As noted in Table 12.2 "The First 10 Straight-Chain Alkanes", the number of isomers increases rapidly as the number of carbon atoms increases. There are 3 pentanes, 5 hexanes, 9 heptanes, and 18 octanes. It would be difficult to assign unique individual names that we could remember. A systematic way of naming hydrocarbons and other organic compounds has been devised by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC). These rules, used worldwide, are known as the IUPAC System of NomenclatureA systematic way of naming chemical substances so that each has a unique name.. (Some of the names we used earlier, such as isobutane, isopentane, and neopentane, do not follow these rules and are called common names.) A stem name (Table 12.3 "Stems That Indicate the Number of Carbon Atoms in Organic Molecules") indicates the number of carbon atoms in the longest continuous chain (LCC). Atoms or groups attached to this carbon chain, called substituents, are then named, with their positions indicated by numbers. For now, we will consider only those substituents called alkyl groups.
Table 12.3 Stems That Indicate the Number of Carbon Atoms in Organic Molecules
| Stem | Number |
|---|---|
| meth- | 1 |
| eth- | 2 |
| prop- | 3 |
| but- | 4 |
| pent- | 5 |
| hex- | 6 |
| hept- | 7 |
| oct- | 8 |
| non- | 9 |
| dec- | 10 |
An alkyl groupA hydrocarbon group derived from an alkane by removal of a hydrogen atom. is a group of atoms that results when one hydrogen atom is removed from an alkane. The group is named by replacing the -ane suffix of the parent hydrocarbon with -yl. For example, the CH3 group derived from methane (CH4) results from subtracting one hydrogen atom and is called a methyl group.
The alkyl groups we will use most frequently are listed in Table 12.4 "Common Alkyl Groups". Alkyl groups are not independent molecules; they are parts of molecules that we consider as a unit to name compounds systematically.
Table 12.4 Common Alkyl Groups
| Parent Alkane | Alkyl Group | Condensed Structural Formula | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| methane |
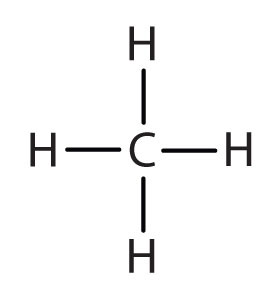
|
methyl |
