Nucleic acidsA polymer formed by linking nucleotides together. are large polymers formed by linking nucleotides together and are found in every cell. Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)The nucleic acid that stores genetic information. is the nucleic acid that stores genetic information. If all the DNA in a typical mammalian cell were stretched out end to end, it would extend more than 2 m. Ribonucleic acid (RNA)The nucleic acid responsible for using the genetic information encoded in DNA. is the nucleic acid responsible for using the genetic information encoded in DNA to produce the thousands of proteins found in living organisms.
Nucleotides are joined together through the phosphate group of one nucleotide connecting in an ester linkage to the OH group on the third carbon atom of the sugar unit of a second nucleotide. This unit joins to a third nucleotide, and the process is repeated to produce a long nucleic acid chain (Figure 19.5 "Structure of a Segment of DNA"). The backbone of the chain consists of alternating phosphate and sugar units (2-deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA). The purine and pyrimidine bases branch off this backbone.
Each phosphate group has one acidic hydrogen atom that is ionized at physiological pH. This is why these compounds are known as nucleic acids.
Figure 19.5 Structure of a Segment of DNA
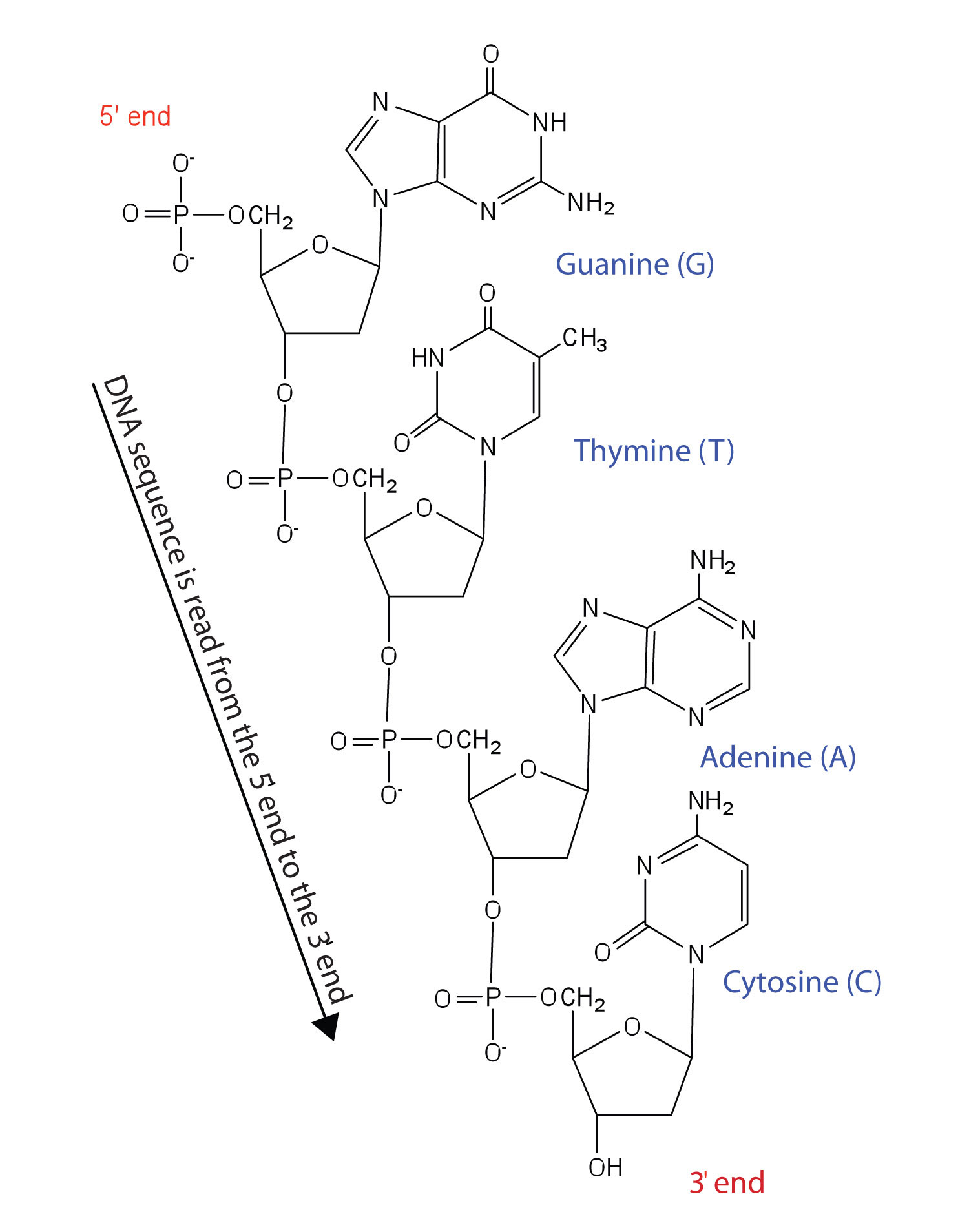
A similar segment of RNA would have OH groups on each C2′, and uracil would replace thymine.
