe Harbor rule do?
Choose one answer.
| a. It allows employers to pay 98% of their taxes 98% of the time. | ||
| b. It requires employers to deposit 98% of taxes due. | ||
| c. It allows employers to deposit 98% of taxes due without a penalty. | ||
| d. It requires employers to increase their liability by 98%. |
Question
64
What type of penalty will be imposed upon any person who fails to deposit any amount of tax in a government depository?
Choose one answer.
| a. A penalty equal to the amount due | ||
| b. A penalty equal to the applicable percentage of the amount of the underpayment | ||
| c. A penalty not to exceed $10,000 | ||
| d. A penalty not to exceed 7 years of imprisonment |