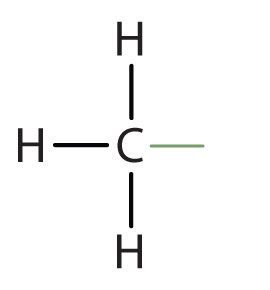
|
CH3– |
| ethane |
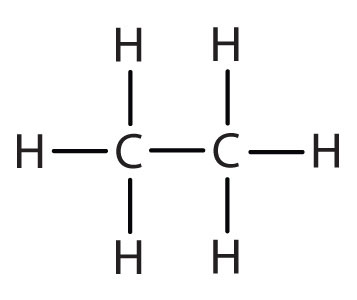
|
ethyl |
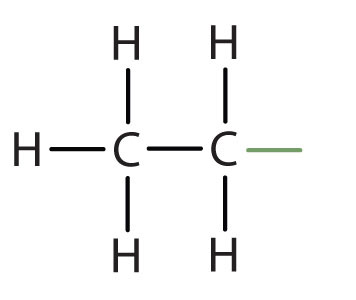
|
CH3CH2– |
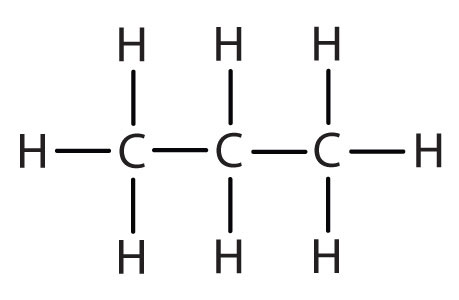
| propane |
|
propyl |
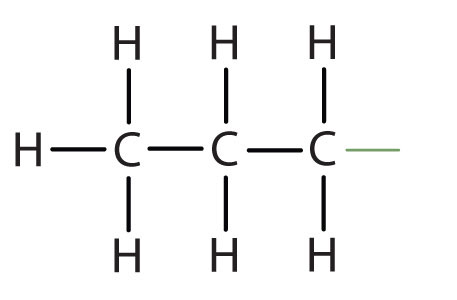
|
CH3CH2CH2– |
| isopropyl |
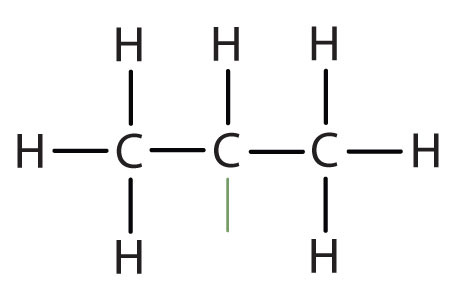
|
(CH3)2CH– | ||
| butane |
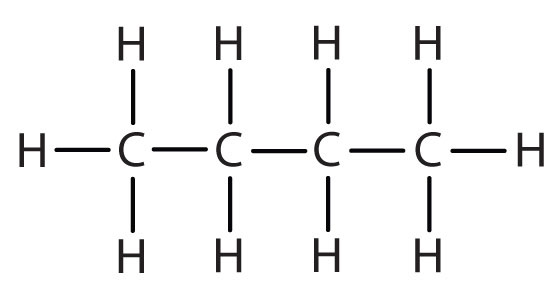
|
butyl* |
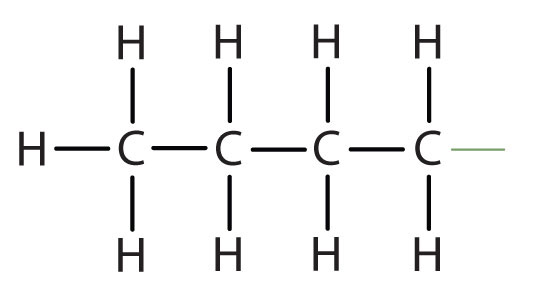
|
CH3CH2CH2CH2– |
| *There are four butyl groups, two derived from butane and two from isobutane. We will introduce the other three where appropriate. | ||||
Simplified IUPAC rules for naming alkanes are as follows (demonstrated in Example 12.1).
1. Name alkanes according to the LCC of carbon atoms in the molecule (rather than the total number of carbon atoms). This LCC, considered the parent chain, determines the base name, to which we add the suffix -ane to indicate that the molecule is an alkane.
2. If the hydrocarbon is branched, number the carbon atoms of the LCC. Numbers are assigned in the direction that gives the lowest numbers to the carbon atoms with attached substituents. Hyphens are used to separate numbers from the names of substituents; commas separate numbers from each other. (The LCC need not be written in a straight line; for example, the LCC in the following has five carbon atoms.)
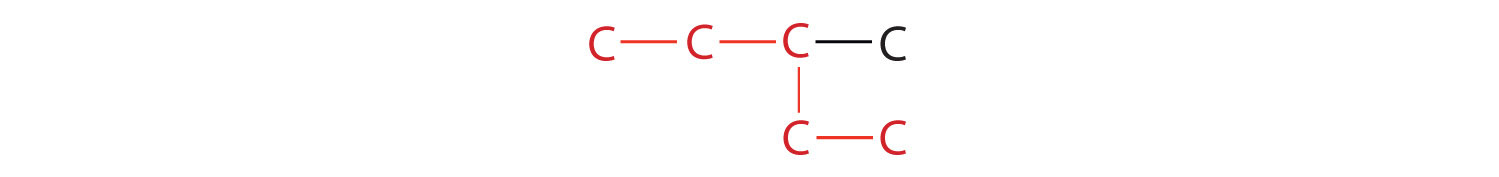
3. Place the names of the substituent groups in alphabetical order before the name of the parent compound. If the same alkyl group appears more than once, the numbers of all the carbon atoms to which it is attached are expressed. If the same group appears more than once on the same carbon atom, the number of that carbon atom is repeated as many times as the group appears. Moreover, the number of identical groups is indicated by the Greek prefixes di-, tri-, tetra-, and so on. These prefixes are not considered in determining the alphabetical order of the substituents. For example, ethyl is listed before dimethyl; the di- is simply ignored. The last alkyl group named is prefixed to the name of the parent alkane to form one word.
