1
A bond with a maturity of less than one year is classified as which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Money market instrument |
||
|
b. Shot-term market instrument |
||
|
c. Capital market instrument |
||
|
d. One year market instrument |
Question 2
A debt instrument can be issued by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Corporation |
||
|
b. Individual |
||
|
c. Government |
||
|
d. All of the above |
Question 3
A deposits funds with B for safekeeping. B lends the funds to C and charges C interest. Which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. C is a financial intermediary. |
||
|
b. B is a financial intermediary. |
||
|
c. A is a financial intermediary. |
||
|
d. A, B, and C do not fulfill any financial role. |
Question 4
A financial instrument that promises to pay the holder a certain fixed amount periodically, and upon maturity pays the face value of the instrument is called which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Bond |
||
|
b. Equity |
||
|
c. Receivable |
||
|
d. Credit |
Question 5
A financial instrument which does not promise the holder any fixed payment but entitles him/her to a claim of the net income is called which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Bond |
||
|
b. Equity |
||
|
c. Receivable |
||
|
d. Credit |
Question 6
A government issues securities with maturities of six months. These securities would be known as which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Equity market instruments |
||
|
b. Capital Market instruments |
||
|
c. Short-term debt instruments |
||
|
d. Medium-term instruments |
Question 7
A new ten-year bond will be bought and sold in what market?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Primary market |
||
|
b. Ten-year market |
||
|
c. Short-term market |
||
|
d. Secondary market |
Question 8
Complete the following statement. Adverse selection occurs when:
Choose one answer.
|
a. borrowers get loans by falsely presenting how profitable their projects really are. |
||
|
b. borrowers do not get the loans, because they suffer discrimination. |
||
|
c. lenders do not lend to borrowers with bad credit. |
||
|
d. lenders lend only to borrowers with good credit. |
Question 9
Complete the following statement. Capital market instruments have maturities of:
Choose one answer.
|
a. Less than one year. |
||
|
b. More than one year. |
||
|
c. Any number of years. |
||
|
d. Usually ten years. |
Question 10
Complete the following statement. Money market instruments have maturities of:
Choose one answer.
|
a. Less than one year. |
||
|
b. More than one year. |
||
|
c. Any number of years. |
||
|
d. Usually ten years. |
Question 11
Complete the following statement. The federal funds market is the market where:
Choose one answer.
|
a. the federal government sells overnight securities. |
||
|
b. the federal government buys overnight securities. |
||
|
c. banks reserves at the Federal Reserve are bought and sold overnight. |
||
|
d. the Federal Reserve Bank loans overnight funds to banks. |
Question 12
Complete the following statement. The problem of adverse selection in financial markets, which financial intermediaries have evolved to minimize, refers to the difficulty in:
Choose one answer.
|
a. Separating creditworthy borrowers from non-credit worthy borrowers |
||
|
b. Not knowing borrowers who will take more risk after the loan contract than those who will not |
||
|
c. Providing incentives for borrowers to behave responsibly |
||
|
d. Punishing borrowers when they default on their loan contracts |
Question 13
Consider whether the following statement is true or false and how so. Money is useful only when it can be held in the hand.
Choose one answer.
|
a. This is true, because that is only when you can use it to buy something. |
||
|
b. This is true, because money has to be a commodity. |
||
|
c. This is false, because money is an accounting device that does not need be tangible. |
||
|
d. None of the above |
Question 14
Corporate bonds are issued by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Any corporation looking for funds |
||
|
b. Corporations emerging from bankruptcy that need funds |
||
|
c. Corporations with strong credit ratings that need funds |
||
|
d. Corporations that have the approval of the Board of Directors |
Question 15
Fill in the blanks. Financial intermediaries are the major means of moving funds from savers to borrowers, because they are able to provide financial services at ______ by taking advantage of ______.
Choose one answer.
|
a. lower cost; economies of scale |
||
|
b. lower cost; adverse selection |
||
|
c. higher cost; economies of scale |
||
|
d. higher cost; adverse selection |
Question 16
Fill in the blanks. Financial intermediaries are efficient at moving funds from savers to borrowers, because they ______ by ______.
Choose one answer.
|
a. lower risk; spreading it among many |
||
|
b. lower risk: confining it to the very rich |
||
|
c. raise risk; charging higher interest rates |
||
|
d. raise risk; charging lower interest rates |
Question 17
Fill in the blanks. In a world where there is only direct financing, small savers would be subject to ______, because their portfolios would not be sufficiently ______.
Choose one answer.
|
a. high risks, diversified |
||
|
b. low risks, large to securitize |
||
|
c. no risk, diversified |
||
|
d. no risk, fully diversified |
Question 18
Fill in the blanks. The presence of asymmetric information in financial markets leads to ______ as people with investment opportunities ______.
Choose one answer.
|
a. less economic growth; will not borrow at low interest rates |
||
|
b. less economic growth; cannot have access to loans |
||
|
c. more economic growth; are force to used their own funds |
||
|
d. more economic growth; can borrow from banks |
Question 19
Fill in the blanks. Underwriting is undertaken by __________ when they __________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. commercial banks, give out loans |
||
|
b. commercial banks, foreclose on properties |
||
|
c. investment banks, guarantee security prices and buy them |
||
|
d. investment banks, guarantee security prices and sell them |
Question 20
Fill in the blanks. When a company wants to raise money from financial markets, it may go to _________, which will help it issue a(n) __________.