Like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that is defined as the sequence of their nucleotides. Unlike proteins, which have 20 different kinds of amino acids, there are only 4 different kinds of nucleotides in nucleic acids. For amino acid sequences in proteins, the convention is to write the amino acids in order starting with the N-terminal amino acid. In writing nucleotide sequences for nucleic acids, the convention is to write the nucleotides (usually using the one-letter abbreviations for the bases, shown in Figure 19.5 "Structure of a Segment of DNA") starting with the nucleotide having a free phosphate group, which is known as the 5′ end, and indicate the nucleotides in order. For DNA, a lowercase d is often written in front of the sequence to indicate that the monomers are deoxyribonucleotides. The final nucleotide has a free OH group on the 3′ carbon atom and is called the 3′ end. The sequence of nucleotides in the DNA segment shown in Figure 19.5 "Structure of a Segment of DNA" would be written 5′-dG-dT-dA-dC-3′, which is often further abbreviated to dGTAC or just GTAC.
The three-dimensional structure of DNA was the subject of an intensive research effort in the late 1940s to early 1950s. Initial work revealed that the polymer had a regular repeating structure. In 1950, Erwin Chargaff of Columbia University showed that the molar amount of adenine (A) in DNA was always equal to that of thymine (T). Similarly, he showed that the molar amount of guanine (G) was the same as that of cytosine (C). Chargaff drew no conclusions from his work, but others soon did.
At Cambridge University in 1953, James D. Watson and Francis Crick announced that they had a model for the secondary structure of DNA. Using the information from Chargaff’s experiments (as well as other experiments) and data from the X ray studies of Rosalind Franklin (which involved sophisticated chemistry, physics, and mathematics), Watson and Crick worked with models that were not unlike a child’s construction set and finally concluded that DNA is composed of two nucleic acid chains running antiparallel to one another—that is, side-by-side with the 5′ end of one chain next to the 3′ end of the other. Moreover, as their model showed, the two chains are twisted to form a double helixThe secondary structure of DNA.—a structure that can be compared to a spiral staircase, with the phosphate and sugar groups (the backbone of the nucleic acid polymer) representing the outside edges of the staircase. The purine and pyrimidine bases face the inside of the helix, with guanine always opposite cytosine and adenine always opposite thymine. These specific base pairs, referred to as complementary basesSpecific base pairings in the DNA double helix., are the steps, or treads, in our staircase analogy (Figure 19.6 "DNA Double Helix").