When these rules are followed, every unique compound receives its own exclusive name. The rules enable us to not only name a compound from a given structure but also draw a structure from a given name. The best way to learn how to use the IUPAC system is to put it to work, not just memorize the rules. It’s easier than it looks.
Name each compound.
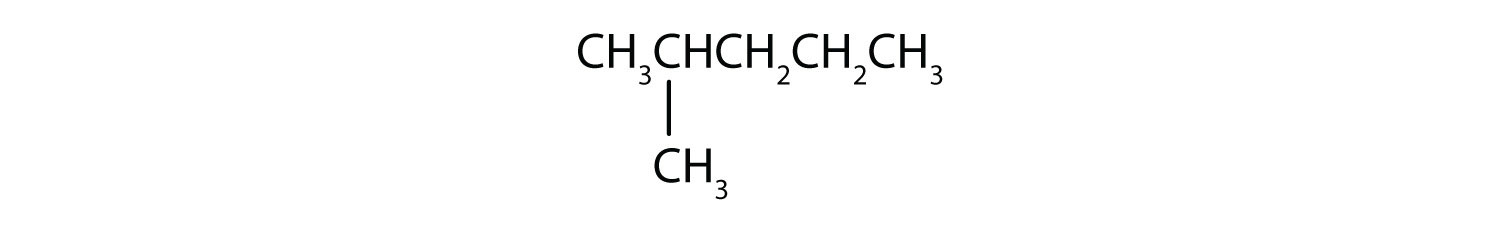
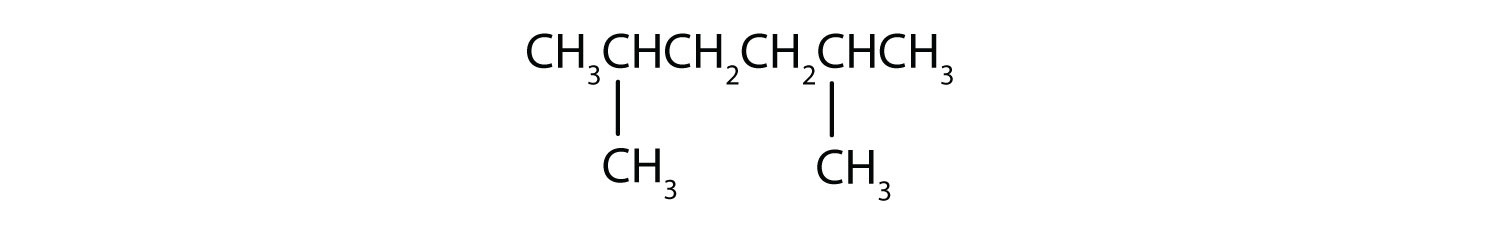
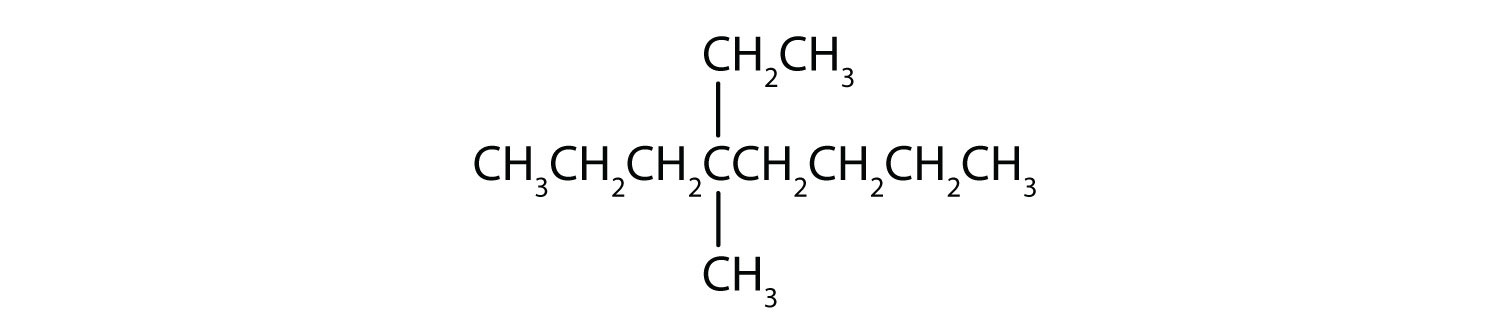
Solution
Name each compound.