Choose one answer.
|
a. the stock market, loan |
||
|
b. the capital market, equity |
||
|
c. an investment bank, initial public offering (IPO) |
||
|
d. commercial bank, initial public offering (IPO) |
Question 21
Financial intermediaries succeed in lending and borrowing by doing which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Reducing moral hazard |
||
|
b. Increasing moral hazard |
||
|
c. Withholding information from borrowers |
||
|
d. Paying attention to borrowers |
Question 22
First All Bank is a financial intermediary. This means that First All Bank does which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Lends its own funds money to borrowers |
||
|
b. Holds deposits for depositors and charges fees for the service |
||
|
c. Takes deposits from depositors and lends them to borrowers |
||
|
d. Seeks borrowers for depositors |
Question 23
How do financial markets promote economic development?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They enable entrepreneurs without funds to have access to funds. |
||
|
b. They make the wealthy wealthier. |
||
|
c. They enable investment bankers to earn higher salaries. |
||
|
d. They make people with capital gains income pay lower taxes. |
Question 24
How do financial markets promote economic efficiency?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They match borrowers who have productive business ideas with savers. |
||
|
b. They enable lenders to minimize the time it takes to find a borrower. |
||
|
c. They enable borrowers to minimize the time it takes to find a lender. |
||
|
d. All of the above |
Question 25
I lend funds to Jake, who has a reputation of being trustworthy. He turns around and lends the funds to Jane, whom I do not know. Which of the following characterizes Jake’s role?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Money lender |
||
|
b. Intermediary |
||
|
c. Broker |
||
|
d. Dealer |
Question 26
If money is a unit of account, then which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Money stores value. |
||
|
b. Money is used to measure the value of things. |
||
|
c. Money is used to buy goods and services. |
||
|
d. Money has no value. |
Question 27
In a certain society, people use shells as a means of payment and store of value. The unit of account is gold. Which of the following is true of this economy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. This economy is not a monetary economy, because shells are not money. |
||
|
b. This economy is not a monetary economy, because there are no denominations. |
||
|
c. This economy is a monetary economy, because all the functions of money are being performed. |
||
|
d. This economy is a monetary economy, because they use gold. |
Question 28
In a public school, everybody will accept a bubblegum as payment for goods or services rendered, even if they do not like bubblegum. Bubblegum in this school is considered which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Income |
||
|
b. Money |
||
|
c. Insurance for when you want to chew gum |
||
|
d. Something to barter with |
Question 29
In direct finance, as opposed to indirect finance, the transaction is between what entities?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The lender and the borrower |
||
|
b. The lender the borrower and the intermediary |
||
|
c. The borrower and the bank |
||
|
d. The lender and the bank |
Question 30
James, John, and Kojo buy houses with funds from First All Bank. First All Bank puts all three loan agreements together, divides them into one hundred pieces of financial instruments, and sells them to several investors. The one hundred financial instruments can be accurately described as which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Financial liabilities |
||
|
b. Financial assets |
||
|
c. Bank securities |
||
|
d. Mortgage-backed securities |
Question 31
Joan borrows $100.00 from her sister with the promise to repay at the end of the month. Her sister goes to the bank to withdraw $100.00 from her bank account to give it to her. This is an instance of which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Direct borrowing |
||
|
b. Direct financing |
||
|
c. Direct lending |
||
|
d. Indirect financing |
Question 32
Loans to households to buy houses generate which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Money market instruments |
||
|
b. Equity market instruments |
||
|
c. Mortgage-backed securities |
||
|
d. Commercial papers |
Question 33
Money functions as which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Medium of exchange, store of value, and unit of account |
||
|
b. Medium of exchange, store of value, and income |
||
|
c. Store of value and income |
||
|
d. Store of value and a payment mechanism |
Question 34
Moral hazard occurs when a borrower does which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Undertakes a less risky business venture after obtaining a loan |
||
|
b. Undertakes a more risky business venture after obtaining a loan |
||
|
c. Absconds with the loan proceeds and does not repay |
||
|
d. Suffers a setback through no fault of his/hers and is unable to repay |
Question 35
Pam asks her mother for a loan. Her mother does not have it, so she borrows from her sister, and gives it to Pam. This transaction can be described as which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Refinance |
||
|
b. Direct finance |
||
|
c. Indirect finance |
||
|
d. Financial market transaction |
Question 36
Repurchase agreements (repos) can be classified as which of the following type of economic instrument?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Short-term debt instruments |
||
|
b. Capital market instruments |
||
|
c. Equity market instruments |
||
|
d. Long-term debt instruments |
Question 37
Stocks are issued by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Individuals |
||
|
b. Partnerships |
||
|
c. Corporations |
||
|
d. Governments |
Question 38
The payment you receive for working is called which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Money |
||
|
b. Income |
||
|
c. Interest |
||
|
d. Rents |
Question 39
Treasury bills are issued by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Domestic corporations |
||
|
b. Individuals |
||
|
c. Governments |
||
|
d. Foreign corporations |
Question 40
What are commercial papers?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Long-term instruments issued by large banks and well-known corporations |
||
|
b. Short-term instruments issued by large banks and well-known corporations |
||
|
c. Medium-term instruments issued by corporations who cannot borrow from banks |
||
|
d. Long-term instruments issued by corporation who do not want to borrow from banks |
Question 41
What are convertible corporate bonds?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Corporate bonds that allow the holder to convert them into shares |
||
|
b. Corporate bonds that can be converted into cash at any time |
||
|
c. Corporate bonds that have no maturity dates |
||
|
d. Corporate bonds that have maturity dates determined by the bondholder |
Question 42
What are equities?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Capital market instruments |
||
|
b. Money market instruments |
||
|
c. Short-term market instruments |
||
|
d. Over-the-counter market instruments |
Question 43
What are Eurodollars?
