“If you don’t know where you’re going, you might not get there.”
Yogi Berra
Every information system is designed to improve business in some way. However, before making an improvement, it is critical to understand the current business process. In this chapter we will develop a technique to diagram business processes. We will first diagram the current business process—the so-called As-Is process. After studying the process, we will be in a position to propose and diagram a future process—the so-called To-Be process. If we have done our job well, the To-Be process will improve upon the As-Is process, making it more efficient, effective, user friendly, and so forth. In other words, every process improvement should move the business closer to achieving its goals.
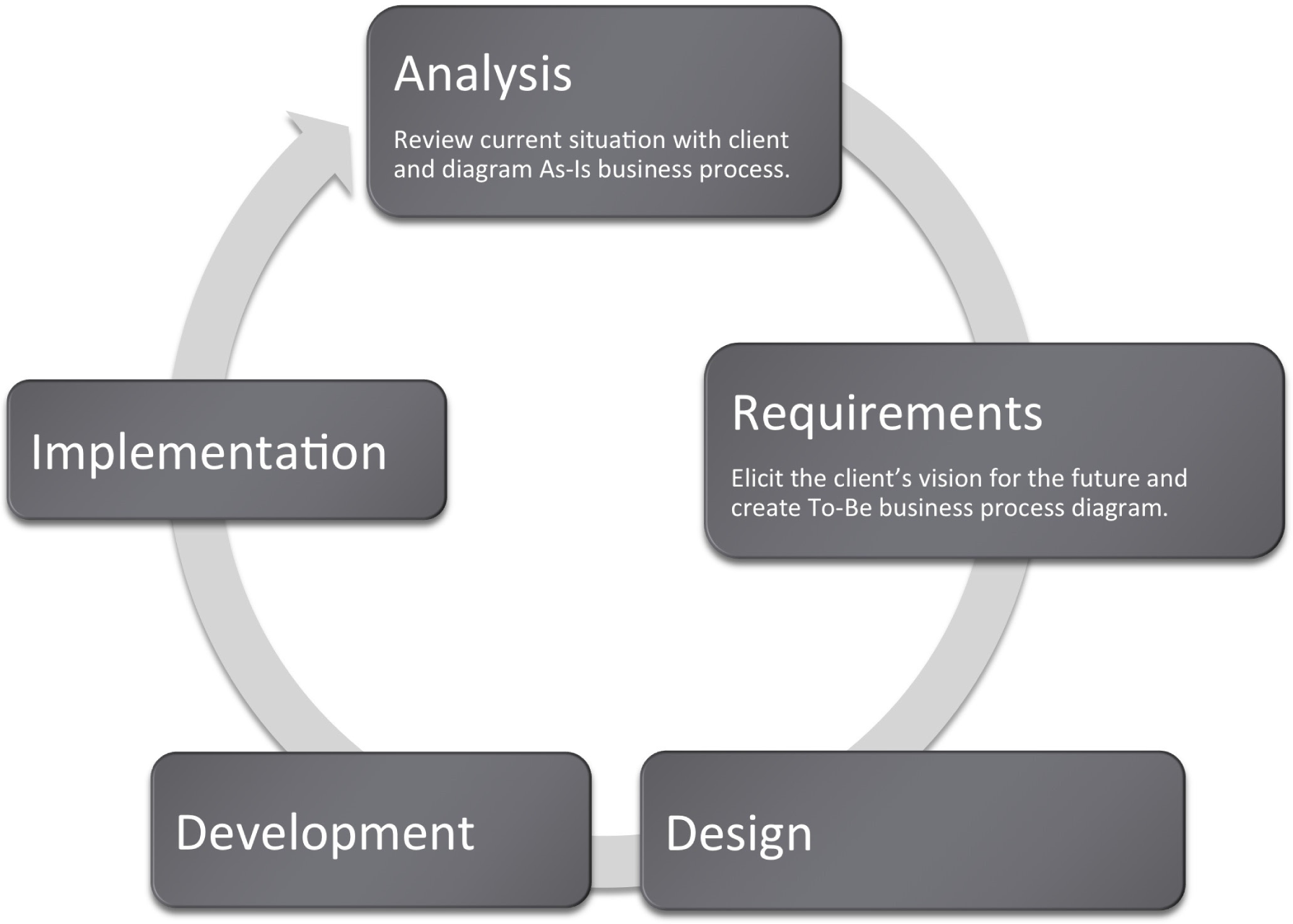
Many information systems projects are conceived of in a life cycle that progresses in stages from analysis to implementation. The diagram below shows the stages that we touch in the current chapter:
Implicit in each current and future state are one or more business processes. A business processA set of goal directed activities. is a set of goal directed activities. In other words, a process describes the actions To-Be taken to accomplish a task. For example, applying to a university, filing taxes, and evaluating employees are all processes. The steps in applying to a university might include filling out an online form, submitting a credit card payment, requesting test scores be sent, and requesting that high school transcripts be sent.