Figure 19.6 DNA Double Helix
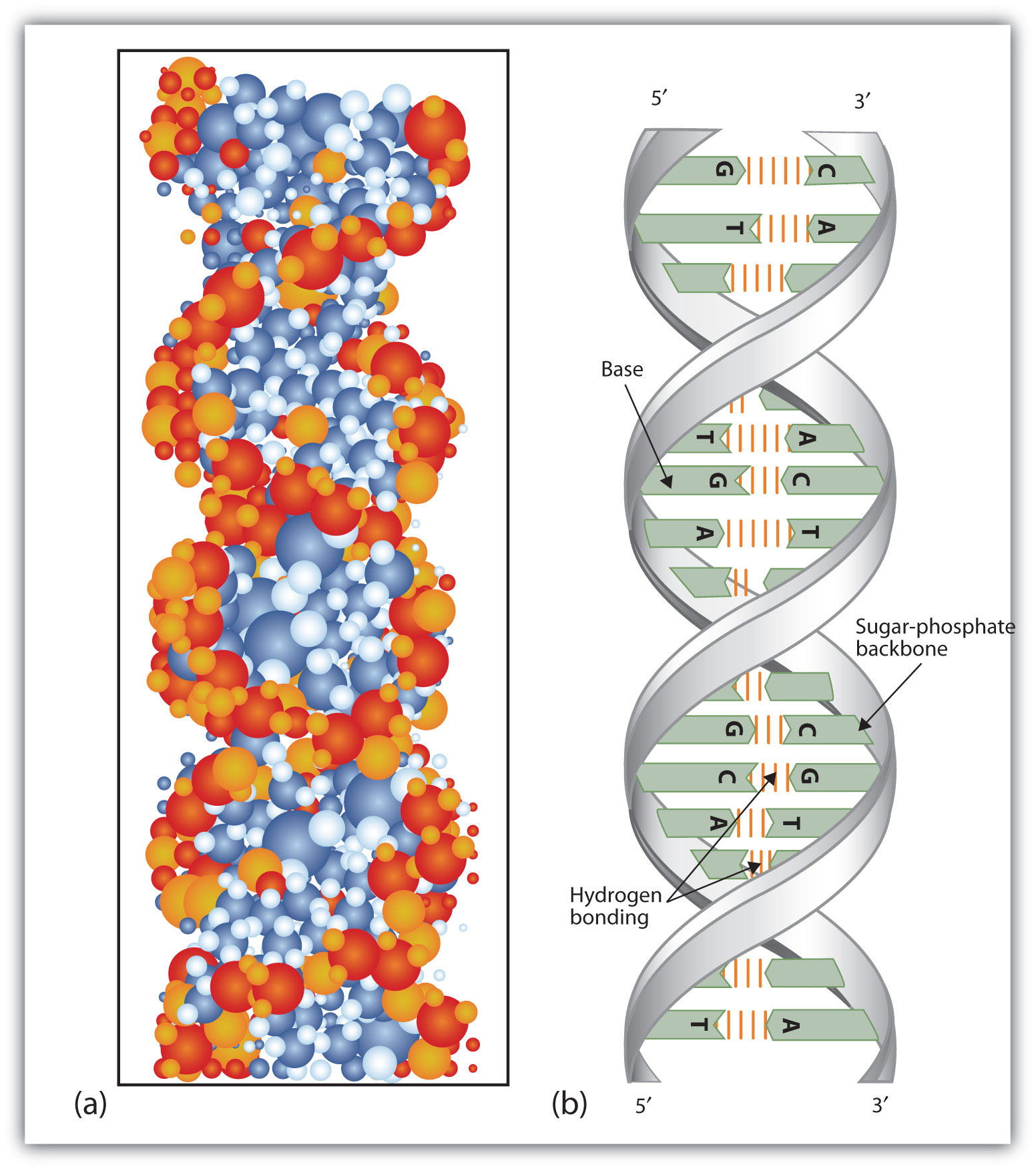
(a) This represents a computer-generated model of the DNA double helix. (b) This represents a schematic representation of the double helix, showing the complementary bases.