Choose one answer.
|
a. U.S. dollars which an individual takes on vacation to Europe |
||
|
b. Bonds issued in Europe but denominated in U.S. dollars |
||
|
c. U.S. dollar deposits owned by Europeans |
||
|
d. U.S. dollars deposited in banks outside the United States |
Question 44
What are treasury bills?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Capital market instruments |
||
|
b. Money market instruments |
||
|
c. Over-the-market instruments |
||
|
d. Equity market instrument |
Question 45
What is a Eurobond?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A bond issued and sold in the UK but denominated in U.S. dollars |
||
|
b. A bond issued by the European Union |
||
|
c. Any bond issued by any country in Europe |
||
|
d. A bond issued in the U.S. in dollars but bought by Europeans |
Question 46
What is a secondary market?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A market where new securities are bought and sold |
||
|
b. A market where U.S. government treasuries are bought and sold |
||
|
c. A market where newly issued and outstanding securities are bought and sold |
||
|
d. A market where outstanding securities are bought and sold |
Question 47
What is an asset-backed security?
Choose one answer.
|
a. A loan to buy an asset |
||
|
b. A loan with an asset as collateral |
||
|
c. A loan with no asset as collateral |
||
|
d. A loan with a co-signer |
Question 48
What is the Federal Funds rate?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate on loans the Federal Reserve Bank makes to banks. |
||
|
b. The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate on loans made in the federal funds market. |
||
|
c. The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate on loans the Federal Reserve Bank makes to the government. |
||
|
d. The Federal Funds rate is the interest rate on loans banks make to the Federal Reserve Bank. |
Question 49
What would be a consequence of the failure of financial markets?
Choose one answer.
|
a. There will be no savings. |
||
|
b. There will be no income earned. |
||
|
c. There will be no money in the economy. |
||
|
d. Economic activity will decline. |
Question 50
When a business borrows directly from a saver, the business incurs which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Liability |
||
|
b. A credit |
||
|
c. Equity |
||
|
d. An asset |
Question 51
When a business borrows directly from financial markets, it issues which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Securities |
||
|
b. Equities |
||
|
c. Dividends |
||
|
d. Credits |
Question 52
When a person lends to a business in the financial market, the person acquires which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An asset |
||
|
b. A liability |
||
|
c. A debt |
||
|
d. A credit |
Question 53
When an individual takes out a loan from a bank to buy a car, the individual issues which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Security |
||
|
b. Equity |
||
|
c. Commercial paper |
||
|
d. Certificate of deposit |
Question 54
Which of the following is a main reason for the dominance of financial intermediaries in the economy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They are able to reduce transaction costs through economies of scale. |
||
|
b. They are able to lend large sums of money to those who need it. |
||
|
c. They employ of a lot of people to market their loans. |
||
|
d. They have good management skills. |
Question 55
Which of the following is the best functional definition of money?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Anything that the government says is money |
||
|
b. Anything that provides utility for people |
||
|
c. Anything that is generally acceptable as a medium of exchange |
||
|
d. Anything that is desirable, because it can be consumed |
Question 56
Which scenario best describes direct finance and not indirect finance?
Choose one answer.
|
a. ABC Corporation uses its retained earnings to finance a new project. |
||
|
b. ABC Corporation sells its old equipment to finance a new project. |
||
|
c. ABC Corporation raises funds by selling commercial paper to DEF Finance Company. |
||
|
d. ABC Corporation raises funds by borrowing from its bank. |
Question 57
Who are the participants in financial markets?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Households |
||
|
b. Households and businesses |
||
|
c. Households, businesses, and governments |
||
|
d. Households, businesses, governments, and foreigners |
Question 58
Why are bonds issued by municipalities to finance large projects attractive to investors?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Because the interest rates on them are higher than the interest rate on corporate bonds |
||
|
b. Because the interest rates are exempt from federal income tax |
||
|
c. Because they are short-term instruments and therefore very liquid |
||
|
d. Because the capital gains on them are higher than on many securities |
Question 59
Why are financial markets important in the economy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They can make a lot of people wealthy. |
||
|
b. They can make businesses and people wealthy. |
||
|
c. They make it possible to transfer savings to borrowers. |
||
|
d. They make it possible for governments to borrow. |
Question 60
Why is an efficient secondary market essential for an efficient financial market?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It makes it easier for firms to sell new bonds in the primary market. |
||
|
b. It makes it easier for firms to sell new bonds in the secondary market. |
||
|
c. It makes it easier for firms to sell new bonds in both the secondary and primary markets. |
||
|
d. It makes it easier for firms to buy and sell new bonds in the secondary and a primary markets. |
Question 61
Why is indirect finance more important than direct finance in the U.S. economy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It moves more funds from savers to borrowers than direct finance. |
||
|
b. It moves as much funds from savers to borrowers as direct finance. |
||
|
c. It is the only means by which funds can move from savers to borrowers. |
||
|
d. It is responsible for all the economic activity in the U.S. |
Question 62
Why would a modern economy not operate efficiently without money?
Choose one answer.
|
a. People could not trade. |
||
|
b. People would not want to work, because there would be no money to pay them. |
||
|
c. People would take time away from work to search for trading partners. |
||
|
d. People would produce only what they want to consume. |
Question 63
Without financial intermediaries, why would small savers not benefit from financial markets?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Nobody would want to borrow from them, because their funds would be too small. |
||
|
b. Nobody would want to borrow from them, because they are not banks. |
||
|
c. The cost of a one-time loan of a small amount would be too high to make it worth their while to lend. |
||
|
d. The return on lending would be too high for them to want to lend. |
Question 64
A commercial paper with a ten year maturity pays an annual interest rate of 7%, while a U.S. government bond with the same maturity pays 5%. What could account for the difference?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The commercial paper is more attractive to investors. |
||
|
b. The commercial paper is less risky. |
||
|
c. The U.S. government bond is more liquid. |
||
|
d. The U.S. government bond is riskier. |
Question 65
Amelia gives Ben a one-hundred dollar loan payable in a year. She tells him that when he repays her, he should make sure that the repayment can buy as many hamburgers as the initial one hundred dollars bought. What would be the correct inference from Amelia’s stipulation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The interest rate on the loan is zero. |
||
|
b. The real interest rate on the loan is zero. |
||
|
c. The nominal interest rate on the loan is zero. |
||
|
d. The nominal interest rate on the loan is equal to the real interest rate. |
Question 66
Arianna took a one-year loan from Sammy at an interest rate of 7% at a time when expected inflation was 3%. The actual inflation turned out to be 10%. Which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. In real terms, Jane paid less than she expected to pay. |
||
|
b. In real terms, Jane paid more than she expected to pay. |
||
|
c. In nominal terms, Jane paid more than she expected to pay. |
||
|
d. Jane paid no more nor less than she expected to pay. |
Question 67
Complete the following statement. Interest rates on Greek Sovereign Bonds are higher than on German Sovereign Bonds. One possible explanation may be that:
Choose one answer.