Note that all of the processes mentioned above took place even before the advent of computers. Try to imagine how. Information systems simply transform the processes with the goal of making the process more efficient, convenient, effective, reliable, and so forth.
First, we represent the current (usually deficient) state As-Is processThe way the process functions right now before any intervention or redesign.. Seeing the As-Is process diagrammed exposes obvious areas for improvement in the process. For example, many years ago students registered for classes in person. The As-Is process in that era might have shown a student waiting in line outside a large auditorium. When his turn comes up, the student enters the auditorium. There are tables representing each department staffed with faculty from that department. For each course that the student wishes to take, he must find the corresponding department table and add his name to the list for that class. Buying concert tickets followed a similar process before services like Ticket Master went online. People used to camp out for days in advance outside the Ticket Master office.
Sometimes information technology may improve processes, other times no technology is required. Sometimes the solution is as simple as providing information for individuals completing a business process at the appropriate time, or simply rearranging the steps in the business process, in which case, no new information technology is needed.
The redesigned and improved business process is called the To-BeThe way the process will function after the redesign. process. This process takes into consideration the deficiencies identified in the As-Is process and the goals of the business. The area of work that focuses on improving business processes is called business process redesign. Individuals performing this work focus on understanding the As-Is process and how to improve it in the To-Be process.
Shopping at a grocery store
The deli
The fish counter
Checkout
Shopping at an online retailer
Product display
Inventory management
Note that most business processes subsume other business processes. One of the toughest challenges is knowing what process to focus on and with what degree of granularity to zoom in on the process. Never lose site of the problem you are trying to solve—and use that as your filter.
Obviously, you can not diagram a business process without understanding the business. This will require meetings with the client. It is best to walk into those meetings with a willingness to listen rather than pretending that you know the client’s business. Ask open ended questions and take lots of notes.