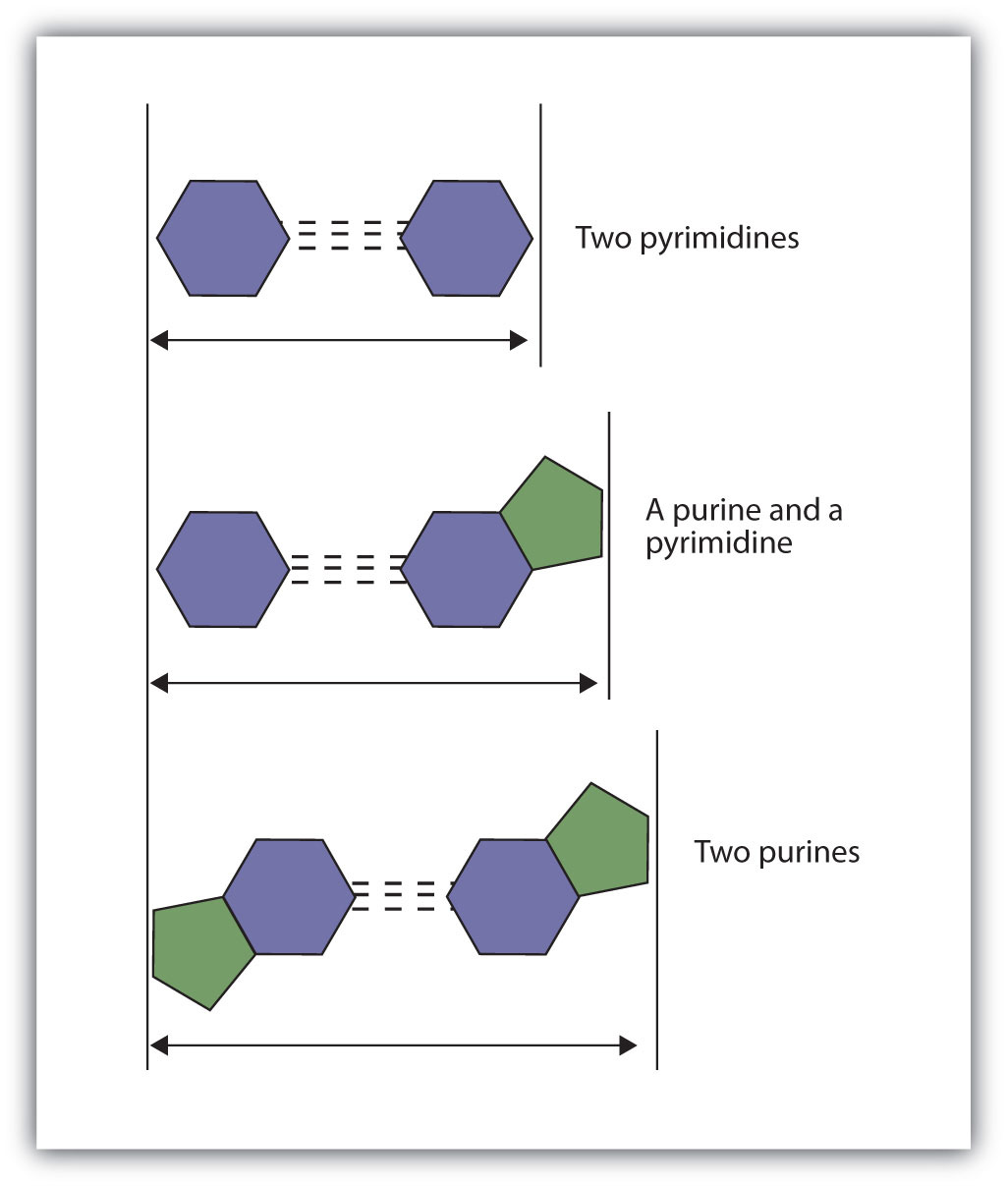
The structure proposed by Watson and Crick provided clues to the mechanisms by which cells are able to divide into two identical, functioning daughter cells; how genetic data are passed to new generations; and even how proteins are built to required specifications. All these abilities depend on the pairing of complementary bases. Figure 19.7 "Complementary Base Pairing" shows the two sets of base pairs and illustrates two things. First, a pyrimidine is paired with a purine in each case, so that the long dimensions of both pairs are identical (1.08 nm). If two pyrimidines were paired or two purines were paired, the two pyrimidines would take up less space than a purine and a pyrimidine, and the two purines would take up more space, as illustrated in Figure 19.8 "Difference in Widths of Possible Base Pairs". If these pairings were ever to occur, the structure of DNA would be like a staircase made with stairs of different widths. For the two strands of the double helix to fit neatly, a pyrimidine must always be paired with a purine. The second thing you should notice in Figure 19.7 "Complementary Base Pairing" is that the correct pairing enables formation of three instances of hydrogen bonding between guanine and cytosine and two between adenine and thymine. The additive contribution of this hydrogen bonding imparts great stability to the DNA double helix.