|
a. there is a higher demand for Greek Sovereign Bonds than there is for German Sovereign Bonds. |
||
|
b. Greek Sovereign Bonds are more liquid than German Sovereign Bonds. |
||
|
c. Greek Sovereign Bonds are more risky than German Sovereign Bonds. |
||
|
d. there is a lower demand for German Sovereign Bonds than there is for Greek Sovereign Bonds. |
Question 68
Complete the following statement. The more easily a security can be sold and bought:
Choose one answer.
|
a. the more risky it is. |
||
|
b. the more liquid it is. |
||
|
c. the less desirable it is. |
||
|
d. the higher the interest rate it pays. |
Question 69
Complete the following statement. The present discounted value of a stream of cash payments will always be:
Choose one answer.
|
a. Less than the sum of the stream of payments. |
||
|
b. More than the sum of the stream of payments. |
||
|
c. About the same as the sum of the stream of payments. |
||
|
d. Exactly equal to the sum of the stream payments. |
Question 70
Consider the following equation, where PV is the present value, CFi is the cash flow at time i, and n is the number of years. Which of the following is a proper interpretation of r?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The interest rate |
||
|
b. The discount rate |
||
|
c. The nominal interest rate |
||
|
d. The real interest rate |
Question 71
Erica borrows $1,000.00 from Jorge. Jorge demands repayment in a year in the amount of $1,100.00. What is the yield to maturity?
Choose one answer.
|
a. $100.00 |
||
|
b. 10.00% |
||
|
c. 90.91% |
||
|
d. 9.09% |
Question 72
Erica borrows $1,000.00 from Jorge. Jorge demands repayment in a year in the amount of $1,100.00. What is the yield to maturity?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The same as the simple interest rate |
||
|
b. Greater than the simple interest rate |
||
|
c. Less than the simple interest rate |
||
|
d. Cannot be determined from the given information |
Question 73
Everything else remaining constant, if the risk associated with holding security increases, what will happen to the price and interest rate?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The price of the security will increase, and the interest rate will increase. |
||
|
b. The price of the security will increase, and the interest rate will decrease. |
||
|
c. The price of the security will decrease, and the interest rate will decrease. |
||
|
d. The price of the security will decrease, and the interest rate will increase. |
Question 74
How is risk premium defined?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The spread between the interest rates on default-free and default-risk bonds of the same maturity |
||
|
b. The spread between interest rates on default-free and default risk bonds with different maturities |
||
|
c. The yield to maturity plus the expected inflation over the period the bond is held |
||
|
d. The yield to maturity plus the actual inflation over the period the bond is held |
Question 75
If the risk associated with holding an asset increases and expected inflation also increases, then what will happen to the equilibrium interest rate?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It will increase. |
||
|
b. It will decrease. |
||
|
c. It will remain the same. |
||
|
d. It cannot be determined. |
Question 76
In Table 1 below, what will be the interest rate on a two-year bond?
TABLE 1
Expected interest rate on one-year bonds over the next five years is as follows:
TABLE 1
Expected interest rate on one-year bonds over the next five years is as follows:
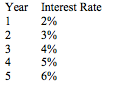
Choose one answer.
|
a. 2% |
||
|
b. 2.5% |
||
|
c. 3.0% |
||
|
d. 5.0% |
Question 77
In Table 1 below, what will be the slope of the yield curve?
TABLE 1
Expected interest rate on one-year bonds over the next five years is as follows:
TABLE 1
Expected interest rate on one-year bonds over the next five years is as follows:
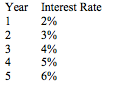
Choose one answer.
|
a. Downward sloping |
||
|
b. Flat |
||
|
c. Upward Sloping |
||
|
d. Flat then upward sloping |
Question 78
The interest rate is determined by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The demand for securities |
||
|
b. The supply of securities |
||
|
c. The demand and supply of securities |
||
|
d. The needs of banks |
Question 79
The rate of return on a security or bond can be negative under which circumstance?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The interest rate falls, and you sell before maturity. |
||
|
b. The interest rate rises, and you sell before maturity. |
||
|
c. The interest rate does not change, and you sell it at par before maturity. |
||
|
d. The interest rate does not change, and you hold it to maturity. |
Question 80
The real interest rate is measured by which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The difference between the actual interest rate and the observed interest rate |
||
|
b. The sum of the nominal interest rate and inflation |
||
|
c. The difference between the nominal interest rate and inflation |
||
|
d. The difference between the nominal interest rate and the prime rate |
Question 81
The U.S. government is running a big budget deficit and plans to finance the deficit by borrowing. If everything else remaining constant, then what will happen to the demand for bonds?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It will increase. |
||
|
b. It will decrease. |
||
|
c. It will not change. |
||
|
d. It cannot be determined since other factors can change. |
Question 82
The U.S. government is running a big budget deficit and plans to finance the deficit by borrowing. If everything else remaining constant, then what will happen to the supply of bonds and the interest rate?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The supply will increase, and the interest rate will decrease. |
||
|
b. The supply will decrease, and the interest rate will decrease. |
||
|
c. The supply will not change, but the interest rate will increase. |
||
|
d. The supply will increase, and the interest rate will increase. |
Question 83
The U.S. government is running a big budget deficit and plans to finance it by borrowing. If everything else remaining constant, then what will happen to the price of bonds and the interest rate?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The price will increase, and the interest rate will increase. |
||
|
b. The price will increase, and the interest rate will decrease. |
||
|
c. The price will decrease, and the interest rate will increase. |
||
|
d. The price will decrease, and the interest rate will decrease. |
Question 84
Under what condition will real interest rate in the economy be negative?