Those that design systems are called business analysts or consultants. Analysts begin their work with an initial client meeting. The quality of the questions asked at that meeting may well determine the success or failure of the project. Using the following four open ended questions can help in this consulting situation (Starr, 2010):
Note that these questions capture the aspirations of the client as well as perceived barriers and enablers to reach that vision. The assumption here is that the client knows her business pretty well, and the goal of the initial meeting is to capture her knowledge and vision without jumping to a solution.
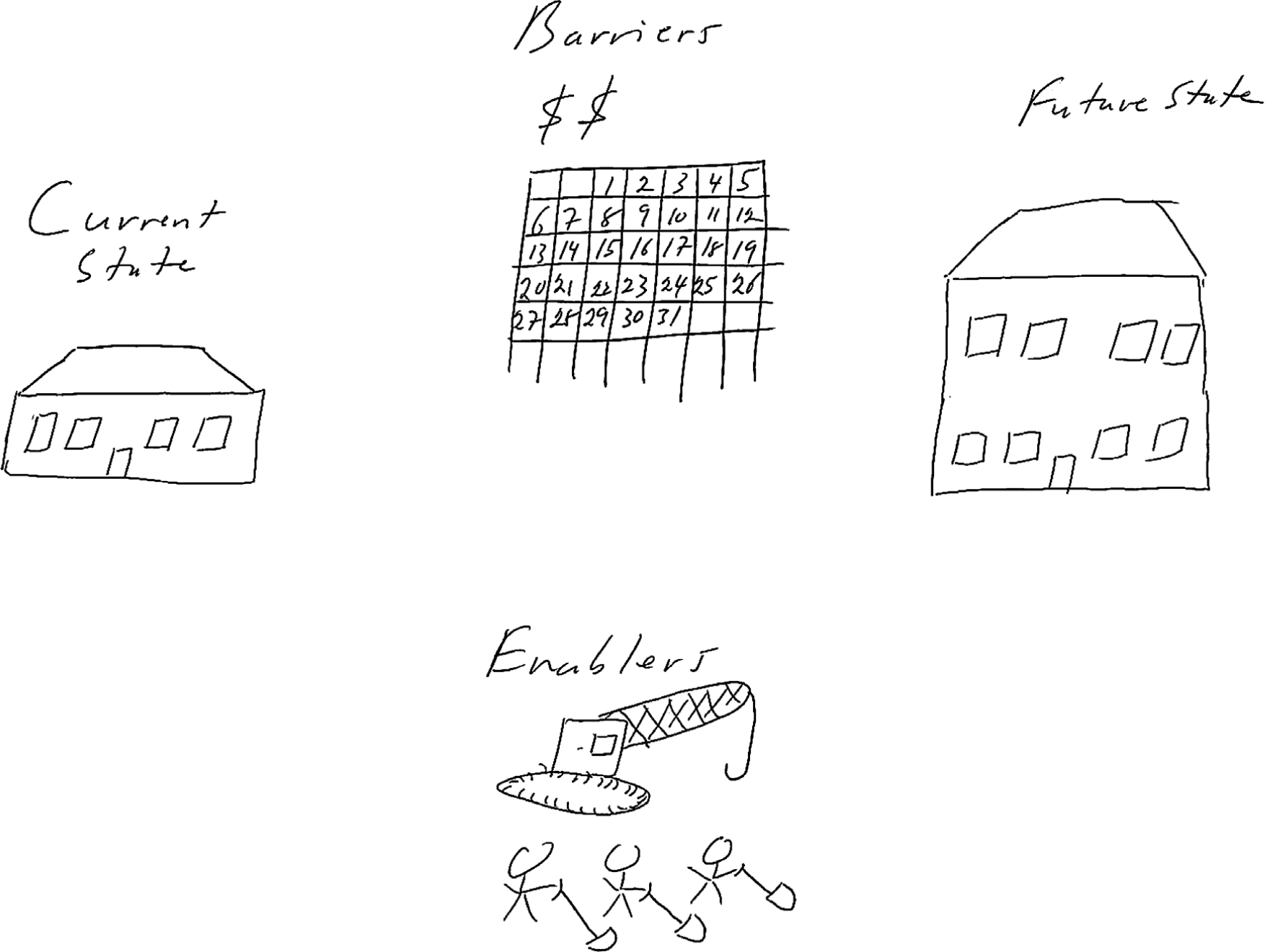
The initial client meeting for a home renovation project adding a second story to a home. Note the barriers, time and money, and the enablers, the crane and manpower. Business problems require a similar type of analysis. Never assume that you know these items. Give the client the opportunity to explain. It will save you a great deal of time in the final analysis.
Improving a business process requires first understanding the process. Diagramming the steps in the process contributes greatly to that understanding. Business process diagramsBusiness processes may be represented by process diagrams containing actors in swim lanes and actions connected by arrows. Decision points in a business process are represented by diamonds. typically consist of actions linked by arrows. However, it is also important to be clear about who is performing each action. For this reason we create a swim laneA vertical portion of a business process diagram. for each actor in the process. The actors pass a metaphorical baton among themselves at different stages of the process.
An easy way to diagram a business process is to first identify all of the actorsA person or computer who takes actions or makes decisions in a business process. and place each in a swim lane. The process begins at the top of the page and continues down the page following the arrows. Arrows represent communication among the actors, while diamonds represent decision points. While actors are normally people, a computer standing in for the role of a person can also be an actor.
At times we can simplify the business process diagram by eliminating all but the essential elements. This makes the diagram less cluttered and easier to read. On the facing page we have a process diagram reduced to just three elements — swim lanes, actions, and arrows.
For the level of analysis needed in this course, the simplified diagram is more than sufficient. However, it is good to know the full lexicon, especially the decision point diamond shown on the next page.