Figure 19.7 Complementary Base Pairing
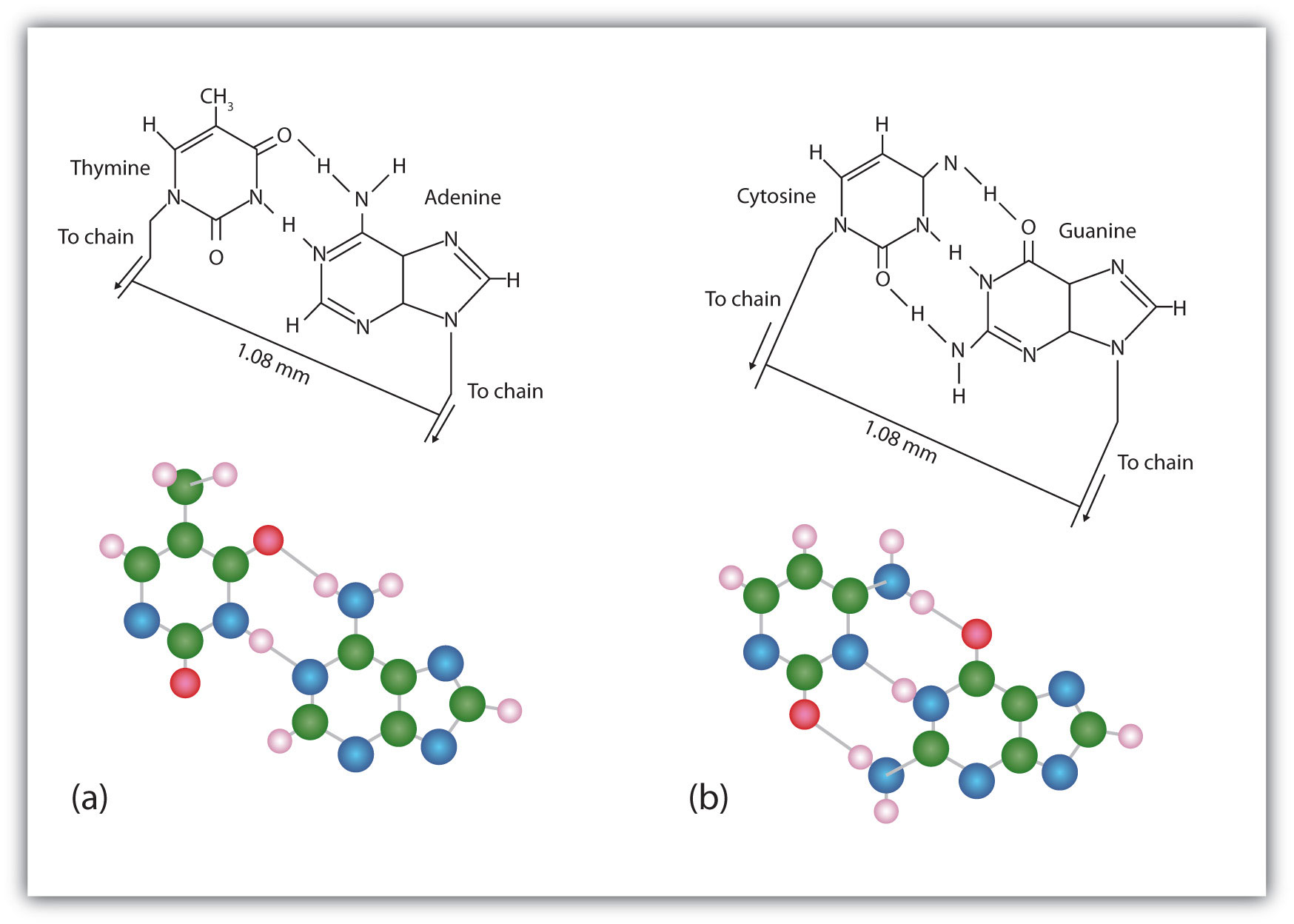
Complementary bases engage in hydrogen bonding with one another: (a) thymine and adenine; (b) cytosine and guanine.
Figure 19.8 Difference in Widths of Possible Base Pairs
What are complementary bases?
Why is it structurally important that a purine base always pair with a pyrimidine base in the DNA double helix?
the specific base pairings in the DNA double helix in which guanine is paired with cytosine and adenine is paired with thymine
The width of the DNA double helix is kept at a constant width, rather than narrowing (if two pyrimidines were across from each other) or widening (if two purines were across from each other).
