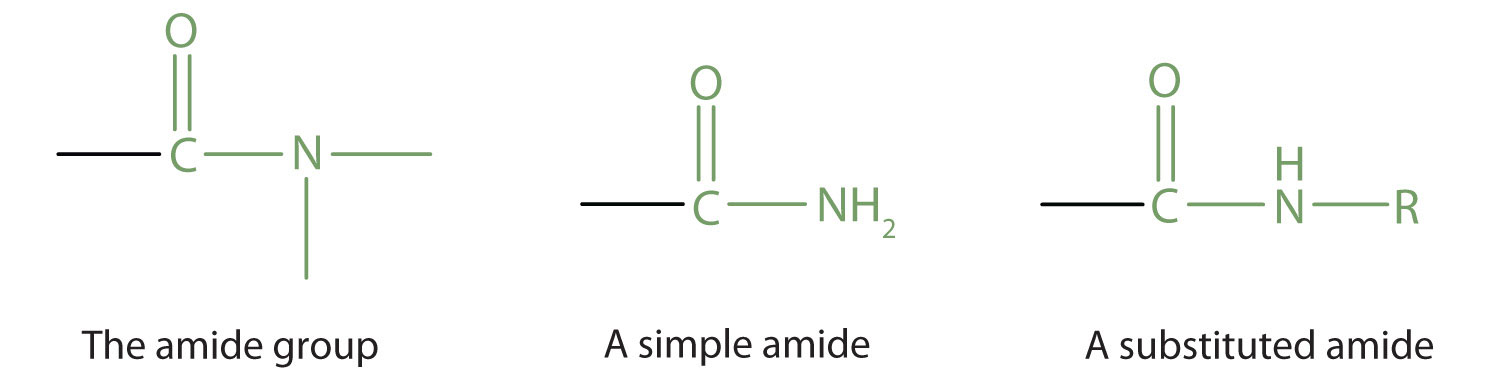
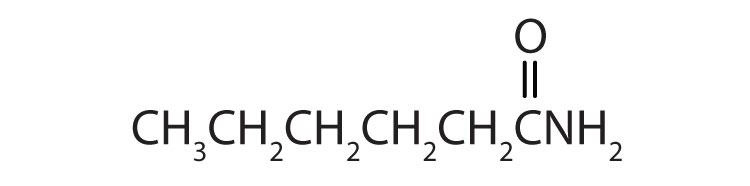The amide functional group has an nitrogen atom attached to a carbonyl carbon atom. If the two remaining bonds on the nitrogen atom are attached to hydrogen atoms, the compound is a simple amide. If one or both of the two remaining bonds on the atom are attached to alkyl or aryl groups, the compound is a substituted amide.
The carbonyl carbon-to-nitrogen bond is called an amide linkage. This bond is quite stable and is found in the repeating units of protein molecules, where it is called a peptide linkage. (For more about peptide linkages, see Chapter 18 "Amino Acids, Proteins, and Enzymes", Section 18.3 "Peptides".)
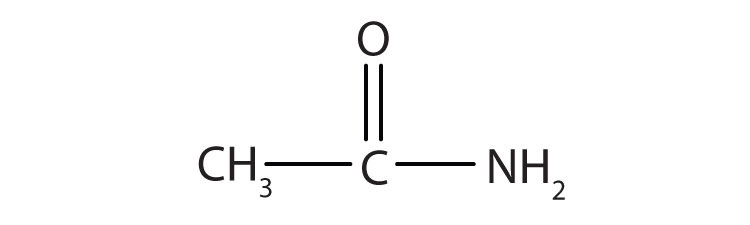
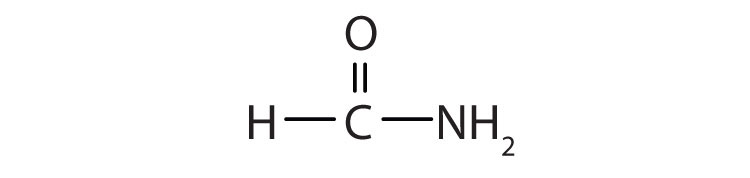
Simple amides are named as derivatives of carboxylic acids. The -ic ending of the common name or the -oic ending of the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name of the carboxylic acid is replaced with the suffix -amide.