Choose one answer.
|
a. When the real interest rate is equal to inflation |
||
|
b. When the nominal interest rate is greater than the real interest rate |
||
|
c. When inflation is greater than the nominal interest rate |
||
|
d. When inflation is equal to the nominal interest rate |
Question 85
What does an upward sloping yield curve imply?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Future short-term rates are expected to fall. |
||
|
b. Future short-term rates are expected to rise. |
||
|
c. Future long-term rates are expected to fall. |
||
|
d. Future long-term rates are expected to fall. |
Question 86
What is the yield to maturity?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The rate at which the stream of cash flows from an instrument must be discounted to equal its value today |
||
|
b. Always the ratio of the price at which the instrument is sold, divided by the price at which it is bought |
||
|
c. The rate at which the stream of cash flow must be increased to equal its future value |
||
|
d. The difference between the future value and the present value |
Question 87
Why is one hundred dollars today not the same as one hundred dollars a year from now?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Because one hundred dollars a year from now will buy less than one hundred dollars-worth of goods and services |
||
|
b. Because one hundred dollars a year from now will buy more than one hundred dollars-worth of goods and services. |
||
|
c. Because the statement does not take account of the time value of money |
||
|
d. Because people value what they receive in the future more than what they receive today |
Question 88
Why is the yield to maturity on municipal bonds with maturity of 15 years lower than the yield to maturity on U.S. government bonds with maturity of 15 years?
Choose one answer.
|
a. U.S. government bonds are riskier than municipal bonds. |
||
|
b. U.S. government bonds are less liquid than municipal bonds. |
||
|
c. Municipal bonds are less liquid than U.S. government bonds. |
||
|
d. Municipal bond interest payments are exempt from federal income taxes. |
Question 89
Why would the interest rate on U.S. government bonds be lower than the interest rate on Mexican government bonds?
Choose one answer.
|
a. U.S. government bonds have shorter maturities than Mexican government bonds. |
||
|
b. The U.S. government’s deficit is larger than the Mexican government deficit. |
||
|
c. The Mexican government’s debt is the same as the U.S. government’s debt, but the former is default-free. |
||
|
d. U.S. government bonds are more liquid than Mexican government bonds. |
Question 90
You buy a municipal bond with a face value of $1,000.00. The fixed interest payment is $100.00 a year. The bond matures in ten years. Five years before maturity, you sell the bond for $1,000.00. What will the rate of return be?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The same as the yield to maturity |
||
|
b. Greater than the yield to maturity |
||
|
c. Less than the yield to maturity |
||
|
d. Cannot be calculated |
Question 91
You buy a municipal bond with a face value of $1,000.00. The fixed interest payment is $100.00 a year. The bond matures in ten years. Five years before maturity, you decide to sell. What will the yield to maturity be?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The same as the fixed interest rate |
||
|
b. Higher than the fixed interest rate |
||
|
c. Lower than the fixed interest rate |
||
|
d. Cannot be calculated |
Question 92
You win a lottery which promises to pay you $1,000.00 over five years in equal installments. The interest rate is 5%. The amount you won is actually closest to what amount?
Choose one answer.
|
a. $1,000.00 |
||
|
b. $965.00 |
||
|
c. $865.00 |
||
|
d. $765.00 |
Question 93
A firm accepts and keeps funds for several people with the promise that they can withdraw them anytime they want. The same firm then lends the funds to borrowers. Which of the following best identifies this type of firm?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An insurance company |
||
|
b. A pension fund |
||
|
c. A depository institution |
||
|
d. A finance company |
Question 94
Banks are regulated, because governments want them to do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Lend to sectors that will make the economy grow |
||
|
b. Lend to sectors dictated by the government |
||
|
c. Avoid excessive risk |
||
|
d. Avoid making too much profit |
Question 95
Complete the following statement. Asymmetric information reduces financial transactions, because:
Choose one answer.
|
a. it makes it costly to borrow and lend. |
||
|
b. it makes it costly to lend, so nobody wants to lend. |
||
|
c. it makes it cheaper to borrow, so nobody wants to lend. |
||
|
d. it makes it cheaper to lend, so nobody wants to lend. |
Question 96
Complete the following statement. Banks are regulated because governments want them to:
Choose one answer.
|
a. Maximize profit. |
||
|
b. Operate safely. |
||
|
c. Minimize cost. |
||
|
d. Increase the money supply. |
Question 97
Fill in the blanks. By lending to many borrowers, financial intermediaries ______ through ______.
Choose one answer.
|
a. lower costs; economies of scale |
||
|
b. raise costs; economies of scale |
||
|
c. raise costs; increasing marginal returns |
||
|
d. lower costs; decreasing marginal returns |
Question 98
Fill in the blanks. Financial markets foster economic growth by facilitating the transfer of funds from ______ to ______.
