The goal of the managers of a firm is to maximize the firm’s profit.
profit = revenues − costs.We can think of a firm as choosing either the price to set or the quantity that it sells. Either way, the firm faces a demand curve and chooses a point on that curve that maximizes its profits. In reality, most firms choose the price of the good that they sell. However, it is often simpler to analyze a firm’s behavior by looking at the quantity that it chooses.
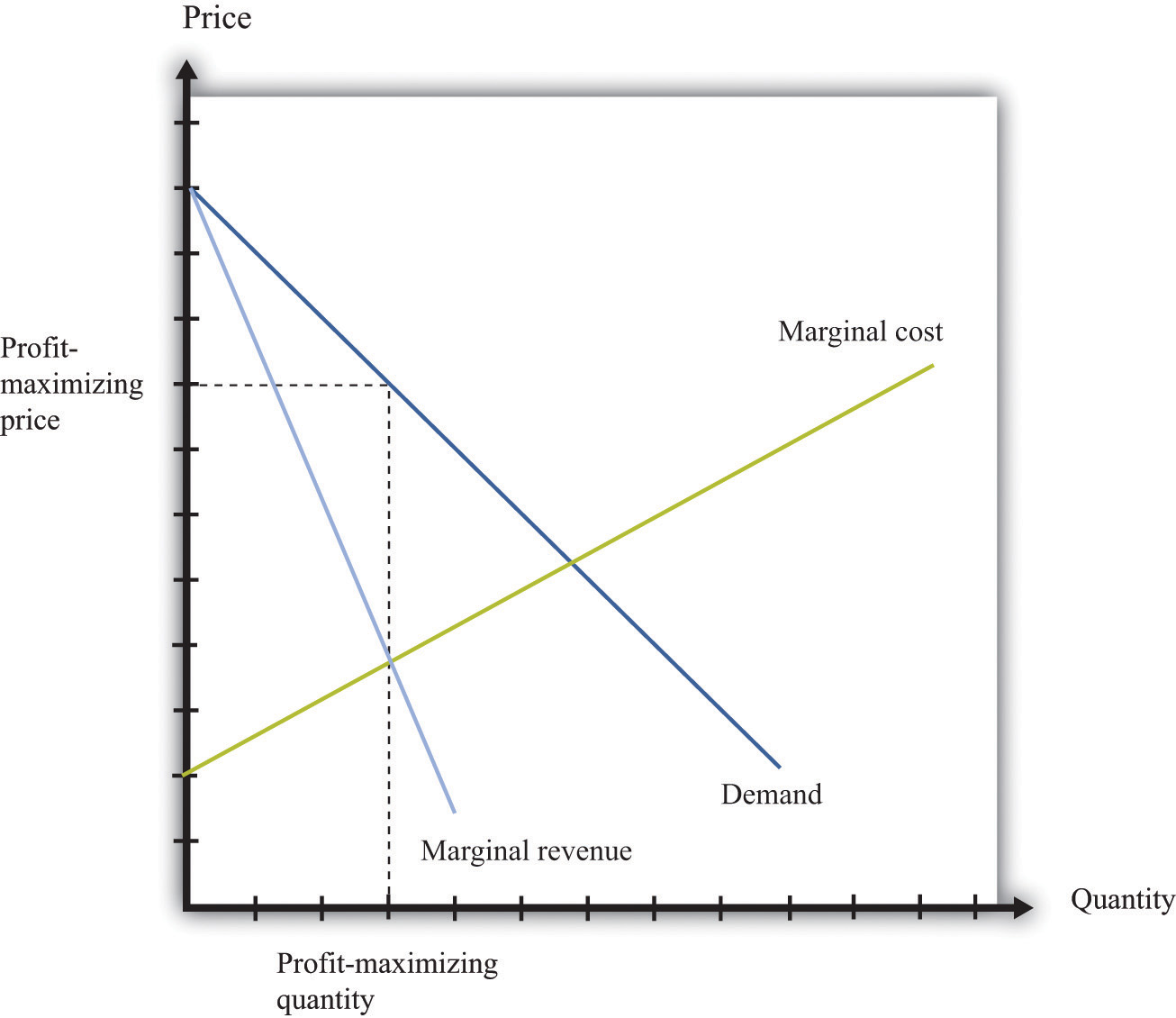
Profits are maximized (Figure 31.12 "Markup Pricing") when the extra revenue from selling one more unit of output (marginal revenue) is equal to the extra cost of producing one more unit (marginal cost). The firm’s decision rule is to select a point on the demand curve such that
marginal revenue = marginal cost.We can rearrange this condition to obtain a firm’s pricing rule:
price = markup × marginal cost.Figure 31.12 "Markup Pricing" illustrates this pricing decision. The markup depends on the price elasticity of demand. When demand is relatively inelastic, firms have a lot of market power and set a high markup. This is not a “plug-and-play” formula because both the markup and marginal cost depend, in general, on the price that a firm chooses. However, it does provide a useful description of a firm’s decision.
Figure 31.12 Markup Pricing
We can derive the markup pricing formula as follows, where π = profit, R = revenues, C = costs, MR = marginal revenue, MC = marginal cost, P = price, Q = output, ε = (ΔQ/Q)/(ΔP/P) = elasticity of demand, and µ = markup.
First we note that
The firm sets marginal revenue equal to marginal cost:
Rearranging, we obtain
P = µ × MC,where the markup is given by