Name each compound with the common name, the IUPAC name, or both.
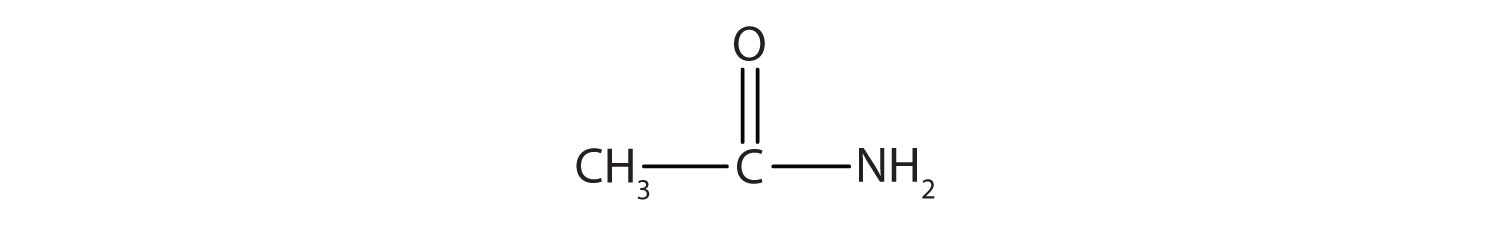
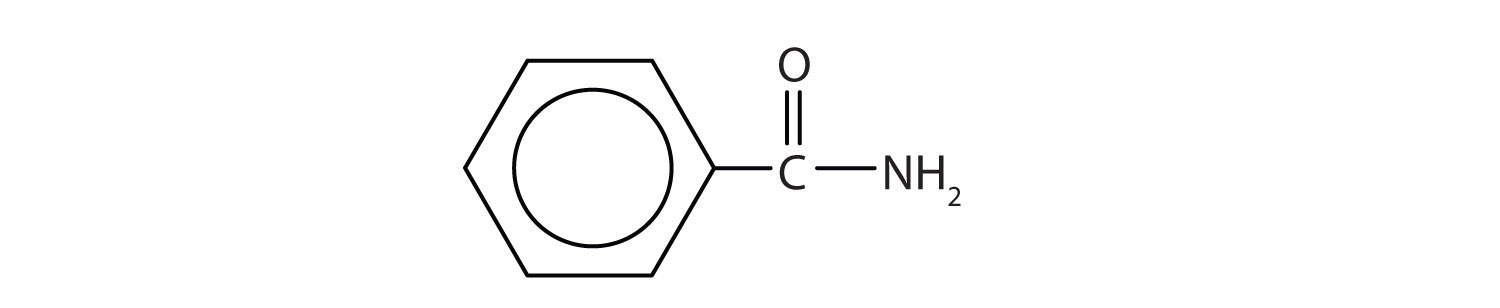
Solution
Name each compound with the common name, the IUPAC name, or both.