Choose one answer.
|
a. the poor; the rich |
||
|
b. the government; the poor |
||
|
c. the rich; the poor |
||
|
d. savers; borrowers |
Question 99
In an effort to minimize bank failures through deposits insurance, regulators may increase which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Moral hazard |
||
|
b. Adverse selection |
||
|
c. Principal agency problems |
||
|
d. Sequential service constraint |
Question 100
The asymmetric information problem that occurs after a financial transaction is called which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Agency problem |
||
|
b. Moral hazard problem |
||
|
c. Adverse selection problem |
||
|
d. Lending problem |
Question 101
To minimize asymmetric information in financial markets, banks and financial institutions have to do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Disclose information to the public and the government |
||
|
b. Disclose information to shareholders |
||
|
c. Keep their proprietary information from potential saboteurs |
||
|
d. Tell the government whenever they change their portfolio of assets |
Question 102
Which of the following reasons accurately explains why governments regulate banks?
Choose one answer.
|
a. To impose capital requirements |
||
|
b. To only allow them to buy safe stocks |
||
|
c. To appoint the members of the Board of Directors |
||
|
d. To only allow them to borrow from the Federal Reserve Bank |
Question 103
Which of the following reasons accurately explains why governments regulate banks?
Choose one answer.
|
a. To require them to be under a bank holding company |
||
|
b. To require them to buy only preferred common stocks |
||
|
c. To supervise their activities |
||
|
d. To prevent them from branching |
Question 104
Which of the following reasons explains why financial institutions are heavily regulated?
Choose one answer.
|
a. When they fail, owners of the bank lose their capital. |
||
|
b. When they fail, depositors lose their deposits. |
||
|
c. When they fail, the government has to bail them out. |
||
|
d. When they fail, it causes disruptions in economic activity. |
Question 105
A central bank mandate might be established in order to do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Maintain price stability |
||
|
b. Make the most profit for shareholders |
||
|
c. Reduce the price level |
||
|
d. Control government spending |
Question 106
Complete the following statement. If the Federal Reserve Bank uses the money supply as a target, then:
Choose one answer.
|
a. it cannot at the same time control the monetary base. |
||
|
b. it cannot at the same time control the reserve deposit ratio. |
||
|
c. it cannot at the same time control the interest rate. |
||
|
d. it cannot at the same time control the price level. |
Question 107
Complete the following statement. The effectiveness of monetary policy is often said to be asymmetric. This means that monetary policy is:
Choose one answer.
|
a. Ineffective during both expansions recessions. |
||
|
b. Ineffective during recessions. |
||
|
c. Ineffective during expansions. |
||
|
d. Ineffective at the trough of the business cycle. |
Question 108
In seeking to increase the money supply, the Federal Reserve Bank could do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Buy government bonds and thus increase reserves |
||
|
b. Sell government bonds and thus increase reserves |
||
|
c. Buy government bonds and thus decrease reserves |
||
|
d. Sell government bonds and thus decrease reserves |
Question 109
One of the ways the Federal Reserve Bank can control the money supply is to do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Alter the required reserve ratio |
||
|
b. Alter the currency to deposit ratio |
||
|
c. Forbid the banks from taking deposits |
||
|
d. Encourage the banks to take more deposits |
Question 110
The central bank can influence economic activity by doing which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Conducting fiscal policy |
||
|
b. Conducting monetary policy |
||
|
c. Advising the president |
||
|
d. Advising Congress |
Question 111
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) of the Federal Reserve Bank is primarily responsible for which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Conducting open market operations |
||
|
b. Conducting closed market operations |
||
|
c. Conducting fiscal policy |
||
|
d. Chartering state banks |
Question 112
The Federal Reserve Bank of the U.S. is often said to have dual mandates. What is the purpose of dual mandates?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They prevent the price level from increasing and keep the exchange rate stable. |
||
|
b. They prevent the price level from increasing and ensure full employment. |
||
|
c. They maintain price stability and ensure full employment. |
||
|
d. They maintain price stability and ensure zero unemployment. |
Question 113
To achieve the mandate of full employment, the Federal Reserve Bank could do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Target the money supply and give up control of the interest rate |
||
|
b. Target the price level and increase the money supply |
||
|
c. Target both the interest rate and the money supply |
||
|
d. Do nothing and let the market decide what the interest rate should be |
Question 114
What is meant by interest rate targeting in the conduct of monetary policy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The practice of keeping the interest rate within a certain range to achieve some macroeconomic goal |
||
|
b. The practice of setting the money supply at a certain level and letting the interest be determined by the market |
||
|
c. The practice of banks telling borrowers how much interest rate they will pay for loans |
||
|
d. The practice of setting the rate at which the money supply will with the level of interest rate |
Question 115
What is one of the major roles of central banks, such as the Federal Reserve Bank?
Choose one answer.
|
a. To make profit for the government |
||
|
b. To make profit for shareholders |
||
|
c. To maintain price stability |
||
|
d. To increase the money supply |
Question 116
What is the preferred method the Federal Reserve Bank uses to control the money supply?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Altering the reserve deposits ratio |
||
|
b. Using moral suasion |
||
|
c. Changing margin requirements |
||
|
d. Conducting open market operations |
Question 117
When the central bank sells securities, what does it seek to do?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Increase the money supply |
||
|
b. Decrease the money supply |
||
|
c. Reduce the interest rate |
||
|
d. Increase the monetary base |
Question 118
When the Federal Reserve Bank increases the monetary base, this is a sign that it wants which of the following to occur?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Money supply to increase and the interest rate and employment to increase |
||
|
b. Money supply to increase and the interest rate and employment to decrease |
||
|
c. Money supply and the interest rate to increase as well as employment to decrease |
||
|
d. Money supply and employment to increase as well as the interest rate to decrease |
Question 119
Who heads the Federal Reserve System?