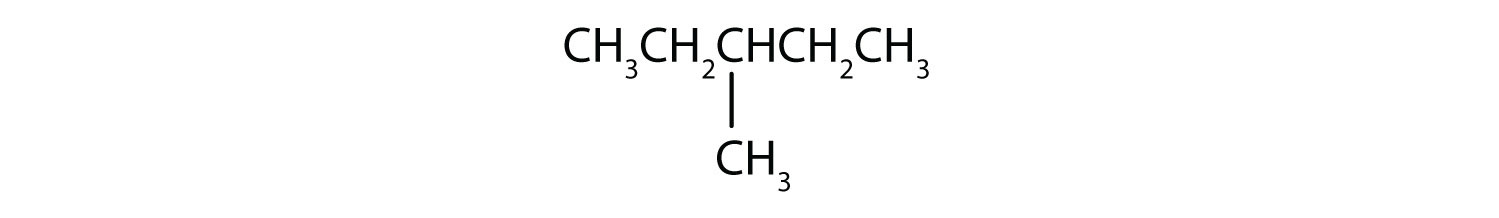
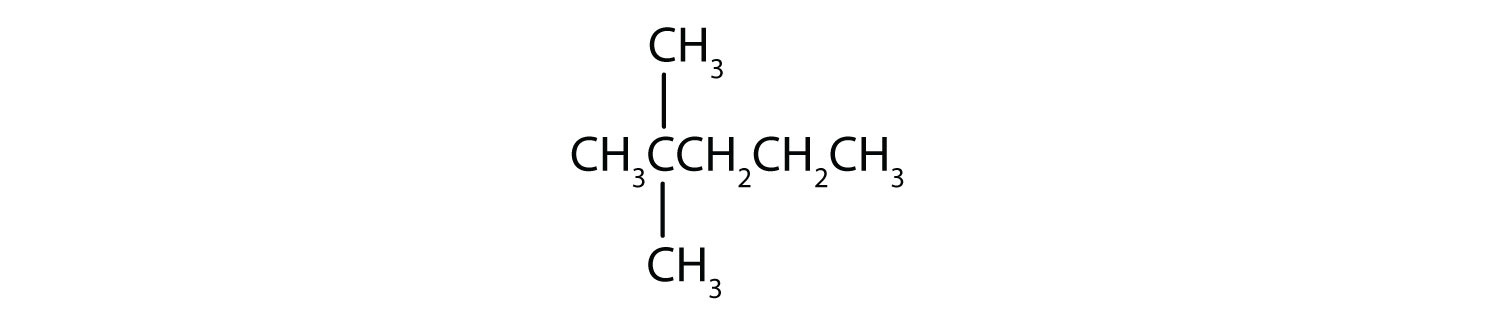
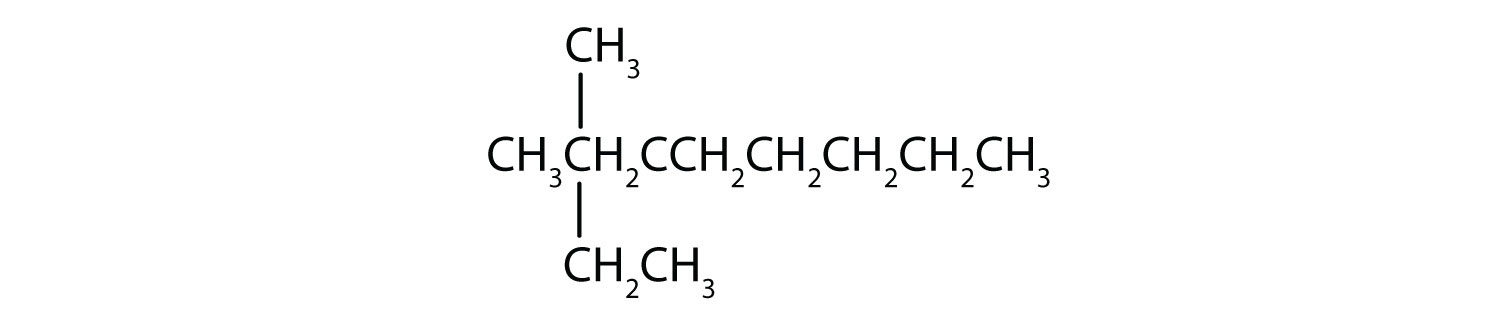
Draw the structure for each compound.