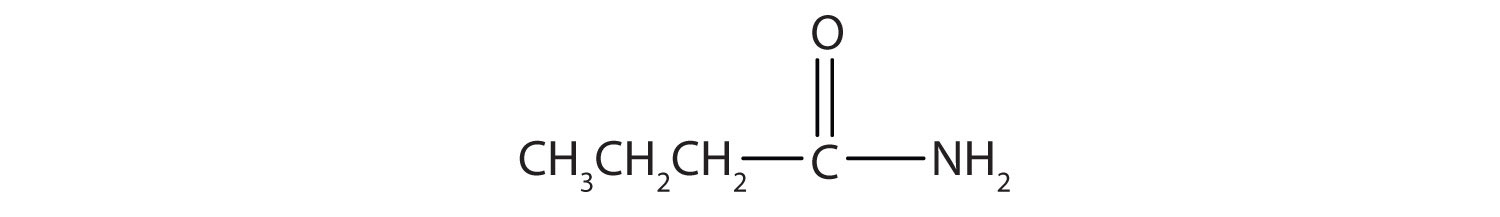
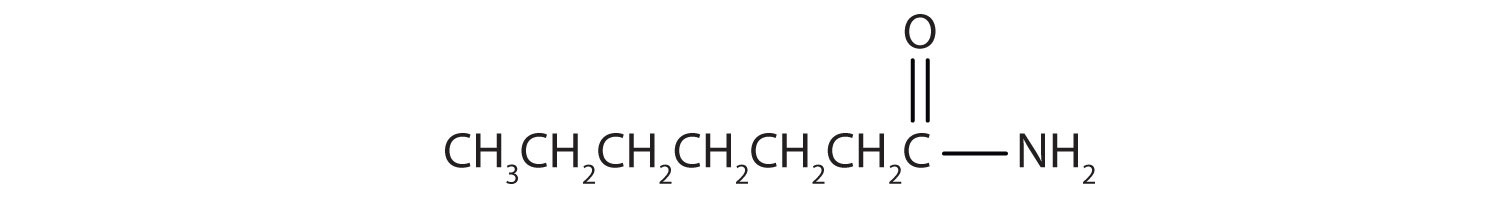
Name this compound with the common name and the IUPAC name.
Draw a the structural formulae for pentanamide.
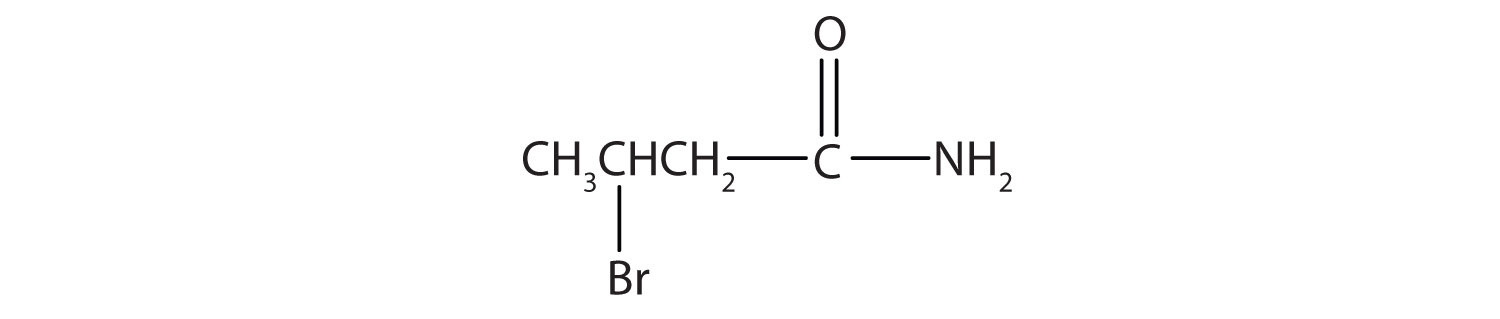
β-bromobutyramide (3-bromobutanamide)
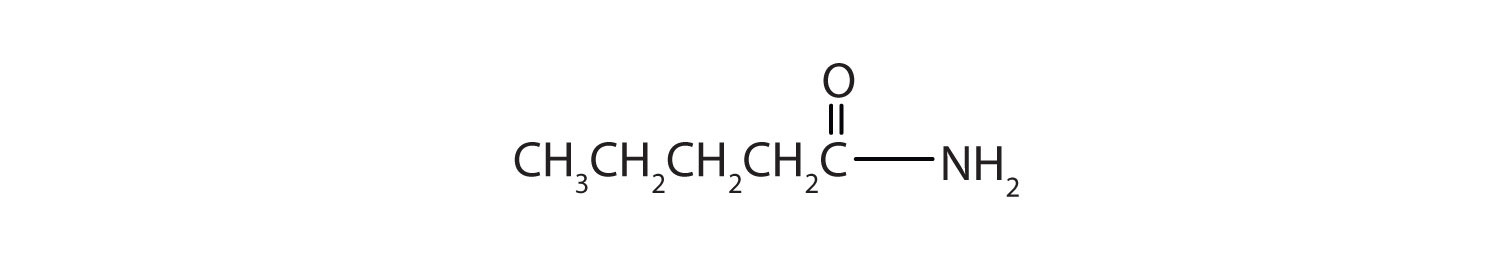