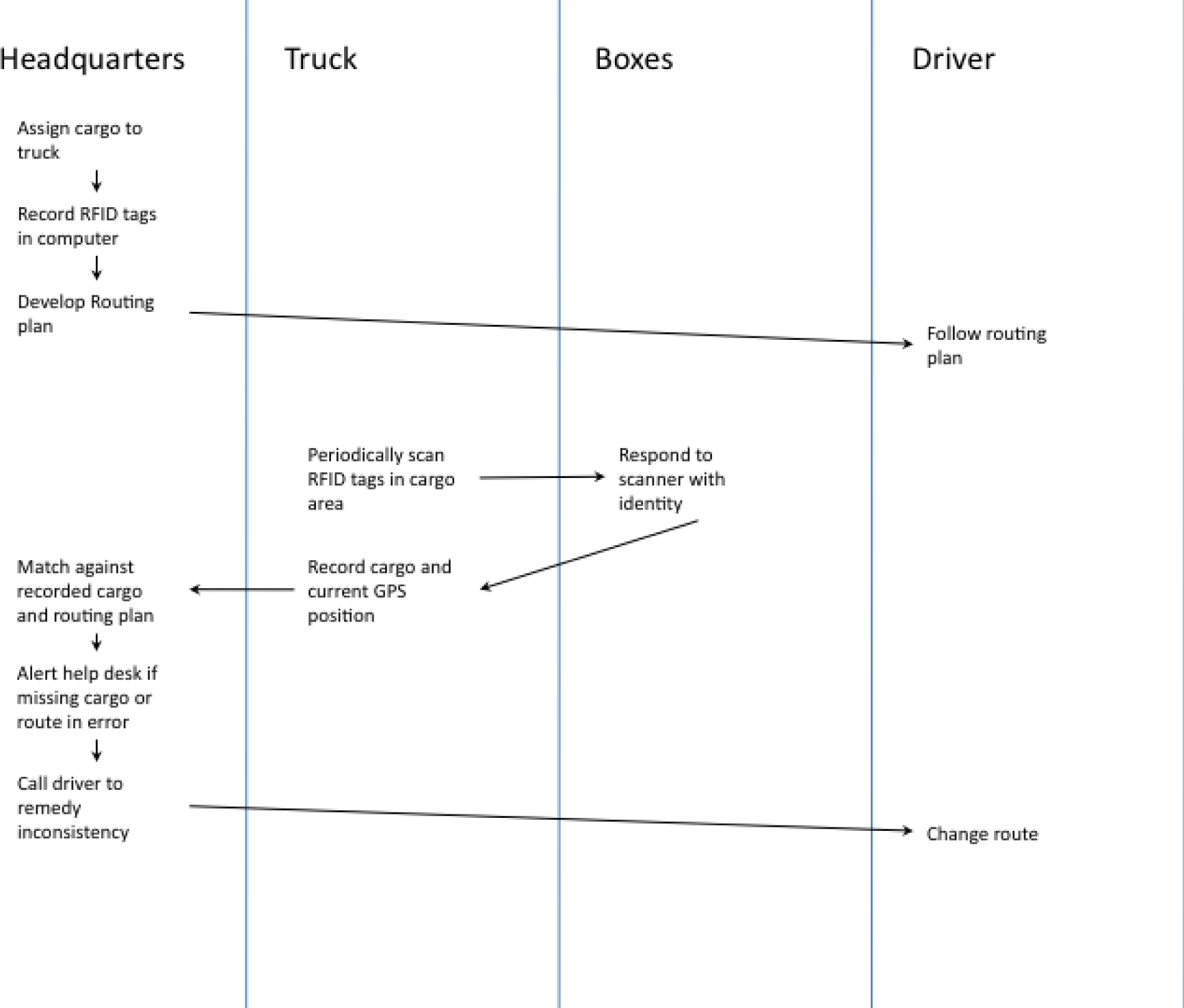
To-Be business process for IBM’s package routing solution. In this solution Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) tags in the boxes communicate with their surroundings to report their geographic position back to the help desk. If a truck has taken the wrong turn, the boxes will notify the help desk. A help desk employee will in turn communicate by phone with the truck driver to reroute the truck.
What we showed on the prior page is actually a simplified form of a business process diagram. For the purpose of this course, the simplified form works just fine. However for the sake of completeness, we show a more advanced diagram more in the spirit of Universal Modeling Language (UML). It is not that the UML style diagram is better—just that you should be prepared to see it. The following table lists some of the symbols that you might encounter in a process flow diagram.