Solution
In drawing structures, always start with the parent chain.
The parent chain is butane, indicating four carbon atoms in the LCC.
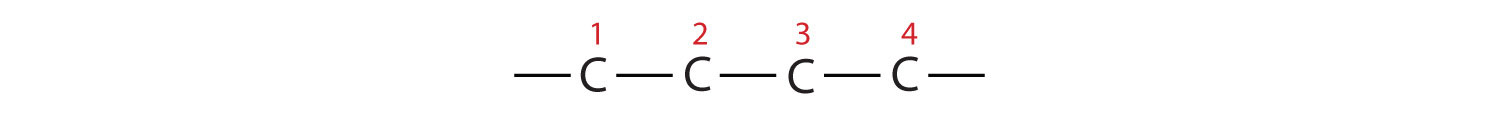
Then add the groups at their proper positions. You can number the parent chain from either direction as long as you are consistent; just don’t change directions before the structure is done. The name indicates two methyl (CH3) groups, one on the second carbon atom and one on the third.
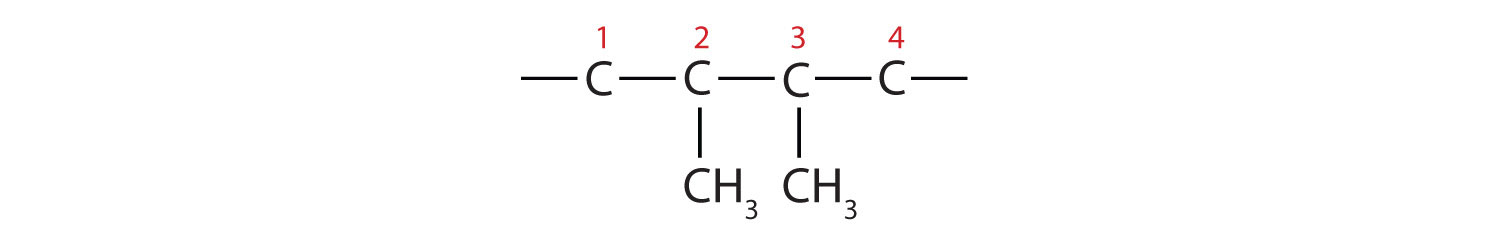
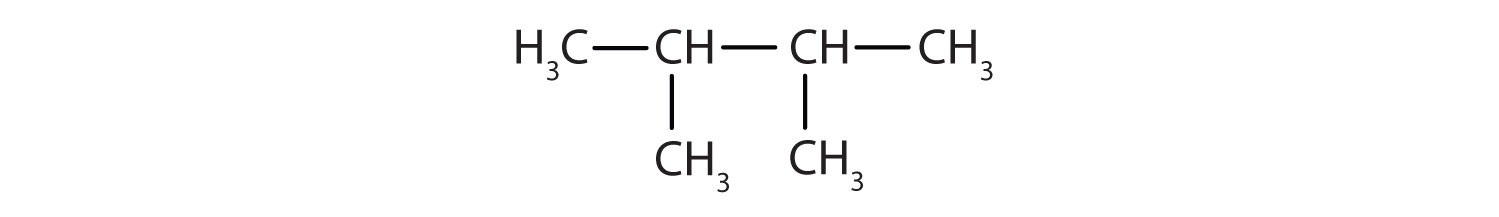
Finally, fill in all the hydrogen atoms, keeping in mind that each carbon atom must have four bonds.