For this short RNA segment,
write the nucleotide sequence of this RNA segment.
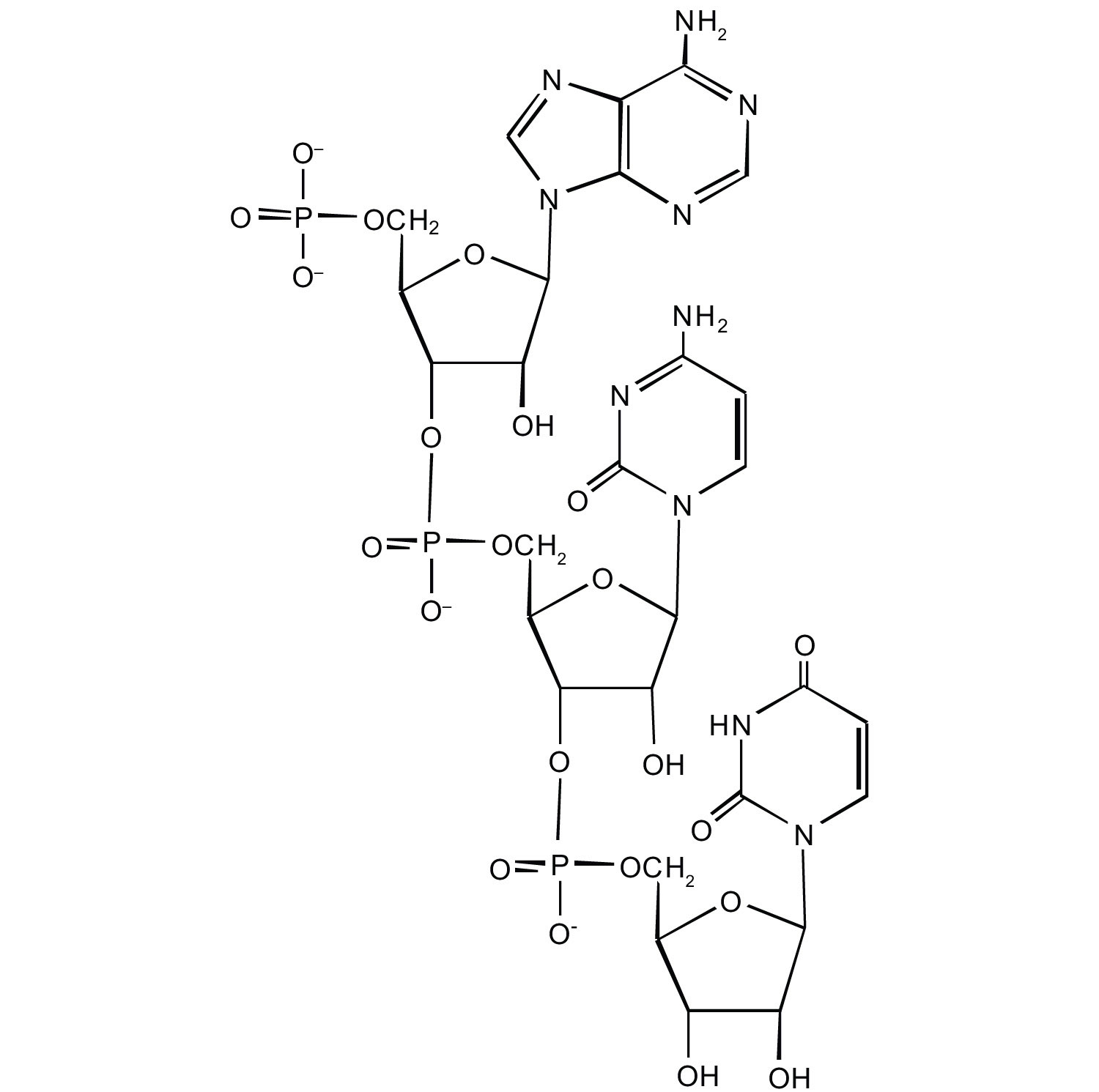
For this short DNA segment,
write the nucleotide sequence of this DNA segment.