Choose one answer.
|
a. FOMC |
||
|
b. Federal Advisory Council |
||
|
c. Board of Governors |
||
|
d. Discount Rate Committee |
Question 120
Who owns the U.S. Federal Reserve?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The government |
||
|
b. Member banks |
||
|
c. All the banks in the U.S. |
||
|
d. Only the state banks |
Question 121
As an economy grows and people’s disposable income rises, what is likely to happen to the demand for foreign goods?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It will decrease, because more goods can be produced at home. |
||
|
b. It will remain the same, because they are foreign goods. |
||
|
c. It will increase, because the demand for all good will increase. |
||
|
d. Exports from the country will increase, but imports will remain the same. |
Question 122
C lowers its exchange rate with its major trading partner, U. With everything else being equal, which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. U will export more to C. |
||
|
b. C will export more to U. |
||
|
c. C will export no more to U than before. |
||
|
d. U will export nor more to C than before. |
Question 123
C produces refrigerators at a lower cost than U. With everything else being equal, the likely consequence might be which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The real exchange rate of U will rise. |
||
|
b. The real exchange rate of U will fall. |
||
|
c. The nominal exchange rate of C will rise. |
||
|
d. The nominal exchange rate of U will fall. |
Question 124
C produces refrigerators at a lower cost than U. With everything else being equal, what are the consequences of this observation?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The real exchange rate of U will fall, and U will import more refrigerators from C. |
||
|
b. The real exchange rate of U will rise, and U will import more refrigerators from C. |
||
|
c. The nominal exchange rate of C will rise, and C will import more from U. |
||
|
d. The nominal exchange rate of C will fall, and C will import more from U. |
Question 125
Complete the following statement. In the long run, the value of the U.S. dollar will rise relative to other currencies:
Choose one answer.
|
a. if U.S. businesses become less productive. |
||
|
b. if U.S. citizens choose to vacation at home. |
||
|
c. if foreigners choose to vacation at home. |
||
|
d. if U.S. businesses become more productive. |
Question 126
Country C commits to maintaining parity of its currency with that of country U. What inference can be drawn from such a policy with everything else being equal?
Choose one answer.
|
a. C’s currency is floating even if U’s currency is not. |
||
|
b. C’s currency is fixed even if U’s currency is not. |
||
|
c. U gains no trade advantage against C from devaluing its currency. |
||
|
d. U and C have currencies that float independently. |
Question 127
If a country’s income rises and the country increases its imports of another country’s goods, what will happen to the exchange rate of the importing country?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It will fall. |
||
|
b. It will rise. |
||
|
c. It will remain the same. |
||
|
d. It cannot be determined. |
Question 128
If European goods are more to U.S. citizens what will be the result?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The value of the dollar will decrease compared to the euro. |
||
|
b. The value of the dollar will increase compared to the euro. |
||
|
c. The U.S. will export more goods to Europe |
||
|
d. More U.S. citizens will travel to Europe. |
Question 129
If the exchange rate is allowed to be determined by the forces of demand and supply, the exchange rate regime is classified as which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Fixed exchange rate regime |
||
|
b. Managed exchange rate regime |
||
|
c. Demand set exchange rate regime |
||
|
d. Floating exchange rate regime |
Question 130
The demand for foreign currency by U.S. businesses and citizens derives from which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The income of foreigners |
||
|
b. The preference of foreigners for U.S. goods |
||
|
c. The income of U.S. residents |
||
|
d. The desire to accumulate foreign currency |
Question 131
The real exchange rate of the U.S. dollar in terms of the euro can be defined as which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The amount of euros one U.S. dollar can buy |
||
|
b. The amount of U.S. dollars one euro can buy |
||
|
c. The value of U.S. dollars that is exchanged for euros daily |
||
|
d. The value of goods one U.S. dollar can buy in a euro area |
Question 132
What will make the equilibrium exchange rate increase?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An increase in the demand for a country’s exports |
||
|
b. A decrease in the demand for a country’s exports |
||
|
c. An increase in the country’s imports |
||
|
d. A reduction in the interest rate in the country |
Question 133
Why is the foreign exchange market important for economic welfare?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The foreign exchange market makes it possible to buy foreign goods. |
||
|
b. The foreign exchange market makes it possible for foreigners to buy our goods. |
||
|
c. The foreign exchange market makes it possible for countries to show pride in their currencies. |
||
|
d. Both A and B |
Question 134
Without foreign exchange markets, citizens of different countries would have to do which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Live without foreign goods |
||
|
b. Travel abroad to get foreign goods |
||
|
c. Produce whatever they wanted to consume |
||
|
d. Barter |
Question 135
An increase in the money supply, with everything else held constant, results in which of the following?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The LM curve will shift to the left and decrease the interest rate. |
||
|
b. The LM curve will shift to the right and decrease the interest rate. |
||
|
c. The IS curve will shift to the right and increase the interest rate. |
||
|
d. The IS curve will shift to the right and decrease the interest rate. |
Question 136
Based on the diagram below, which of the following best describes what will happen when the money supply increases?
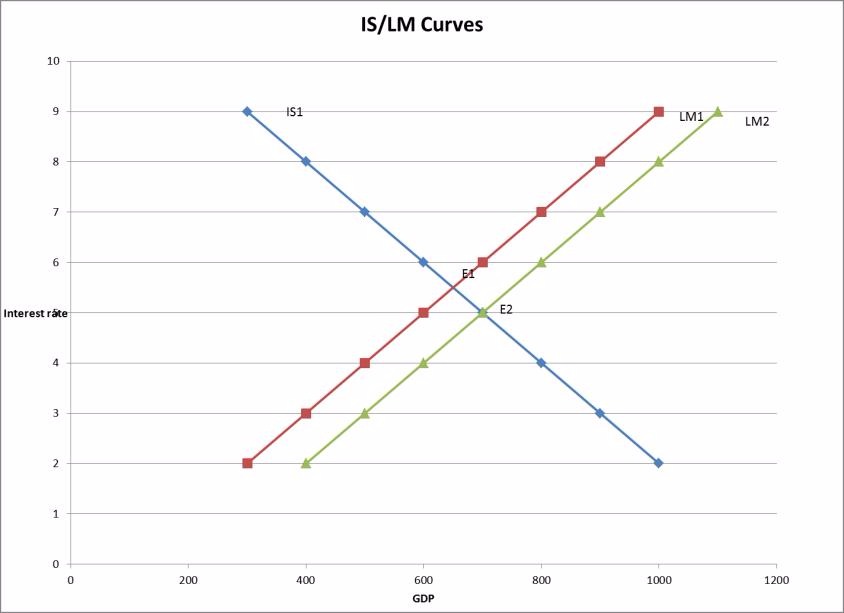
Choose one answer.