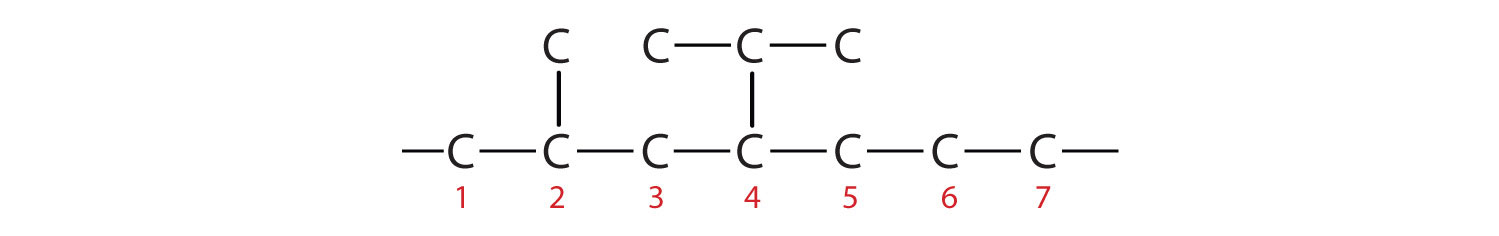
The parent chain is heptane in this case, indicating seven carbon atoms in the LCC.
–C–C–C–C–C–C–C–Adding the groups at their proper positions gives
Filling in all the hydrogen atoms gives the following condensed structural formulas:
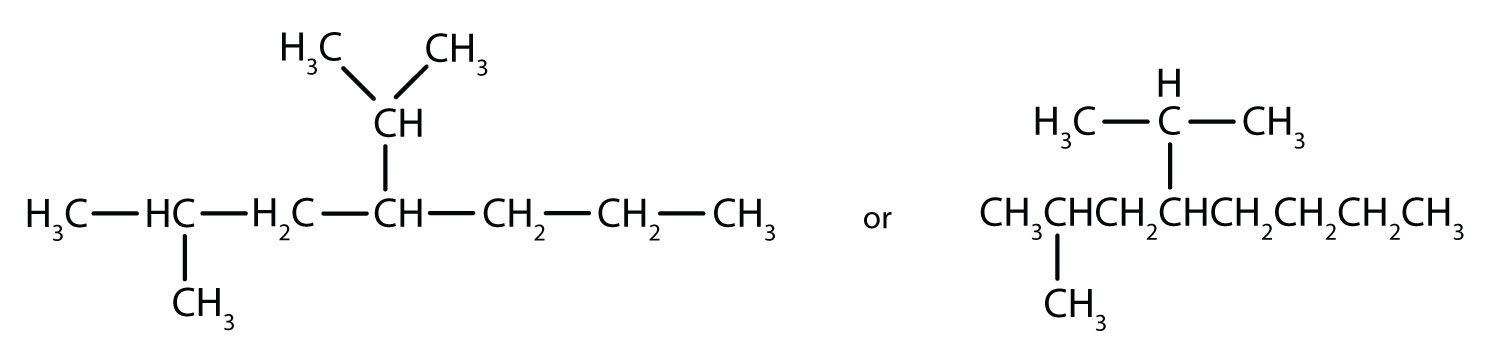
Note that the bonds (dashes) can be shown or not; sometimes they are needed for spacing.
Draw the structure for each compound.
4-ethyloctane
3-ethyl-2-methylpentane
3,3,5-trimethylheptane
What is a CH3 group called when it is attached to a chain of carbon atoms—a substituent or a functional group?
Which type of name uses numbers to locate substituents—common names or IUPAC names?
substituent
IUPAC names
Briefly identify the important distinctions between an alkane and an alkyl group.
How many carbon atoms are present in each molecule?
How many carbon atoms are present in each molecule?
Draw the structure for each compound.
Draw the structure for each compound.
Name each compound according to the IUPAC system.
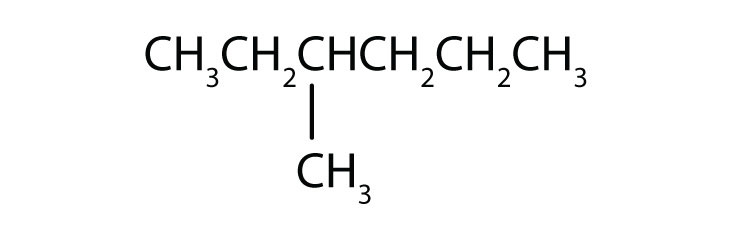
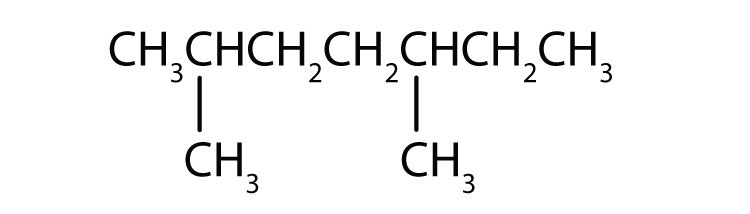
Name each compound according to the IUPAC system.