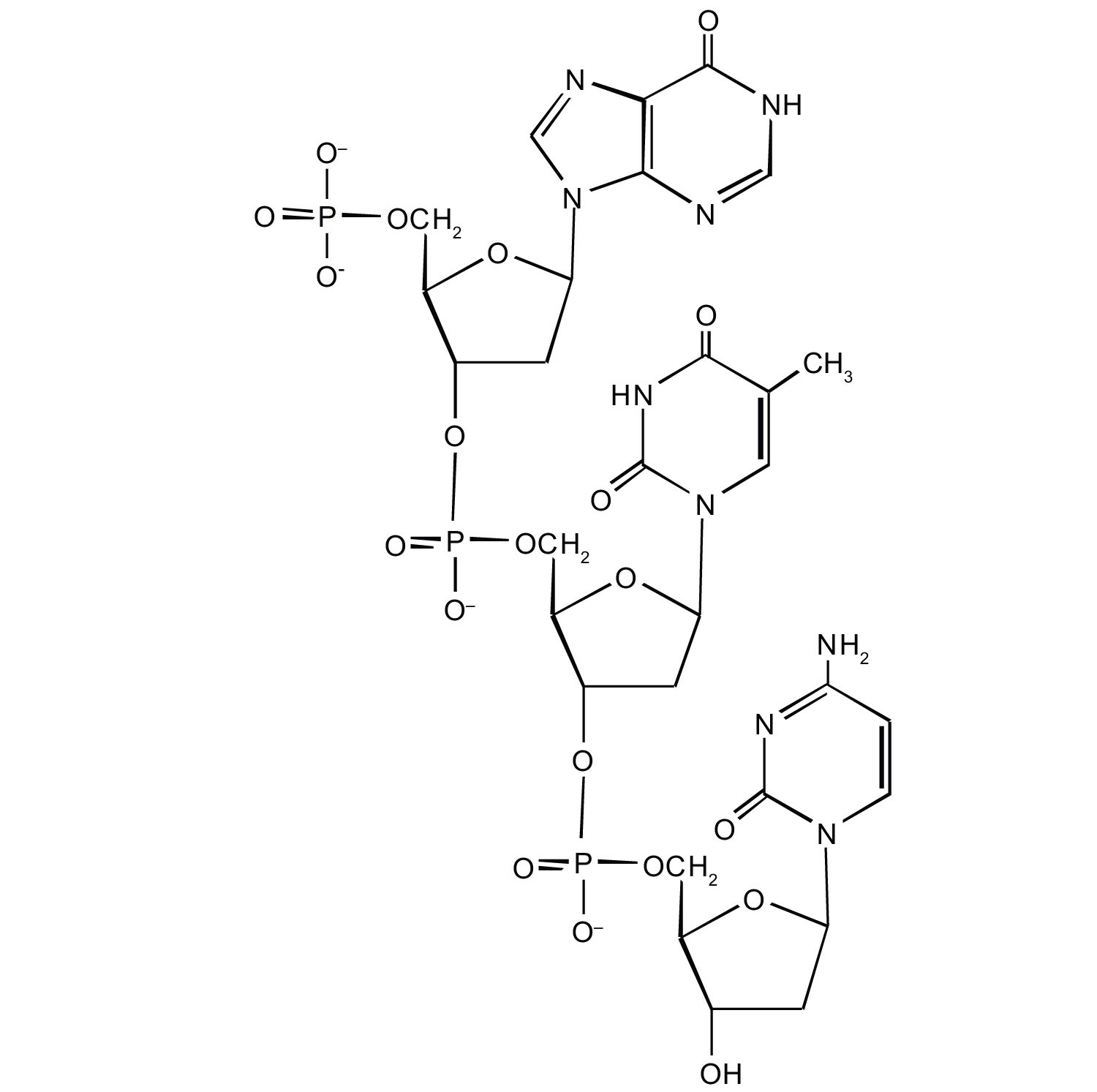
Which nitrogenous base in DNA pairs with each nitrogenous base?
Which nitrogenous base in RNA pairs with each nitrogenous base?
How many hydrogen bonds can form between the two strands in the short DNA segment shown below?