Table 2.1
|
Action state |

|
An action taken in the flow |
|
Start state |

|
A beginning of a flow; only one start state can be used |
|
End state |

|
An end of a flow; any number of end states are allowed |
|
Transition |

|
Indicates the control passing from one object to another |
|
Decision point |

|
Showing possible options and paths to follow |
|
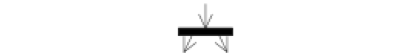
Fork |
|
The beginning of parallel processes |
|
Join |
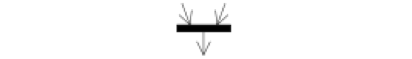
|
The integration of parallel processes |
|
Swim lane |

|
Represents ownership or assignment of a group of actions |
|
Artifact |

|
An object involved in the system, such as a server or database |
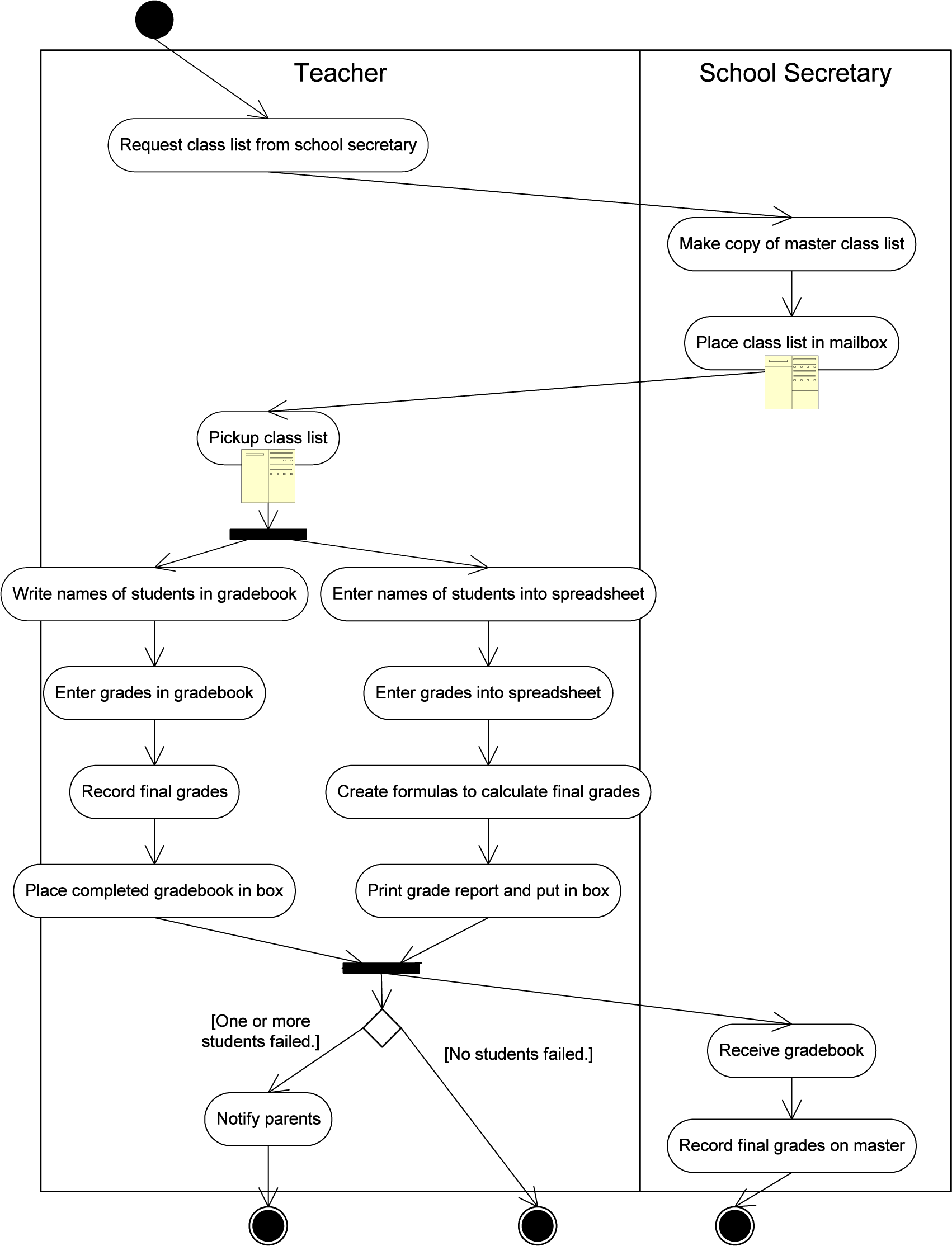
Universal Modeling Language (UML) style As-Is process flow for recording grades.
The following techniques, found in the PowerPoint section of the software reference, may be useful in completing the assignments for this chapter.: Layout-Change • Align • Shape-Insert • Text Box-Insert
Create As-Is and To-Be diagrams of a business process, given a video commercial. Many commercials on TV are really advertisements for improved business processes. IBM has been particularly active in this arena. IBM’s focus on business process improvement makes sense given that IBM is one of the largest consulting organizations in the world. In this exercise, you will view a commercial on YouTube and then create the As-Is and To-Be business process diagrams that the commercial implicitly represents.