|
a. Interest rate falls, and GDP rises. |
||
|
b. Interest rate rises, and GDP rises. |
||
|
c. Interest rate falls, and GDP rises. |
||
|
d. Interest rate rises, and GDP falls. |
Question 137
Complete the following statement. According to a monetarist, attempts to use policy to stabilize the economy:
Choose one answer.
|
a. is likely to succeed in stabilizing the economy. |
||
|
b. is likely to introduce instability in the economy. |
||
|
c. will create higher inflation. |
||
|
d. will create higher deflation. |
Question 138
If the money supply is growing at a rate of 3% a year, velocity is constant and real GDP is growing is growing at 2% a year, at what will inflation be in the economy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 6% |
||
|
b. 5% |
||
|
c. 3% |
||
|
d. 1% |
Question 139
If the money supply is growing at a rate of 5%, real GDP is growing at a rate of 2% and velocity is growing at a rate of 1%, what will inflation be in the economy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. 8% |
||
|
b. 7% |
||
|
c. 5% |
||
|
d. 1% |
Question 140
What are the implications for policy when economic agents form rational expectations in making forecasts?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Monetary policy is effective. |
||
|
b. Monetary policy is only effective when coupled with fiscal policy. |
||
|
c. Fiscal policy is only effective when it is not accommodated by monetary policy. |
||
|
d. Monetary policy is ineffective. |
Question 141
What are the implications for the economy when economic agents form expectations adaptively?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Real GDP cannot be increased by monetary policy. |
||
|
b. Real GDP can be increased only by reducing the money supply. |
||
|
c. Real GDP can be increased by monetary policy over time. |
||
|
d. Only nominal GDP can be increased by monetary policy. |
Question 142
What do economists mean by the demand for money?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The amount of money people want to hold at different interest rates |
||
|
b. The amount of income people want to hold at different interest rates |
||
|
c. The amount of money the central bank wants people to hold at different interest rates |
||
|
d. The amount of money supplied by the central bank at different interest rates |
Question 143
What will be the impact of monetary policy if the LM curve is horizontal?
Choose one answer.
|
a. There will be no effect on the interest rate. |
||
|
b. The interest rate will increase. |
||
|
c. The interest rate will decrease. |
||
|
d. The interest rate will immediately fall to zero. |
Question 144
What would an increase in the money supply do in the economy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Lower the interest rate, reduce the demand for money and increase GDP |
||
|
b. Lower the interest, increase investment and increase GDP |
||
|
c. Raises the interest rate, increase investment and reduce GDP |
||
|
d. Raises interest rate, increase investment and reduce GDP |
Question 145
When the economy is caught in a liquidity trap, which of the following is true?
Choose one answer.
|
a. An increase in money supply will not lower the interest rate. |
||
|
b. An increase in the money supply will lower interest rate. |
||
|
c. An increase in the money supply will raise the GDP. |
||
|
d. An increase in the money supply will lower the GDP. |
Question 146
Which of the following statements is true of the demand for money?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The demand for money is positively related to the interest rate but negatively to income. |
||
|
b. The demand for money is positively related to the interest rate and positively to income. |
||
|
c. The demand for money is negatively related to the interest rate and negatively to income. |
||
|
d. The demand for money is negatively related to the interest rate but positively to income. |
Question 147
Why do Keynesians advocate activist fiscal policy as opposed to activist monetary policy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They believe that the economy is inherently stable and fiscal policy is more effective than monetary policy in stabilizing the economy. |
||
|
b. They believe that the economy is inherently unstable and fiscal policy is more effective than monetary policy in stabilizing the economy. |
||
|
c. They believe that monetary policy is too effective in stabilizing an inherently unstable economy and should be used sparingly. |
||
|
d. They believe fiscal policy is quick, flexible, and more effective compared to monetary policy in stabilizing the economy. |
Question 148
Why do monetarists see monetary policy as more effective than fiscal policy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. They believe that monetary policy will have a bigger impact on nominal income than an increase in government expenditure. |
||
|
b. They believe that monetary policy will have as big an impact on nominal income as a change in government expenditure. |
||
|
c. They believe that monetary policy will cause real GDP to increase by a larger amount than an increase in government expenditure. |
||
|
d. They believe that monetary policy will cause the price level to increase by a larger amount than an increase in government expenditure. |
Question 149
Why is the constant money-growth-rate rule (CMG) a non-activist monetary policy instead of an activist monetary policy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. Because under CMG policy makers are using their discretion |
||
|
b. Because under CMG policy makers are not using their discretion |
||
|
c. Because under CMG policy makers have flexibility |
||
|
d. Because under CMG the money supply can grow at a rate that is variable |
Question 150
Why might monetary policy be preferred to fiscal policy in stabilizing the economy?
Choose one answer.
|
a. It does not have a recognition lag and is therefore timely. |
||
|
b. It is always effective whether the economy is in a recession or in expansion. |
||
|
c. It is flexible and can be speedily implemented. |
||
|
d. It follows rules that are times tested to be effective. |
Question 151
With everything else held constant, when income increases, what happens to the demand for money?
Choose one answer.
|
a. The demand for money decreases. |
||
|
b. The demand for money increases. |
||
|
c. The quantity demanded of money decreases. |
||
|
d. The quantity demanded of money increases. |