5′ ATGCGACTA 3′ 3′ TACGCTGAT 5′How many hydrogen bonds can form between the two strands in the short DNA segment shown below?
5′ CGATGAGCC 3′ 3′ GCTACTCGG 5′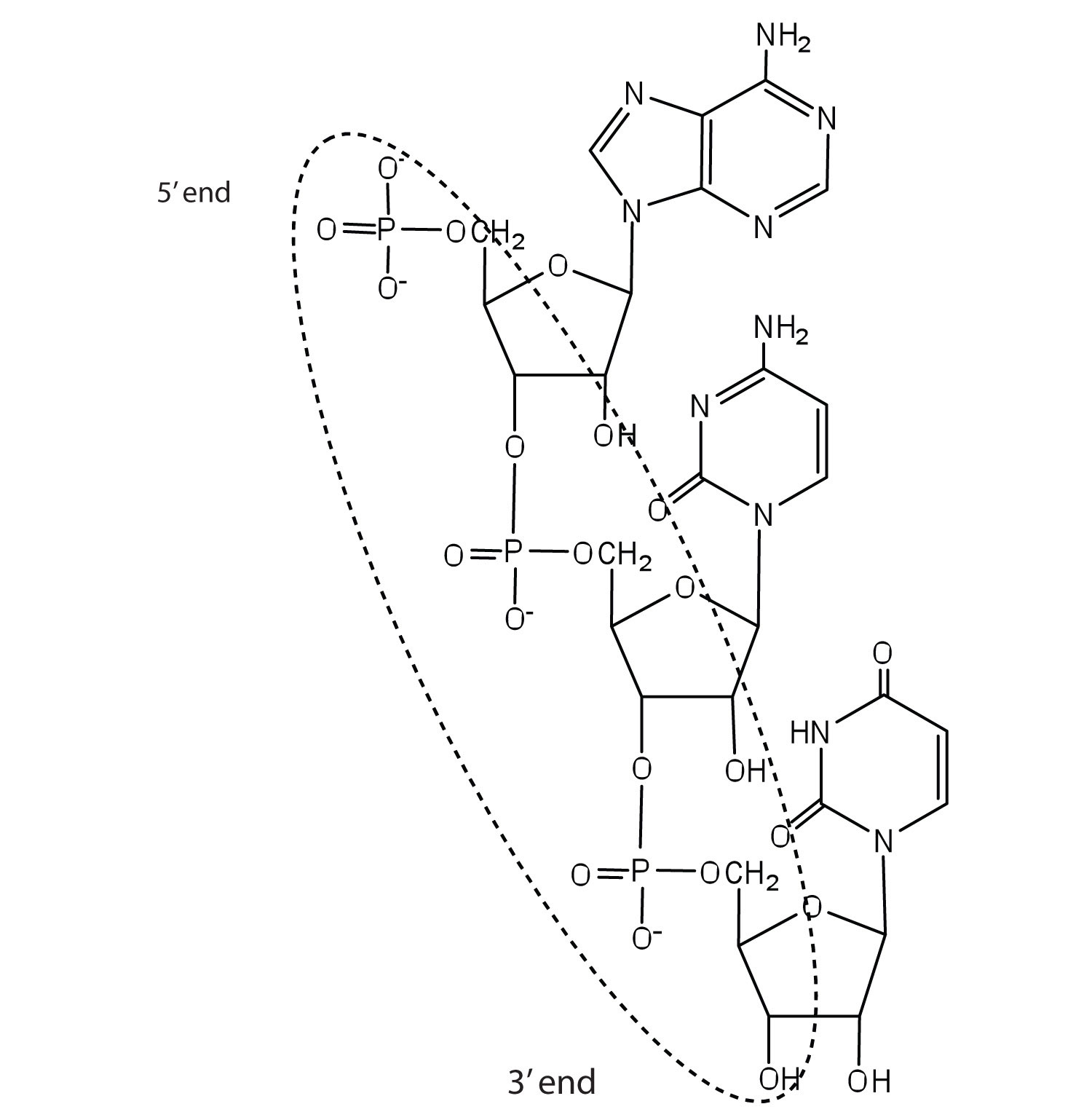
c. ACU
22 (2 between each AT base pair and 3 between each GC base pair)