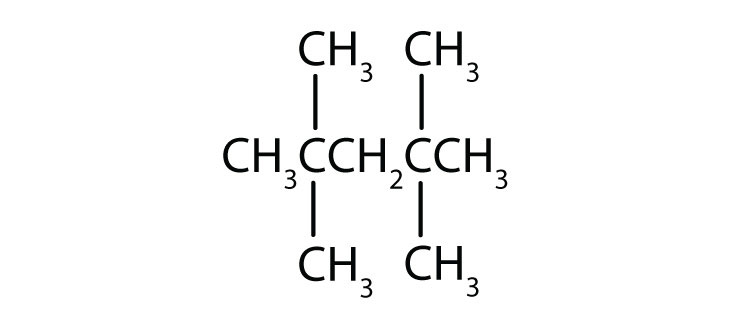
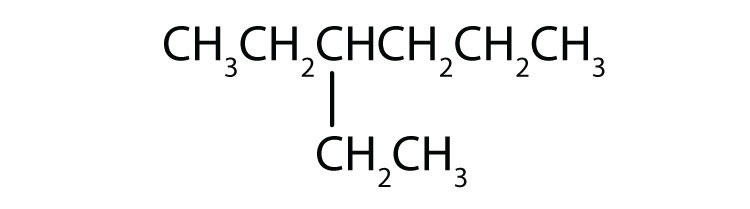
What is a substituent? How is the location of a substituent indicated in the IUPAC system?
Briefly identify the important distinctions between a common name and an IUPAC name.
An alkane is a molecule; an alkyl group is not an independent molecule but rather a part of a molecule that we consider as a unit.
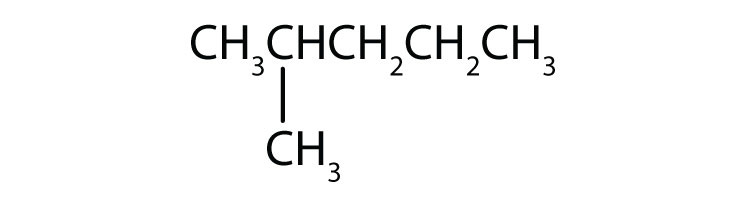
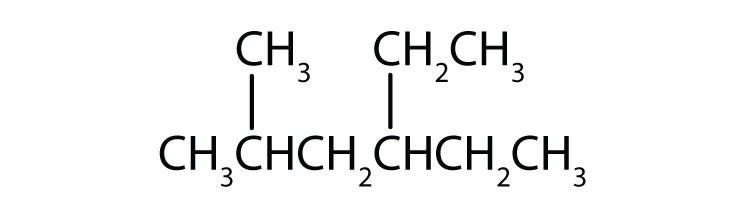
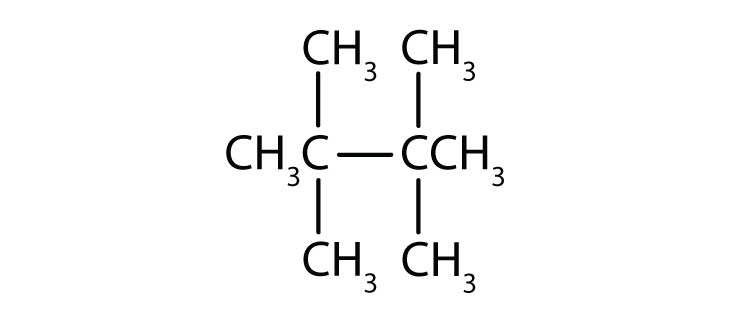
Common names are widely used but not very systematic; IUPAC names identify a parent compound and name other groups as substituents.