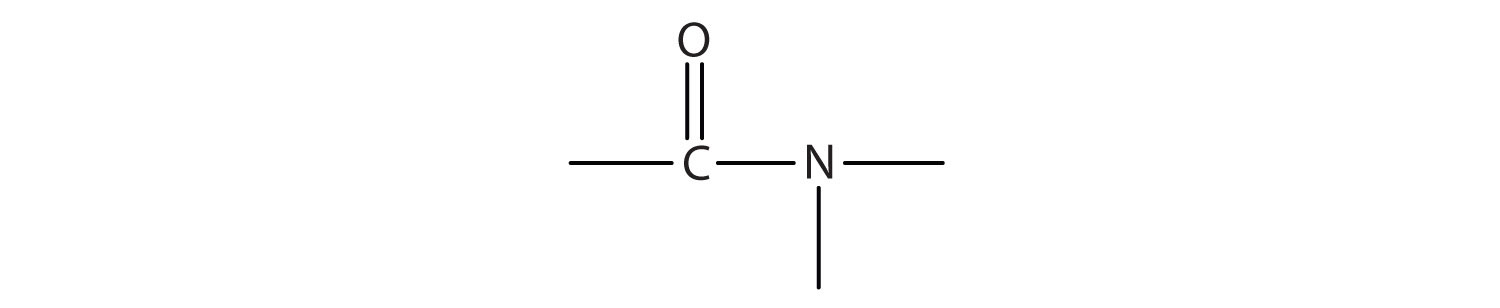
The functional group for an amide is as follows:
Draw the structure for each compound.
Draw the structure for each compound.
Name each compound with the common name, the IUPAC name, or both.
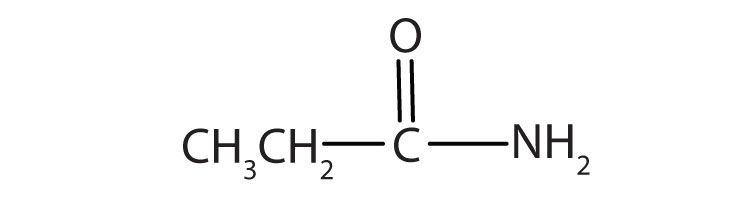
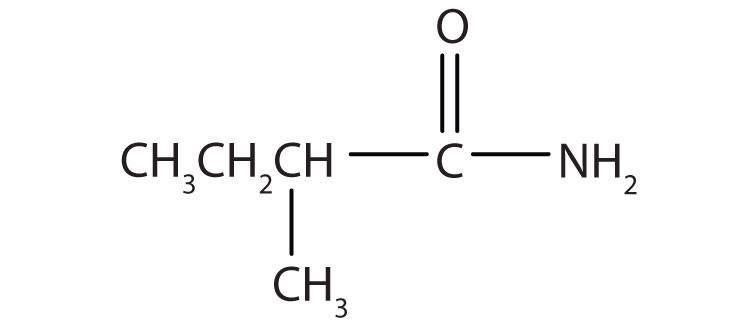
Name the compound.