Setup
Start up PowerPoint.
Content and Style
Deliverable
Electronic submission: Save your file as a PowerPoint presentation. Submit it electronically.
Paper submission: Create a printout by printing the slides directly out of PowerPoint.
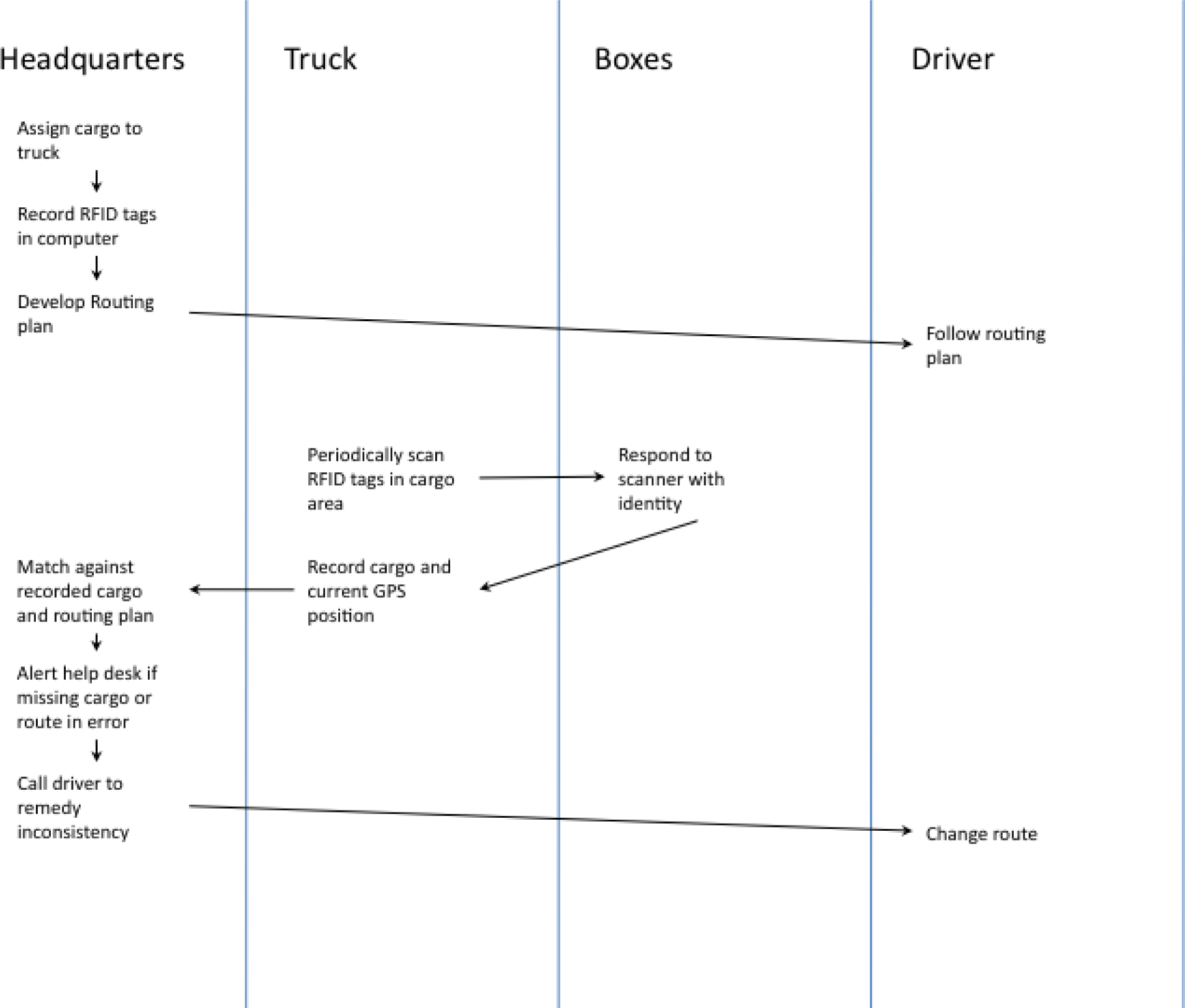
Sample To-Be deliverable for the IBM RFID trucking commercial.